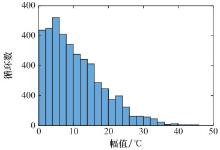
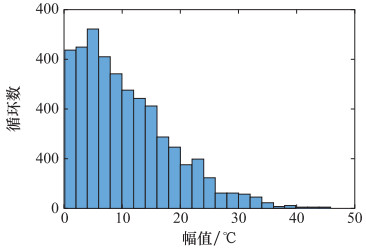
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (9): 3031-3039.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.09.15
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Modeling and analysis of IGBT performance degradation based on solder layer crack propagation
Rui KANG1,2, Yubing CHEN1,2, Meilin WEN2,*, Qingyuan ZHANG1, Tianpei ZU1
- 1. Hangzhou International Innovation Institute, Beihang University, Hangzhou 311115, China
2. School of Reliability and Systems Engineering, Beihang University, Beijing 100191, China
-
Received:2024-06-07Online:2024-08-30Published:2024-09-12 -
Contact:Meilin WEN
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Rui KANG, Yubing CHEN, Meilin WEN, Qingyuan ZHANG, Tianpei ZU. Modeling and analysis of IGBT performance degradation based on solder layer crack propagation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(9): 3031-3039.
share this article
| 1 |
YANG S , BRYANT A , MAWBY P , et al. An industry-based survey of reliability in power electronic converters[J]. IEEE Trans.on Industry Applications, 2011, 47 (3): 1441- 1451.
doi: 10.1109/TIA.2011.2124436 |
| 2 | LASKA T. A Si IGBT review and outlook in competition to WBG power devices[C]//Proc. of the Components of Power Electronics and their Applications, 2023: 15-22. |
| 3 |
SHAHJALAL M , SHAMS T , HOSSAIN S B , et al. Thermal analysis of Si-IGBT based power electronic modules in 50kW traction inverter application[J]. e-Prime-Advances in Electrical Engineering, Electronics and Energy, 2023, 3, 100112.
doi: 10.1016/j.prime.2023.100112 |
| 4 | CIAPPA M . Selected failure mechanisms of modern power mo-dules[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2002, 42 (4/5): 653- 667. |
| 5 |
MOROZUMI A , YAMADA K , MIYASAKA T , et al. Reliabi-lity of power cycling for IGBT power semiconductor modules[J]. IEEE Trans.on Industry Applications, 2003, 39 (3): 665- 671.
doi: 10.1109/TIA.2003.810661 |
| 6 |
ABUELNAGA A , NARIMANI M , BAHMAN A S . A review on IGBT module failure modes and lifetime testing[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 9643- 9663.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3049738 |
| 7 | 刘海涛, 刘兴平, 康力璇, 等. 牵引变流器IGBT失效特性与寿命预测方法研究[EB/OL]. [2024-05-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1408.tm.20240516.1541.002.html. |
| LIU H T, LIU X P, KANG L X, et al. Study on failure characteristics and life prediction method of IGBT in traction converter[EB/OL]. [2024-05-10]. http://kns.cnki.net/kcms/detail/23.1408.tm.20240516.1541.002.html. | |
| 8 |
RAHIMPOUR S , TARZAMNI H , KURDKANDI N V , et al. An overview of lifetime management of power electronic conver-ters[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 109688- 109711.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3214320 |
| 9 | JIA Y J , HUANG Y L , XIAO F , et al. Impact of solder degradation on V_CE of IGBT module: experiments and modeling[J]. IEEE Journal of Emerging Selected Topics in Power Electronics, 2019, 10 (4): 4536- 4545. |
| 10 |
刘宾礼, 刘德志, 唐勇, 等. 基于加速寿命试验的IGBT模块寿命预测和失效分析[J]. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 34 (5): 556- 563.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7775.2013.05.011 |
|
LIU B L , LIU D Z , TANG Y , et al. Lifetime prediction and fai-lure analysis of IGBT module based on accelerated lifetime test[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 34 (5): 556- 563.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-7775.2013.05.011 |
|
| 11 | ZHANG Y, WANG H, WANG Z X, et al. Impact of lifetime model selections on the reliability prediction of IGBT modules in modular multilevel converters[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Energy Conversion Congress and Exposition, 2017: 4202-4207. |
| 12 |
LIU L , TANG L , JIANG H P , et al. Reliability evaluation of IGBT power module on electric vehicle using big data[J]. Journal of Semiconductors, 2024, 45 (5): 052301.
doi: 10.1088/1674-4926/45/5/052301 |
| 13 | 李文鹏, 张林林, 王为介, 等. 计及电热参数更新的高速列车牵引整流器IGBT模块寿命评估[J]. 铁道机车车辆, 2024, 44 (2): 74- 81. |
| LI W P , ZHANG L L , WANG W J , et al. Life evaluation of high-speed train traction rectifier IGBT module considering electric and thermal parameters update[J]. Railway Locomotive & Car, 2024, 44 (2): 74- 81. | |
| 14 | LAI W , CHEN M Y , RAN L , et al. Low △T_j stress cycle effect in IGBT power module die-attach lifetime modeling[J]. IEEE Trans.on Power Electronics, 2015, 31 (9): 6575- 6585. |
| 15 | 李玲玲, 孙进, 张鑫保. 考虑性能退化的IGBT模块可靠性度量模型[J]. 半导体技术, 2018, 43 (12): 930- 935. |
| LI L L , SUN J , ZHANG X B . Reliability measurement model of IGBT modules considering the performance degradation[J]. Semiconductor Technology, 2018, 43 (12): 930- 935. | |
| 16 | 高兵. 基于温度梯度及统计特性的IGBT模块失效评估方法研究[D]. 重庆: 重庆大学, 2016. |
| GAO B. Study on failure evaluation method of IGBT module based on temperature gradient and statistic characteristic[D]. Chongqing: Chongqing University, 2016. | |
| 17 | HUANG H , MAWBY P . A lifetime estimation technique for voltage source inverters[J]. IEEE Trans.on Power Electronics, 2012, 28 (8): 4113- 4119. |
| 18 |
AKBARI M , BINA M T , BAHMAN A S , et al. An extended multilayer thermal model for multichip IGBT modules considering thermal aging[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 84217- 84230.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3083063 |
| 19 | LAI W , CHEN M Y , RAN L , et al. Experimental investigation on the effects of narrow junction temperature cycles on die-attach solder layer in an IGBT module[J]. IEEE Trans.on Power Electronics, 2016, 32 (2): 1431- 1441. |
| 20 |
DARVEAUX R . Effect of simulation methodology on solder joint crack growth correlation and fatigue life prediction[J]. Journal of Electronic Packaging, 2002, 124 (3): 147- 154.
doi: 10.1115/1.1413764 |
| 21 | STEINHORST P , POLLER T , LUTZ J . Approach of a physically based lifetime model for solder layers in power modules[J]. Microelectronics Reliability, 2013, 53 (9/11): 1199- 1202. |
| 22 | ZHANG Y C, ZHANG Y, YAO B, et al. Impact of bond wire degradation on thermal estimation and temperature coefficient of IGBT modules in power cycling test[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition, 2024: 2443-2447. |
| 23 |
ALAVI O , DE-CEUNINCK W , DAENEN M . Optimizing insulated-gate bipolar transistors' lifetime estimation: a critical evaluation of lifetime model adjustments based on power cycling tests[J]. Energies, 2024, 17 (11): 2616.
doi: 10.3390/en17112616 |
| 24 | JESD 51-14. Transient dual interface test method for the measurement of the thermal resistance junction to case of semiconductor devices with heat flow through a single path[S]. Arlington: Joint Electron Device Engineering Council, 2010. |
| 25 | 张志红, 何桢, 郭伟. 在响应曲面方法中三类中心复合设计的比较研究[J]. 沈阳航空工业学院学报, 2007, 24 (1): 87- 91. |
| ZHANG Z H , HE Z , GUO W . A comparative study of three central composite designs in response surface methodology[J]. Journal of Shenyang Institute of Aeronautical Engineering, 2007, 24 (1): 87- 91. | |
| 26 | CHEN W H , CHEN W H , CHEIN R Y , et al. Optimization of hydrogen purification via vacuum pressure swing adsorption[J]. Energy Conversion, 2023, 20, 100459. |
| 27 |
MOHTARAM M S , SABBAGHI S , RASOULI J , et al. Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline using a novel WO3-ZnO/AC under visible light irradiation: optimization of effective factors by RSM-CCD[J]. Environmental Pollution, 2024, 347, 123746.
doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2024.123746 |
| 28 | 邢广鹏. 循环计数法在航空发动机载荷谱统计中的适用性研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2017. |
| XING G P. Research on the applicability of the cycle counting methods in the statistics of aero-engine load spectrum[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2017. | |
| 29 | WANG Y T , QIU Y Y , LI J , et al. A hybrid frequency-time domain life prediction method based on the critical plane theory[J]. Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures, 2024, 47 (7): 2351- 2368. |
| 30 |
YUAN K L , PENG S F , SUN Z C . An artificial neural network model for fatigue damage analysis of wide-band non-Gaussian random processes[J]. Applied Ocean Research, 2024, 144, 103896.
doi: 10.1016/j.apor.2024.103896 |
| [1] | Hongzhou ZHAI, Hua ZHANG, Linna WU, Hequn BU, Kaixiang GONG. Optimization algorithm for reliability redundancy design based on collaborative balance [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(12): 4084-4089. |
| [2] | Anqi ZHANG, Shengpeng ZHANG, Hongmin LI, Yao ZHU, Sikun MI. Efficient environmental stress screening method based on key quality characteristic [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(11): 3706-3713. |
| [3] | Fan ZHANG, Runcao TIAN, Peng WANG, Lei DONG. Multi-stress accelerated life evaluation method considering generalized coupling [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(10): 3350-3361. |
| [4] | Xiangyu LI, Hongzhong HUANG, Xiaoyan XIONG. Reliability modeling of phased mission system considering shocks and phase backups [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 2280-2286. |
| [5] | Leilei ZHANG, Xi LIU, Xulin LIU, Hongjun YANG, Feng ZHANG. Accelerated storage life assessment method under zero-failure data for electromechanical products of missile [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 2287-2294. |
| [6] | Jiang LI, Hecheng WU, Chen ZHU. Reliability assessment of long-life products based on semi-parametric degradation model [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(6): 1893-1901. |
| [7] | Ting ZENG, Shuai GAO, Fuqiang SUN, Xiaoming LAI, Yun LI, Xiaopeng LI. Probabilistic risk analysis of satellite antenna assembly considering man-machine-environment coupling effect [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 606-613. |
| [8] | Peng WANG, Zijing SUN, Fan ZHANG, Guosong XIAO. Reliability analysis model for phased-mission system considering probabilistic common cause failures [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3887-3898. |
| [9] | Tingchun HU, Yufeng SUN, Xiaoxiao LI, Guangyan ZHAO. Solution of reliability of cold standby voting system with arbitrary distribution [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2357-2363. |
| [10] | Dongdong ZHANG, Xiaochuan AI, Chang LIU. Research on equipment performance degradation based on feature extraction of similar samples [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2374-2380. |
| [11] | Han YANG, Haowei WANG, Qingrong LI, Min CHEN, Bo PENG. Application research of creep life model based on belief reliability theory [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 1044-1051. |
| [12] | Jingfeng LI, Yunxiang CHEN, Huachun XIANG, Jian WANG. Joint optimization of condition-based maintenance and spare part inventory for multi-component system considering random shock effect [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 875-883. |
| [13] | Zhicong CHEN, Rui KANG, Tianpei ZU, Qingyuan ZHANG. Belief reliability allocation method based on technology readiness [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 327-337. |
| [14] | Yunxiang CHEN, Jingfeng LI, Huachun XIANG, Hengnian LI. A CBM optimization model for mission-oriented system based on inverse Gaussian degradation process [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 338-346. |
| [15] | Zelong MAO, Zhihua WANG, Qiong WU, Chengrui LIU. Bivariate and two-stage degradation modeling and reliability analysis [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3725-3731. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||