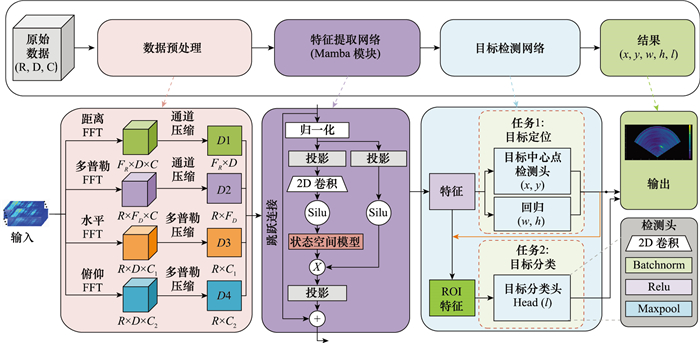
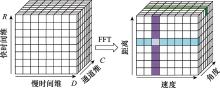
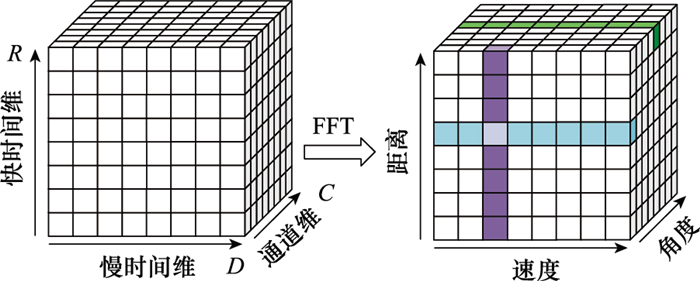
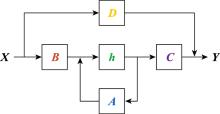
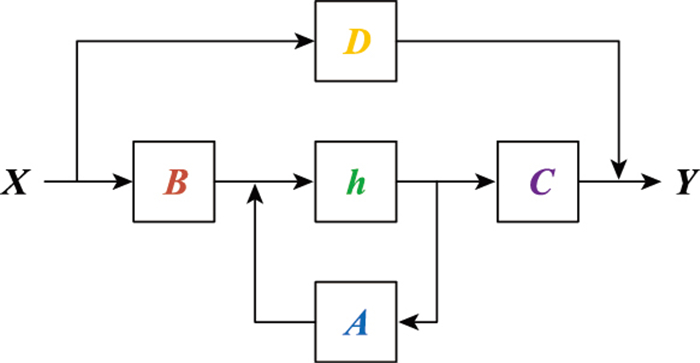
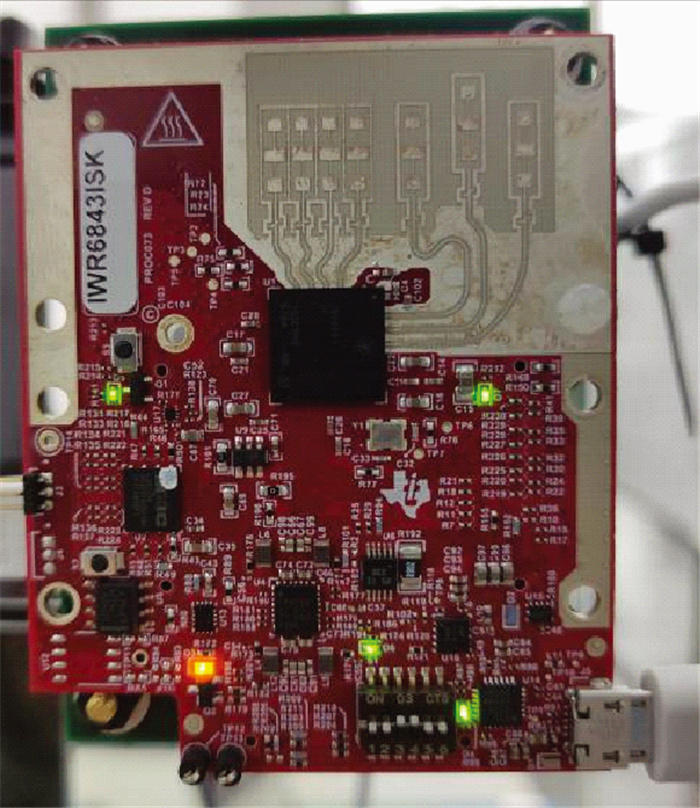
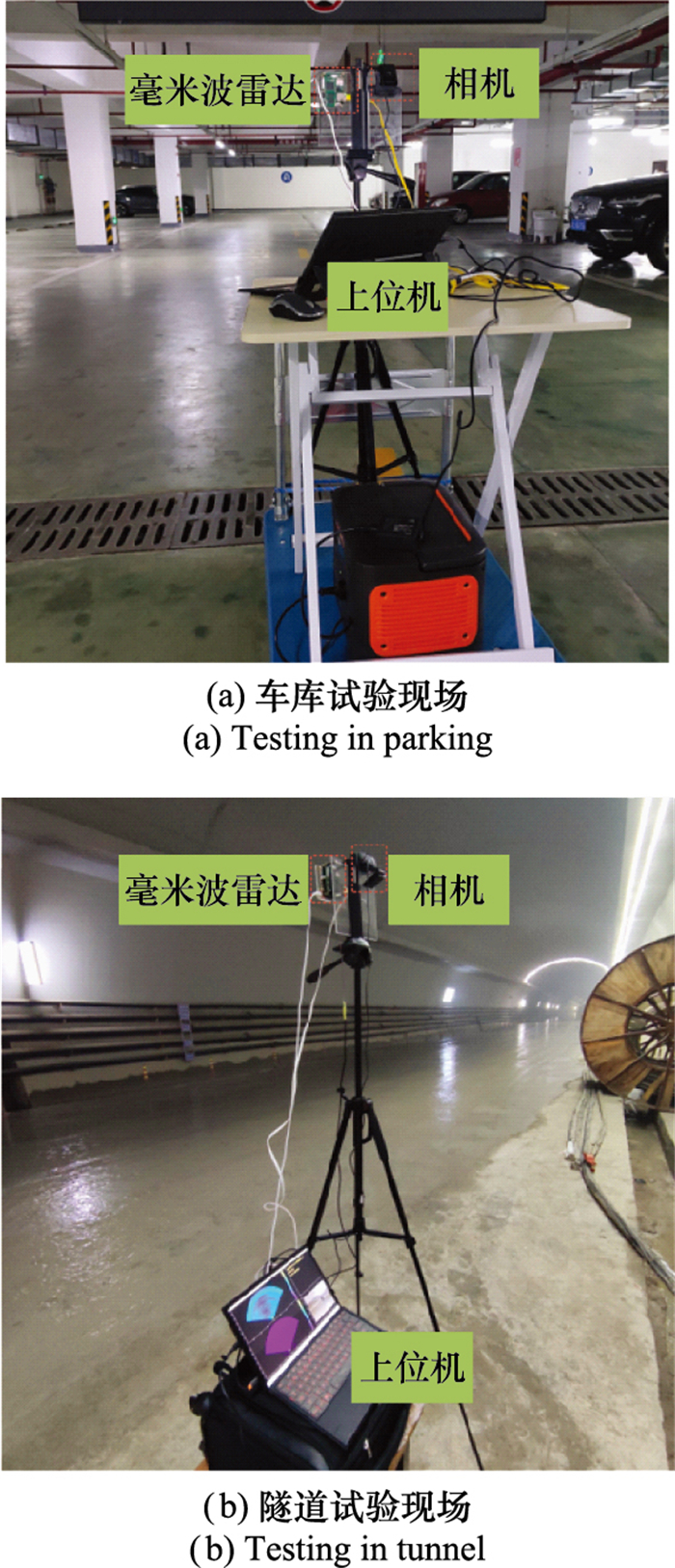
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1453-1460.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.05.08
• Sensors and Signal Processing • Previous Articles
Target recognition and classification algorithm of MMW radar in tunnel
Zhijie JIANG1,2, Heng SONG3,*, Nan HU3, Lanxi DUAN3, Ping CAO1,4
- 1. State Key Laboratory of Particle Detection and Electronics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
2. Department of Modern Physics, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
3. Management and Technology Institute, China Railway No.4 Engineering Group CO., LTD, Hefei 230041, China
4. School of Nuclear Science and Technology, University of Science and Technology of China, Hefei 230026, China
-
Received:2024-04-23Online:2025-06-11Published:2025-06-18 -
Contact:Heng SONG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhijie JIANG, Heng SONG, Nan HU, Lanxi DUAN, Ping CAO. Target recognition and classification algorithm of MMW radar in tunnel[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(5): 1453-1460.
share this article
| 1 | 郑艾辰, 黄锋, 林志, 等. 2008年至2016年我国隧道工程施工安全事故统计与分析[J]. 施工技术, 2017, 46 (S1): 833- 836. |
| ZHENG A C , HUANG F , LIN Z , et al. Statistics and analysis of tunnel construction safety accidents in China from 2008 to 2016[J]. Construction Technology, 2017, 46 (S1): 833- 836. | |
| 2 | LUKE R A . Diamonds with dispatch: computerized LHD dispatching at DeBeers Finsch-a progress report[J]. World Mining Equipment, 1992, 16 (6): 24-25, 27-28. |
| 3 | 宋磊. ZigBee技术在物联网中的应用展望[J]. 现代制造技术与装备, 2017 (2): 43- 44. |
| SONG L . Application prospect of ZigBee technology in internet of things[J]. Modern Manufacturing Technology and Equipment, 2017 (2): 43- 44. | |
| 4 |
AHMED N , GHARGHAN S K , MUTLAG A H , et al. Children tracking system based on zigbee wireless network and neural network[J]. Journal of Techniques, 2023, 5 (1): 103- 113.
doi: 10.51173/jt.v5i1.838 |
| 5 | 徐潇潇, 谢林柏, 彭力. 基于WiFi信号强度特征的室内定位系统设计[J]. 计算机工程, 2015, 41 (4): 87- 91. |
| XU X X , XIE L B , PENG L . Design of indoor positioning system based on WiFi signal strength characteristics[J]. Computer Engineering, 2015, 41 (4): 87- 91. | |
| 6 |
LEIRA F S , HELGESEN H H , JOHANSEN T A , et al. Object detection, recognition, and tracking from UAVs using a thermal camera[J]. Journal of Field Robotics, 2021, 38 (2): 242- 267.
doi: 10.1002/rob.21985 |
| 7 | RAVINDRAN R , SANTORA M J , JAMALI M M . Multi-object detection and tracking, based on DNN, for autonomous vehicles: a review[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 21 (5): 5668- 5677. |
| 8 | 李伟杰, 戴亚文, 唐雨, 等. 基于UWB的地铁隧道定位系统设计[J]. 计算机测量与控制, 2019, 27 (8): 198-201, 206. |
| LI W J , DAI Y W , TANG Y , et al. Design of subway tunnel positioning system based on UWB[J]. Computer Measurement and Control, 2019, 27 (8): 198-201, 206. | |
| 9 | ANISH S , NEHARIKA V , ENVER B , et al. A review of millimeter wave device-based localization and device-free sensing technologies and applications[J]. IEEE Communications Surveys & Tutorials, 2022, 24 (3): 1708- 1749. |
| 10 | 魏军, 韩君龙, 王巍, 等. 基于毫米波雷达的铁路隧道人员定位技术研究[J]. 隧道建设(中英文), 2023, 43 (S2): 223- 229. |
| WEI J , HAN J L , WANG W , et al. Research on personnel location technology of railway tunnel based on millimeter wave radar[J]. Tunnel Construction, 2023, 43 (S2): 223- 229. | |
| 11 | XING Y C, KANHERE O, JU S H, et al. Indoor wireless channel properties at millimeter wave and sub-terahertz frequencies[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Global Communications Conference, 2019. |
| 12 |
WANG Y Z , JIANG Z Y , LI Y D , et al. RODNet: a real-time radar object detection network cross-supervised by camera-radar fused object 3D localization[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Signal Processing, 2021, 15 (4): 954- 967.
doi: 10.1109/JSTSP.2021.3058895 |
| 13 | CHENG J H, KUAN S Y, LATAPIE H, et al. CenterRadarNet: joint 3D object detection and tracking framework using 4D FMCW radar[EB/OL]. [2024-03-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2311.01423. |
| 14 | GU A, DAO T. Mamba: linear-time sequence modeling with selective state spaces[EB/OL]. [2024-03-24]. https://arxiv.org/abs/2312.00752. |
| 15 |
PEARCE A , ZHANG J A , XU R , et al. Multi-object tracking with MMwave radar: a review[J]. Electronics, 2023, 12 (2): 308.
doi: 10.3390/electronics12020308 |
| 16 | 张晨, 叶舟, 吕宇宙, 等. 基于ResNet的智能恒虚警目标检测方法[J]. 上海航天(中英文), 2023, 39 (5): 71- 78. |
| ZHANG C , YE Z , LV Y Z , et al. Intelligent constant false alarm detection method based on ResNet[J]. Aerospace ShangHai (Chinese & English), 2023, 39 (5): 71- 78. | |
| 17 |
CHENG Y W , SU J R , JIANG M X , et al. A novel radar point cloud generation method for robot environment perception[J]. IEEE Trans. on Robotics, 2022, 38 (6): 3754- 3773.
doi: 10.1109/TRO.2022.3185831 |
| 18 | SUN Y, HUANG Z, ZHANG H Z, et al. 3DRIMR: 3D reconstruction and imaging via mmWave radar based on deep learning[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Performance, Computing, and Communications Conference, 2021. |
| 19 | 周驰, 李智, 徐灿. 基于深度神经网络的空间目标结构识别[J]. 中国空间科学技术, 2019, 39 (1): 32- 39. |
| ZHOU C , LI Z , XU C . Spatial target structure recognition based on deep neural network[J]. China Space Science and Technology, 2019, 3, 9. | |
| 20 | 孟继成, 杨万麟. 基于核函数的雷达一维距离像目标识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2005, 27 (3): 462- 466. |
| MENG J C , YANG W L . Radar one-dimensional range image target recognition based on kernel function[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information, 2005, 27 (3): 462- 466. | |
| 21 | JITHESH V, SAGAYARAJ M J, SRINIVASA K G, et al. LSTM recurrent neural networks for high resolution range profile based radar target classification[C]//Proc. of the 3rd International Conference on Computational Intelligence & Communication Technology, 2017. |
| 22 | GAO C, LIU H W, ZHOU S H, et al. Maneuvering target tracking with recurrent neural networks for radar application[C]// Proc. of the International Conference on Radar, 2018. |
| 23 | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017: 6000-6010. |
| 24 | DUAN K W, BAI S, XIE L X, et al. CenterNet: keypoint triplets for object detection[C]//Proc. of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, 2019: 6568-6577. |
| 25 |
HUSSAIN M . YOLOv1 to v8: unveiling each variant-a comprehensive review of YOLO[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 42816- 42833.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3378568 |
| 26 |
JIANG P Y , ERGU D J , LIU F Y , et al. A review of Yolo algorithm developments[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2022, 199, 1066- 1073.
doi: 10.1016/j.procs.2022.01.135 |
| 27 | LEE Y H , KIM Y . Comparison of CNN and YOLO for object detection[J]. Journal of the Semiconductor & Display Technology, 2020, 19 (1): 85- 92. |
| 28 | GIRSHICK R. Fast R-CNN[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2015: 1440-1448. |
| 29 |
LI W Z . Analysis of object detection performance based on Faster R-CNN[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series, 2021, 1827 (1): 012085.
doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1827/1/012085 |
| 30 | WEI L, DRAGOMIR A, DUMITRU E, et al. SSD: single shot MultiBox detector[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 21-37. |
| 31 |
ZHAI S P , SHANG D R , WANG S H , et al. DF-SSD: an improved SSD object detection algorithm based on DenseNet and feature fusion[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 24344- 24357.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.2971026 |
| 32 | LU X C , JI J , XING Z Q , et al. Attention and feature fusion SSD for remote sensing object detection[J]. IEEE Trans. on Instrumentation and Measurement, 2021, 70, 5501309. |
| [1] | Zekun GUO, Hongfei YANG, Zheng LIU, Rong XIE, Lei RAN, Jia'nan LI. Narrow-band radar airborne target recognition method based on MGMD space [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1136-1145. |
| [2] | Qianqi NIE, Minghui SHA, Yingshen ZHU, Chongyu WANG, Nianqiang CUI. Radar multi-component signal recognition method based on blind source separation combined with singular spectrum analysis [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1168-1175. |
| [3] | Lei YUAN, Yanjuan YANG, Yi GUO, Peng DAI. Deep learning-based semi-blind identification algorithm for code rates of LDPC codes with correlated noise [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1335-1345. |
| [4] | Jiakuan LI, Bo FENG, Hongliang LIU, Chunmao YE, Jizhou YU. Angle-guided attention-based wideband PD recognition method for aerodynamic targets [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(3): 807-816. |
| [5] | Xiarun SHEN, Ruonan LI, Haotian ZHANG. Server KPI anomaly detection based on CVAE-LSTM [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(3): 1019-1027. |
| [6] | Xiaolin LIU, Mengjiao GUO, Zhuo LI. Adaptive graph convolutional recurrent network prediction method for flight delay based on Dueling DQN optimization [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(2): 568-579. |
| [7] | Weihong FU, Xinyu ZHANG, Naian LIU. Single-channel blind source separation algorithm for co-frequency and co-modulation based on multi-scale fusion neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(2): 641-649. |
| [8] | Jun CHI, Rongchen SUN, Zhiguo SUN, Zhenyu YI. Tunnel channel modeling based on propagation graph theory at 6 GHz [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(1): 316-323. |
| [9] | Wei CAI, Xin WANG, Xinhao JIANG, Zhiyong YANG, Dong CHEN. Research on few shot target detection method based on decoupling [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(9): 2941-2950. |
| [10] | Jianguo YIN, Wen SHENG, Wei JIANG. Radar air target recognition based on deep residual shrinkage network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(9): 3012-3018. |
| [11] | Xiaoxuan CHEN, Shuwen XU, Shaohai HU, Xiaole MA. Infrared and visible light image fusion based on convolution and self attention [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(8): 2641-2649. |
| [12] | Caiyun WANG, Huiwen ZHANG, Jianing WANG, Yida WU, Yun CHANG. Ballistic midcourse target RCS recognition based on DTCWT-VAE [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(7): 2269-2275. |
| [13] | Qianglong WANG, Xiaoguang GAO, Bicong WU, Zijian HU, Kaifang WAN. Review of research on restricted Boltzmann machine and its variants [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(7): 2323-2345. |
| [14] | Xiantao SUN, Wangyang JIANG, Wenjie CHEN, Weihai CHEN, Yali ZHI. Object grasp pose detection based on the region of interest [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 1867-1877. |
| [15] | Yida WU, Caiyun WANG, Jianing WANG, Xiaofei LI. Infrared multi-sensor fusion recognition method based on ISVM-DS [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(5): 1555-1560. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||