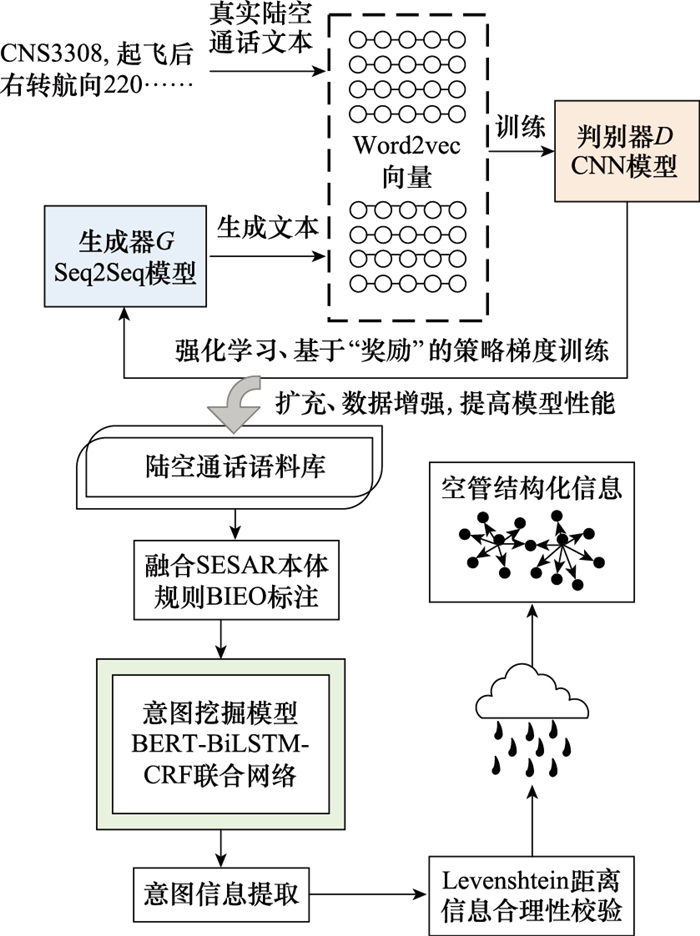
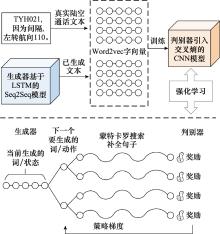
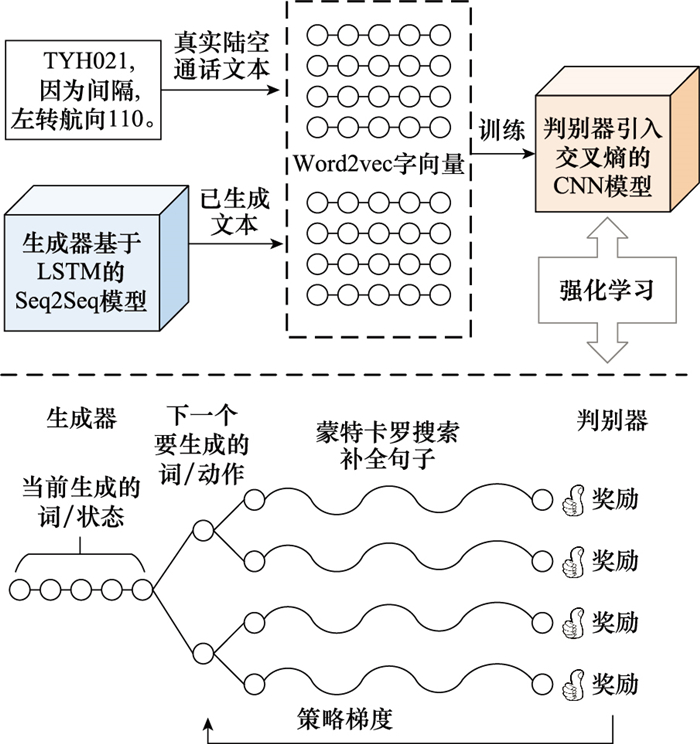
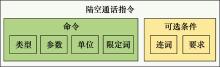
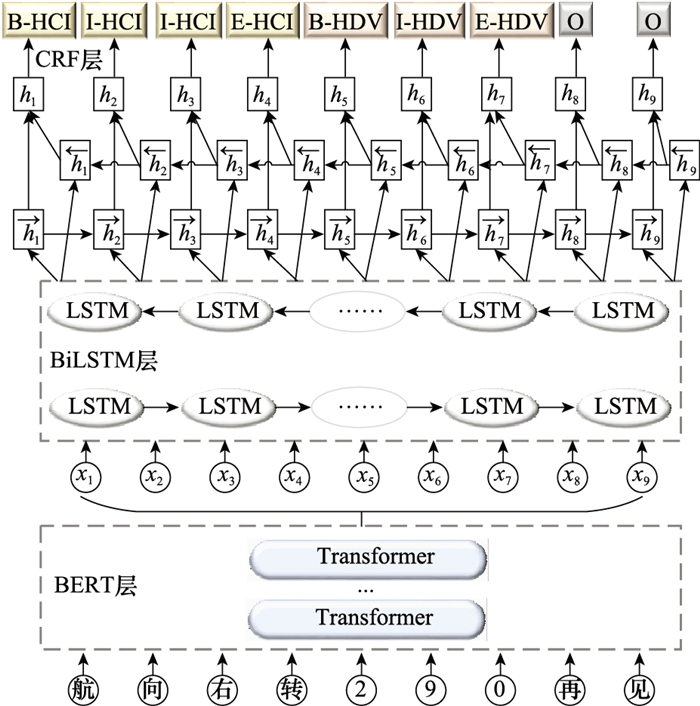
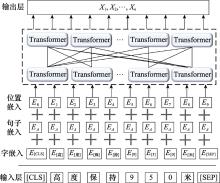
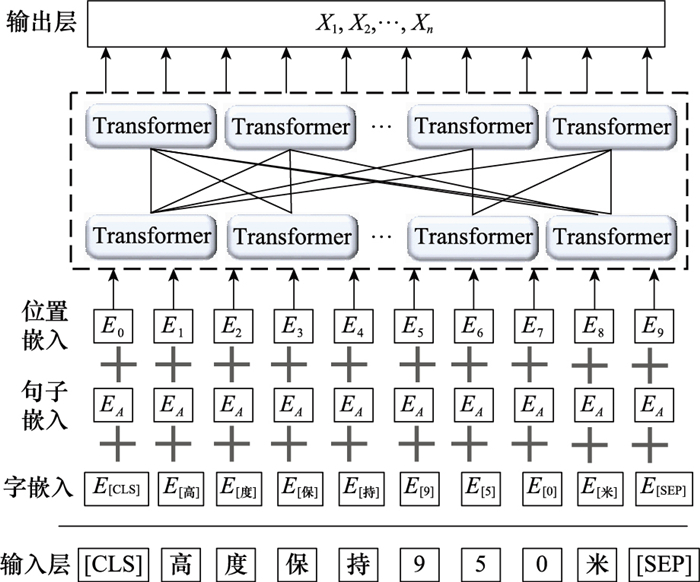
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (2): 740-750.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.02.38
• Communications and Networks • Previous Articles
Intention mining for civil aviation radiotelephony communication based on BERT and generative adversarial
Lan MA1,*, Shijun MENG2, Zhijun WU3
- 1. School of Air Traffic Management, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China
2. School of Electronic Information and Automation, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China
3. School of Safety Science and Engineering, Civil Aviation University of China, Tianjin 300300, China
-
Received:2022-12-05Online:2024-01-25Published:2024-02-06 -
Contact:Lan MA
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lan MA, Shijun MENG, Zhijun WU. Intention mining for civil aviation radiotelephony communication based on BERT and generative adversarial[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(2): 740-750.
share this article
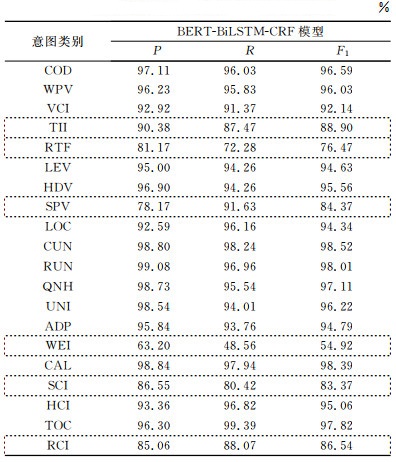
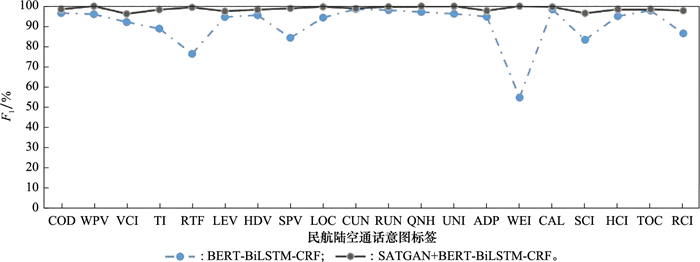
Table 9
Recognition results of GAN+BERT-BiLSTM-CRF model with fused ontology on various types of intent labels %"
| 意图类别 | GAN+BERT-BiLSTM-CRF模型 | ||
| P/% | R/% | F1/% | |
| COD | 96.97 | 100.00 | 98.46 |
| WPV | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| VCI | 98.70 | 93.83 | 96.20 |
| TII | 98.85 | 97.64 | 98.25 |
| RTF | 99.20 | 99.60 | 99.40 |
| LEV | 98.73 | 96.30 | 97.50 |
| HDV | 98.82 | 97.67 | 98.25 |
| SPV | 100.00 | 97.83 | 98.90 |
| LOC | 99.55 | 99.79 | 99.67 |
| CUN | 99.24 | 98.48 | 98.86 |
| RUN | 99.49 | 100.00 | 99.75 |
| QNH | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| UNI | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| ADP | 98.48 | 97.01 | 97.74 |
| WEI | 100.00 | 100.00 | 100.00 |
| CAL | 99.49 | 99.75 | 99.62 |
| SCI | 98.47 | 94.59 | 96.49 |
| HCI | 100.00 | 96.83 | 98.39 |
| TOC | 99.60 | 97.30 | 98.44 |
| RCI | 100.00 | 95.65 | 97.78 |
| 1 | ZULUAGA G J , VESELY K , BLATT A , et al. Automatic call sign detection: matching air surveillance data with air traffic spoken communications[J]. Multidisciplinary Digital Publishing Institute Proceedings, 2020, 59 (1): 14. |
| 2 | HELMKE H, KLEINERT M, OHNEISER O, et al. Machine learning of air traffic controller command extraction models for speech recognition applications[C]//Proc. of the AIAA/IEEE 39th Digital Avionics Systems Conference, 2020. |
| 3 | ZULUAGA G J, SARFGOO S S, PRASAD A, et al. BERTraffic: a robust BERT-based approach for speaker change detection and role identification of air-traffic communications[EB/OL]. [2022-11-05]. https:doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2110.05781. |
| 4 |
GUIMIN J I A , JUNXIAN L I . A novel strategy for fine-grained semantic verification of civil aviation radiotelephony read-backs[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35 (12): 266- 277.
doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2022.05.005 |
| 5 | HELMKE H, SLOTTY M, POIGER M, et al. Ontology for transcription of ATC speech commands of SESAR 2020 solution PJ. 16-04[C]//Proc. of the IEEE/AIAA 37th Digital Avionics Systems Conference, 2018. |
| 6 |
LI J , SUN A X , HAN J L , et al. A survey on deep learning for named entity recognition[J]. IEEE Trans. on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2022, 34 (1): 50- 70.
doi: 10.1109/TKDE.2020.2981314 |
| 7 | SUTSKEVER I, MARTENS J, HINTON G E. Generating text with recurrent neural networks[C]//Proc. of the 28th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2011: 1017-1024. |
| 8 | BENGIO S, VINYALS O, JAITLY N, et al. Scheduled sampling for sequence prediction with recurrent neural networks[EB/OL]. [2015-09-23]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1506.03099. |
| 9 | KOO S. Automatic colorization with deep convolutional generative adversarial networks[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, 2017: 212-217. |
| 10 | ZHANG Y Z, GAN Z, FAN K, et al. Adversarial feature matching for text generation[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017, 70: 4006-4015. |
| 11 | YU L T, ZHANG W N, WANG J, et al. Seqgan: sequence generative adversarial nets with policy gradient[C]//Proc. of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2017: 2852-2858. |
| 12 | CHE T, LI Y R, ZHANG R X, et al. Maximum-likelihood augmented discrete generative adversarial networks[EB/OL]. [2022-11-30]. https:dio.org/10.48550/arxiv.1702.07983. |
| 13 | LI J W, MONROE W, SHI T L, et al. Adversarial learning for neural dialogue generation[C]//Proc. of Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing, 2017: 2157-2169. |
| 14 | GUO J X, LU S D, CAI H, et al. Long text generation via adversarial training with leaked information[C]//Proc. of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018. |
| 15 |
KIM S , YOON B . Multi-document summarization for patent documents based on generative adversarial network[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 207, 117983.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2022.117983 |
| 16 |
SHAHRIAR S . GAN computers generate arts? A survey on visual arts, music, and literary text generation using generative adversarial network[J]. Displays, 2022, 73, 102237.
doi: 10.1016/j.displa.2022.102237 |
| 17 | 邱意, 赵子豪, 李丹, 等. 基于GAN的民航陆空通话文本生成方法[J]. 计算机科学与应用, 2018, 8 (12): 1870- 1877. |
| QIU Y , ZHAO Z H , LI D , et al. Text generation in civil aviation radiotelephony communication using generative adversarial network[J]. Computer Science and Application, 2018, 8 (12): 1870- 1877. | |
| 18 |
WIMALASURIYA D C , DOU D . Ontology-based information extraction: an introduction and a survey of current approaches[J]. Journal of Information Science, 2010, 36 (3): 306- 323.
doi: 10.1177/0165551509360123 |
| 19 | CHANG J , HAN X T . Multi-level context features extraction for named entity recognition[J]. Computer Speech & Language, 2023, 77, 101412. |
| 20 | 邓学鸣. 基于Python正则表达式的管制指令匹配与提取[J]. 数字通信世界, 2019, (5): 13- 14. |
| DENG X M . Control command matching and extraction based on Python regular expressions[J]. Digital Communication World, 2019, (5): 13- 14. | |
| 21 | 杨昱昕. 基于自然语义提取的空中交通辅助决策方法研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2018. |
| YANG Y X. Research on air traffic decision-making method based on extraction of natural semanteme[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2018. | |
| 22 | 王煊, 盛寅, 丁辉, 等. 一种基于自然语言处理的结构化管制指令提取方法[P]. 中国: CN109460547A, 2019.03.12. |
| WANG X, SHENG Y, DING H, et al. A structured control instruction extraction method based on natural language processing[P]. China: CN109460547A, 2019.03.12. | |
| 23 |
LIU K J , GOHARY N E . Ontology-based semi-supervised conditional random fields for automated information extraction from bridge inspection reports[J]. Automation in Construction, 2017, 81, 313- 327.
doi: 10.1016/j.autcon.2017.02.003 |
| 24 | CHENG J R , LIU J X , XU X B , et al. A review of chinese named entity recognition[J]. KSII Trans. on Internet & Information Systems, 2021, 15 (6): 2012- 2031. |
| 25 | LIU C , YANG S W . Using text mining to establish knowledge graph from accident/incident reports in risk assessment[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 207 (11): 117991. |
| 26 |
LUO R Q , SUN L A , XIA Y C , et al. BioGPT: generative pre-trained transformer for biomedical text generation and mining[J]. Briefings in Bioinformatics, 2022, 23 (6): 409.
doi: 10.1093/bib/bbac409 |
| 27 |
LIN Y , TAN X L , YANG B , et al. Real-time controlling dynamics sensing in air traffic system[J]. Sensors, 2019, 19 (3): 679.
doi: 10.3390/s19030679 |
| 28 | LIN Y , DENG L J , CHEN Z M , et al. A real-time ATC safety monitoring framework using a deep learning approach[J]. IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2019, 21 (11): 4572- 4581. |
| 29 | 张兴明. 基于深度学习的地空通信文本命名实体识别研究[J]. 现代计算机, 2021, (2): 28- 33. |
| ZHANG X M . A study of named entity recognition for radiotelephony communication text based on deep learning[J]. Modern Computer, 2021, (2): 28- 33. | |
| 30 | KOCOUR M , VESELY K , SZOKE I , et al. Automatic processing pipeline for collecting and annotating air-traffic voice communication data[J]. Engineering Proceedings, 2021, 13 (1): 8- 18. |
| 31 | 段立, 封皓君, 张碧莹, 等. 融合语义路径与语言模型的元学习知识推理框架[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2022, 44 (12): 4376- 4383. |
| DUAN L , FENG H J , ZHANG B Y , et al. A meta-learning knowledge reasoning framework combining semantic path and language model[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2022, 44 (12): 4376- 4383. | |
| 32 | 刘磊. 基于生成式对抗网络与异质集成学习的文本情感分类研究[D]. 南京: 南京邮电大学, 2020. |
| LIU L. Research on text sentiment classfication based on gene-rative adversarial network and heterogenous ensemble learning[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2020. | |
| 33 | HU X , CHU L Y , PEI J , et al. Model complexity of deep learning: a survey[J]. Knowledge and Information Systems, 2021, 63 (2): 2585- 2619. |
| [1] | Shiyan PANG, Jingjing HAO, Lining XING, Xu TAN. Weakly supervised domain adaptation algorithm for building extraction from remote sensing images [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(6): 1616-1623. |
| [2] | Li CHEN, Zihan FANG, Liquan MEI. DSS signal generation algorithm based on GAN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(5): 1544-1552. |
| [3] | Bin LIU, Jiacai YI, Li YAO, Yanjuan WANG, Zhaoyun DING, Xianqiang ZHU. Situational awareness ontology modeling for threat from space cyber operations [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(3): 745-754. |
| [4] | Haoran ZENG, Yunwen FENG, Cheng LU, Weihuang PAN. Spare parts consumption forecast method based on improved generative adversarial network for domestic civil aircraft [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(10): 3132-3138. |
| [5] | Bowei QIN, Lei JIANG, Hua XU, Weiyu NIU. Open-set recognition algorithm for modulation signal based on RE-GAN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(10): 3321-3328. |
| [6] | Rongxiang LIU, Lin WU, Zhige XIE, Honglin LIU. Auxiliary situation analysis for air defense system based on generative adversarial network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2522-2529. |
| [7] | Ruilin XU, Boying GENG, Shukan LIU. Research on structural knowledge extraction and organization for multi-modal governmental documents [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2241-2250. |
| [8] | Yiyang LUO, Qingsong ZHAO, Huachao LI, Yong LI, Jianbin SUN. Framework and modeling method of weaponry utilization knowledge [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 841-849. |
| [9] | Weijian PANG, Hui LI, Qian HUANG, Peng LI, Xianming MA. Review on ontology-based task planning for unmanned systems [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 908-920. |
| [10] | Kai SHAO, Miaomiao ZHU, Guangyu WANG. Modulation recognition method based on generative adversarial andconvolutional neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 1036-1043. |
| [11] | Shuting WANG, Xiaobing LIU, Junhua ZHOU, Zhaoyang BAI, Xiang ZHAI. Ontology based knowledge representation and reuse method for complex product maintenance engineering cases [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 557-568. |
| [12] | Xue SUN, Zhiqiu HUANG, Guohua SHEN, Jinyong WANG, Heng XU. Behavior decision method of autonomous vehicle based on ontology and BN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(2): 452-465. |
| [13] | HE Hongyue, WANG Zhixue, LIANG Haomo, WANG Qinglong. Approach to mission modeling and analysis for system of systems based on ontology [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1973-1978. |
| [14] | CHENG Kai, CHEN Gang, YIN Chengxiang, KANG Ruizhi, KANG Xingdang. Core ontology modeling and reasoning method for course of action [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 805-814. |
| [15] | SUN Yufei, MA Liangli, LV Minhui, QIN Jiwei. Improved co-training based ontology matching method [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(2): 459-464. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||