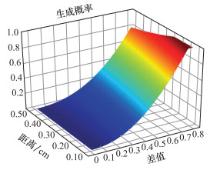
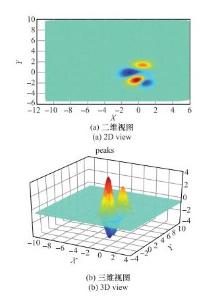
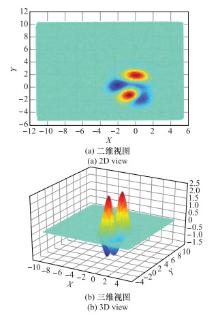
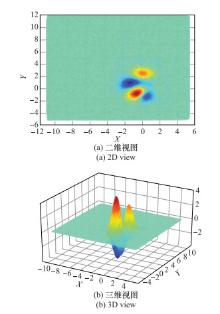
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (5): 1232-1239.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.05.10
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Design method of sequential neighbor exploratory experimental for complex simulation metamodeling
Yonglin LEI1( ), Yan WANG1(
), Yan WANG1( ), Qinzhang YU2,*(
), Qinzhang YU2,*( ), Zhi ZHU1(
), Zhi ZHU1( ), Wei DONG1(
), Wei DONG1( ), Yifan ZHU1(
), Yifan ZHU1( )
)
- 1. College of Systems Engineering, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
2. TheKey Laboratory for Complex Systems Simulation, Beijing 100010, China
-
Received:2020-04-20Online:2021-05-01Published:2021-04-27 -
Contact:Qinzhang YU E-mail:yllei@nudt.edu.cn;wangyan19a@163.com;yuqinzh2321@sina.com;zhuzhi@nudt.edu.cn;dongwei@nudt.edu.cn;yfzhu@nudt.edu.cn
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yonglin LEI, Yan WANG, Qinzhang YU, Zhi ZHU, Wei DONG, Yifan ZHU. Design method of sequential neighbor exploratory experimental for complex simulation metamodeling[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(5): 1232-1239.
share this article
| 1 |
SANTOS M I R D , SANTOS P M R D . Sequential experimental designs for nonlinear regression metamodels in simulation[J]. Simulation Modelling Practice and Theory, 2008, 16 (9): 1365- 1378.
doi: 10.1016/j.simpat.2008.07.001 |
| 2 | SIMPSON T W , LIN D K J . Sampling strategies for computer experiments: design and analysis[J]. International Journal of Reliability & Application, 2001, 2 (3): 209- 240. |
| 3 | GIUNTA A A, WOJTKIEWICZ S F, ELDRED M S. Overview of modern design of experiments methods for computational simu-lations[C]//Proc. of the 41st Aerospace Sciences Meeting and Exhibit, 2003. |
| 4 | KLEIJNEN J P C. An overview of the design and analysis of simulation experiments for sensitivity analysis[C]//Proc. of the European Journal of Operational Research, 2005: 287-300. |
| 5 | ALAM F M, MCNAUGHT K R, RINGROSE T J. A comparison of experimental designs in the development of a neural network simulation metamodel[C]//Proc. of the Simulation Modelling Practice & Theory, 2004: 559-578. |
| 6 | ALAM F M, MCNAUGHT K R, RINGROSE T J. An artificial neural network based metamodel for analyzing a stochastic combat simulation[C]//Proc. of the International Journal of Enterprise Information Systems, 2006: 38-57. |
| 7 | DONOHUE J M, HOUCK E C, MYERS R H. A sequential experimental design procedure for the estimation of first-and second-order simulation metamodels[C]//Proc. of the ACM Tran-sactions on Modeling and Computer Simulation, 1993: 190-224. |
| 8 | ROSSETTI M D, HILL R R, JOHANSSON B. A novel sequential design strategy for global surrogate modeling[C]//Proc. of the Winter Simulation Conference, 2009: 731-742. |
| 9 | 崔庆安. 面向多极值质量特性的全局式序贯性实验设计方法[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2012, 32 (10): 2143- 2153. |
| CUI Q A . Global sequential experimental design method for multi-extreme quality characteristics[J]. Systems Engineering Theory & Practice, 2012, 32 (10): 2143- 2153. | |
| 10 | ZHU R. Gradient-based sampling: an adaptive importance sampling for least-squares[C]//Proc. of the 30th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2016. |
| 11 |
GRAMACY R B , LEE H K H . Adaptive design and analysis of supercomputer experiments[J]. Technometrics, 2009, 51 (2): 130- 145.
doi: 10.1198/TECH.2009.0015 |
| 12 | GORISSEN D, CROMBECQ K, HENDRICKX W, et al. Adaptive distributed metamodeling[C]//Proc. of the 7th International Conference on High Performance Computing for Computational Science, 2006: 579-588. |
| 13 | HENDRICKX W, DHAENE T. Sequential design and rational metamodelling[C]//Proc. of the Winter Simulation Confe-rence, 2005: 290-298. |
| 14 |
LEI Y L , ZHU N , YAO J , et al. Model architecture-oriented combat system effectiveness simulation based on MDE[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28 (5): 900- 922.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.05.09 |
| 15 | 孔晨妍, 朱晶, 焦松, 等. 基于序贯仿真实验的作战体系能力分析优化方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2018, 30 (9): 3333- 3339. |
| KONG C Y , ZHU J , JIAO S , et al. Combat system capability analysis and optimization method based on sequential simulation experiment[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2018, 30 (9): 3333- 3339. | |
| 16 | GOMEZ-HERNANDEZ J J , CASSIRAGE E F . Geostatistical simulations[M]. Holland: Kluwer Academic Publishers, 2008: 111- 124. |
| 17 | SHAROM M W , TABIKA K , EMMANUEL A , et al. Sequential simulation used as a novel educational tool aimed at healthcare ma-nagers: a patient-centred approach[J]. BMJ Simulation & Technology Enhanced Learning, 2018, 4 (1): 13- 18. |
| 18 | HAO C. Sequential change-point detection based on nearest neighbors[D]. California: University of California, 2018. |
| 19 | ISGREN C M , SALEM S E , TOWNSEND N B , et al. Sequential bacterial sampling of the midline incision in horses under-going exploratory laparotomy[J]. Equine Veterinary Journal, 2018, 111 (10): 38- 44. |
| 20 | NOH Y K, PARK F C, LEE D D. K-nearest neighbor classification algorithm for multiple choice sequential sampling[C]//Proc. of the Annual Meeting of the Cognitive Science Society, 2013: 3151-3156. |
| 21 | HOU W F, LI D W, XU C, et al. An advanced k-nearest neighbor classification algorithm based on KD-tree[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Safe Production and Informatization, 2018. |
| 22 | YUAN L M, HUANG Q C, LIU J F, et al. Salience-based prototype selection for k-nearest neighbor classification in multiple-instance learning[C]//Proc. of the 3rd Sino-Foreign-Interchange Conference on Intelligent Science and Intelligent Data Engineering, 2012. |
| 23 | 赵学远, 王康, 秦亮, 等. 基于仿真数据的测试性验证序贯设计方案[J]. 海军航空工程学院学报, 2019, 34 (1): 146- 150. |
| ZHAO X Y , WANG K , QIN L , et al. A sequential design scheme for testability verification based on simulation data[J]. Journal of Naval Aeronautical Engineering Institute, 2019, 34 (1): 146- 150. | |
| 24 | 王华松, 李鹏, 张家叶子, 等. 基于卡尔曼滤波的序贯融合对机动目标跟踪算法与仿真[J]. 工业控制计算机, 2020, 33 (7): 122- 124. |
| WANG H S , LI P , ZHANG J Y Z , et al. Sequential fusion based on Kalman filtering algorithm and simulation of maneuvering target trac-king[J]. Industrial Control Computer, 2020, 33 (7): 122- 124. | |
| 25 | PATRICK T B. A methodology for capability-based technology evaluation for systems-of-systems[D]. Georgia: Georgia Institute of Technology, 2007. |
| 26 |
ZHANG W X , LI W D , ZHANG C R , et al. Parallel computing solutions for Markov chain spatial sequential simulation of categorical fields[J]. International Journal of Digital Earth, 2019, 12 (5): 566- 582.
doi: 10.1080/17538947.2018.1464073 |
| 27 | BRANKE J, ZHANG W. A new myopic sequential sampling algorithm for multi-objective problems[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Winter Simulation Conference, 2015: 859-870. |
| 28 |
CHICK S E , BRANKE J , SCHMIDT C . Sequential sampling to myopically maximize the expected value information[J]. Informs Journal on Computing, 2010, 22 (1): 71- 80.
doi: 10.1287/ijoc.1090.0327 |
| 29 |
CHEN E J , KELTON W D . Sequential selection procedures: using sample means to improve efficiency[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2005, 166 (1): 133- 153.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2003.01.003 |
| 30 | HU J W , HU X F , ZHANG W M , et al. Monotonic indices space method and its application in the capability indices effectiveness analysis of a notional anti-stealth information system[J]. IEEE Trans.on System, Man, Cybernetics, 2008, 39 (2): 404- 413. |
| [1] | Wei ZHANG, Jing HE, Xiaowei XIE, Guoqiang ZHAO, Zhen CHEN. Design and implementation of simulation evaluation system for joint battlefield navigation countermeasure [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3182-3189. |
| [2] | Jun MA, Jingyu YANG, Xi WU. Evaluation of operational system of systems effectiveness based on pre-clustering active semi-supervised learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1889-1896. |
| [3] | Luying REN, Qingguo WANG, Qian MA, Haifeng ZHANG, Weiwei XU. Modeling method study for virtual prototyping of complex products based on meta model [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1609-1614. |
| [4] | Yuanyuan ZHANG, Yang GAO, Peng ZHU, Jintao LIU, Shushan GU. UAV reconnaissance tactical planning based on colored Petri nets [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 900-907. |
| [5] | Tongliang LU, Wenhao CHEN, Bingfeng GE, Qiling DENG. Multi-layer network modeling for combat system-of-systems under information support [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 520-528. |
| [6] | Ketao FENG, Xiaoyi LI, Chen QU, Shentao WANG, Mou CHEN. Simulation research on effective coverage of civil aviation ground to air VHF communication based on DEM [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 684-695. |
| [7] | Jun MA, Jingyu YANG, Liyan ZOU. Generation method of operational system of systems capability graph based on Stacking integrated meta-model [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 154-163. |
| [8] | Ziyan LIU, Shanshan MA, Jing LIANG, Mingcheng ZHU, Lei YUAN. Attention mechanism based CNN channel estimation algorithm in millimeter-wave massive MIMO system [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 307-312. |
| [9] | Guangxun ZENG, Guanghong GONG, Ni LI. Combat system-of-systems simulation scenario generation approach based on semantic matching [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2154-2162. |
| [10] | Chunsi XIE, Zhiying LIU, Yu SANG. Target recognition model of ship-to-land missile based on feature matching [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2244-2253. |
| [11] | Guowei CHEN, Yujing ZHOU, Lei REN. SD optimization of equipment cost structure facing system performance maximization [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(4): 1022-1029. |
| [12] | Zehai GAO, Cunbao MA, Haotian NIU. Performance degradation Lévy model of integrated modular avionics [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(4): 1144-1152. |
| [13] | Zhiying LIU, Chunsi XIE, Jinjun LI, Yu SANG. Smoke region segmentation recognition algorithm based on improved Deeplabv3+ [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(2): 328-335. |
| [14] | Xiangxuan TIAN, Zhiqiang SHI. Simulation data generation algorithm based on evolutional generative adversarial networks for command information system [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(1): 163-170. |
| [15] | Fei WANG, Guangya SI, Zongping HE, Qiang WANG. Theory and calculation method of confrontational potential energy [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(12): 2771-2778. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||