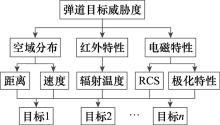
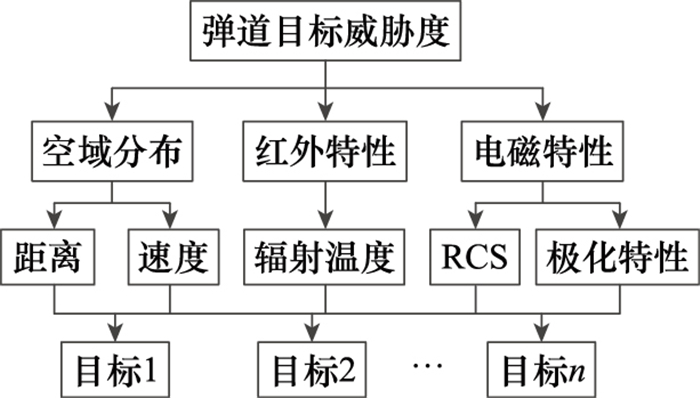
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 1230-1238.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.04.20
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Missile defense target threat assessment based on improved similarity measure and information entropy of IFRS
Yingqi LU, Chengli FAN*, Qiang FU, Xiaowen ZHU, Wei LI
- School of Air And Missile Defense, Air Force Engineering University, Xi'an 710051, China
-
Received:2020-12-31Online:2022-04-01Published:2022-04-01 -
Contact:Chengli FAN
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yingqi LU, Chengli FAN, Qiang FU, Xiaowen ZHU, Wei LI. Missile defense target threat assessment based on improved similarity measure and information entropy of IFRS[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1230-1238.
share this article
Table 3
The corresponding relationship between 9-level quantization results and IFRS"
| 威胁度 | IFRS | 威胁度 | IFRS | |
| 极大 | 〈0.85, 0.95, 0.15, 0.05〉 | 小 | 〈0.40, 0.50, 0.60, 0.50〉 | |
| 很大 | 〈0.80, 0.90, 0.20, 0.10〉 | 较小 | 〈0.35, 0.45, 0.65, 0.55〉 | |
| 较大 | 〈0.70, 0.80, 0.30, 0.20〉 | 很小 | 〈0.20, 0.30, 0.80, 0.70〉 | |
| 大 | 〈0.60, 0.70, 0.40, 0.30〉 | 极小 | 〈0.10, 0.20, 0.90, 0.80〉 | |
| 中 | 〈0.45, 0.60, 0.55, 0.35〉 | - | - |
Table 4
Decision matrix"
| 目标 | 目标属性 | ||||
| 距离r1 | 速度r2 | 辐射温度r3 | RCS r4 | 极化特性r5 | |
| x1 | 〈0.20, 0.30, 0.60, 0.10〉 | 〈0.30, 0.70, 0.40, 0.20〉 | 〈0.55, 0.65, 0.40, 0.25〉 | 〈0.25, 0.60, 0.50, 0.35〉 | 〈0.70, 0.80, 0.30, 0.20〉 |
| x2 | 〈0.30, 0.75, 0.50, 0.25〉 | 〈0.45, 0.75, 0.30, 0.20〉 | 〈0.70, 0.85, 0.30, 0.10〉 | 〈0.50, 0.85, 0.35, 0.10〉 | 〈0.45, 0.60, 0.55, 0.35〉 |
| x3 | 〈0.10, 0.80, 0.65, 0.15〉 | 〈0.30, 0.65, 0.40, 0.10〉 | 〈0.45, 0.60, 0.50, 0.25〉 | 〈0.55, 0.95, 0.25, 0.05〉 | 〈0.35, 0.45, 0.65, 0.55〉 |
| x4 | 〈0.25, 0.85, 0.15, 0.10〉 | 〈0.20, 0.70, 0.60, 0.30〉 | 〈0.50, 0.60, 0.45, 0.30〉 | 〈0.60, 0.80, 0.30, 0.15〉 | 〈0.80, 0.90, 0.20, 0.10〉 |
| 信息熵 | 0.975 6 | 0.992 8 | 0.998 8 | 0.994 3 | 0.999 8 |
| 属性权重 | 0.203 4 | 0.199 8 | 0.198 7 | 0.199 6 | 0.198 5 |
Table 5
Weighted decision matrix"
| 目标 | 目标属性 | ||||
| 距离r1 | 速度r2 | 辐射温度r3 | RCS r4 | 极化特性r5 | |
| x1 | 〈0.040 7, 0.061 0, 0.122 0, 0.020 3〉 | 〈0.059 9, 0.139 8, 0.079 9, 0.039 9〉 | 〈0.109 3, 0.129 1, 0.079 5, 0.049 7〉 | 〈0.049 9, 0.119 7, 0.099 8, 0.069 8〉 | 〈0.138 9, 0.158 8, 0.059 5, 0.039 7〉 |
| x2 | 〈0.061 0, 0.152 5, 0.101 7, 0.050 8〉 | 〈0.089 9, 0.149 8, 0.059 9, 0.039 9〉 | 〈0.139 1, 0.168 9, 0.16 8 9, 0.019 8〉 | 〈0.099 8, 0.169 6, 0.06 9 8, 0.019 9〉 | 〈0.089 3, 0.119 1, 0.10 9 2, 0.069 5〉 |
| x3 | 〈0.020 3, 0.162 7, 0.132 2, 0.030 5〉 | 〈0.059 9, 0.129 9, 0.079 9, 0.199 9〉 | 〈0.089 4, 0.119 2, 0.099 3, 0.049 7〉 | 〈0.109 8, 0.189 6, 0.049 9, 0.099 8〉 | 〈0.069 5, 0.089 3, 0.129 0, 0.109 2〉 |
| x4 | 〈0.050 8, 0.172 9, 0.030 5, 0.020 3〉 | 〈0.039 9, 0.139 8, 0.119 9, 0.059 9〉 | 〈0.099 3, 0.119 2, 0.089 4, 0.168 9〉 | 〈0.119 7, 0.159 7, 0.059 9, 0.029 9〉 | 〈0.158 8, 0.178 6, 0.039 7, 0.019 8〉 |
Table 6
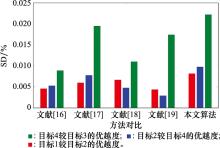
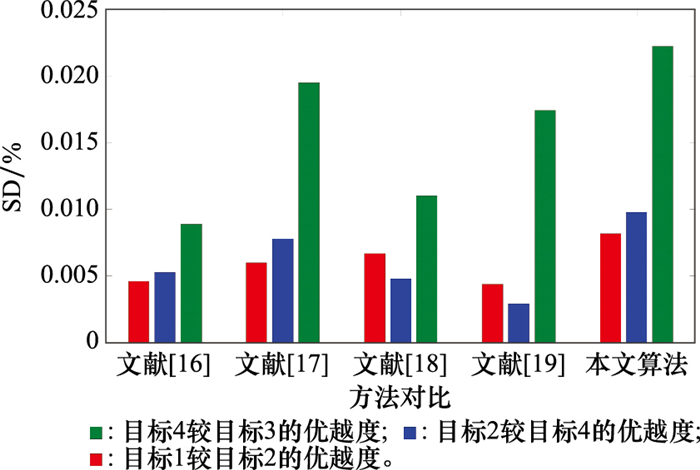
Target threat ranking and SD of different methods"
| 方法 | 目标ζ1 | 目标ζ2 | 目标ζ3 | 目标ζ4 | 排序结果 | SDij/% | ||
| 文献[ | 0.704 6 | 0.698 3 | 0.691 4 | 0.695 1 | 1>2>4>3 | SD12=0.008 9 | SD24=0.004 6 | SD43=0.005 3 |
| 文献[ | 0.645 2 | 0.632 6 | 0.623 9 | 0.628 8 | 1>2>4>3 | SD12=0.019 5 | SD24=0.006 0 | SD43=0.007 8 |
| 文献[ | 0.830 1 | 0.820 9 | 0.811 5 | 0.815 4 | 1>2>4>3 | SD12=0.011 0 | SD24=0.006 7 | SD43=0.004 8 |
| 文献[ | 0.532 9 | 0.523 6 | 0.519 8 | 0.521 3 | 1>2>4>3 | SD12=0.017 4 | SD24=0.004 4 | SD43=0.002 9 |
| 文献[ | 0.604 6 | 0.587 4 | 0.583 2 | 0.593 6 | 1>4>2>3 | SD14=0.018 2 | SD42=0.010 4 | SD23=0.007 1 |
| 本文算法 | 0.513 6 | 0.502 2 | 0.493 2 | 0.498 1 | 1>2>4>3 | SD12=0.022 2 | SD24=0.008 2 | SD43=0.009 8 |
| 1 | 孙海文, 谢晓方, 孙涛, 等. 小样本数据缺失状态下DBN舰艇编队防空目标威胁评估方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41 (6): 1300- 1308. |
| SUN H W , XIE X F , SUN T , et al. Threat assessment method of warships formation air defense based on DBN under the condition of small sample data missing[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41 (6): 1300- 1308. | |
| 2 |
杨海燕, 韩城, 张帅文. 基于FDBN的空中目标威胁评估方法[J]. 火力与指挥控制, 2019, 44 (1): 29- 33.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2019.01.006 |
|
YANG H Y , HAN C , ZHANG S W . Research of aerial target threat assessment based on fuzzy dynamic Bayesian network[J]. Fire Control & Command Control, 2019, 44 (1): 29- 33.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0640.2019.01.006 |
|
| 3 |
徐浩, 邢清华. 基于证据理论的助推段弹道导弹目标威胁评估[J]. 军事运筹与系统工程, 2016, 30 (2): 9- 14.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8211.2016.02.002 |
|
XU H , XING Q H . Target threat assessment of boost phase ballistic missile based on evidence theory[J]. Military Operations Research and Systems Engineering, 2016, 30 (2): 9- 14.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-8211.2016.02.002 |
|
| 4 | 宋亚飞, 王晓丹, 雷蕾. 基于直觉模糊集的时域证据组合方法研究[J]. 自动化学报, 2016, 42 (9): 1322- 1338. |
| SONG Y F , WANG X D , LEI L . Combination of temporal evidence sources based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2016, 42 (9): 1322- 1338. | |
| 5 |
李俊生, 梁伟, 刘雪梅, 等. 基于离差最大化的导弹中段目标威胁度评估[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2007, 27 (5): 164- 167.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2007.05.025 |
|
LI J S , LIANG W , LIU X M , et al. The multi-attribute evaluation of menace of targets in midcourse of ballistic missile based on maximal windage method[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2007, 27 (5): 164- 167.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-6788.2007.05.025 |
|
| 6 |
张浩为, 谢军伟, 葛佳昂, 等. 改进TOPSIS的多态融合直觉模糊威胁评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40 (10): 2263- 2269.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.16 |
|
ZHANG H W , XIE J W , GE J A , et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy set threat assessment based on improved TOPSIS and multiple times fusion[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40 (10): 2263- 2269.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.16 |
|
| 7 | GAO Y , LI D S , ZHONG H . A novel target threat assessment method based on three-way decisions under intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making environment[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 87 (1): 103276- 103284. |
| 8 | ZHANG Q , HU J H , FENG J F , et al. Air multi-target threat assessment method based on improved GGIFSS[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2019, 36 (2): 4127- 4139. |
| 9 | 陈德江, 王君. 基于直觉模糊集的防空作战目标威胁评估[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2019, 41 (4): 46- 51. |
| CHEN D J , WANG J . Air defense target threat assessment based on intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2019, 41 (4): 46- 51. | |
| 10 | 肖力铭, 齐海生, 屈济坤, 等. 基于直觉模糊层次分析法的空中目标威胁评估[J]. 探测与控制学报, 2019, 41 (3): 108- 111. |
| XIAO L M , QI H S , QU J K , et al. Air target threat assessment based on intuitionistic fuzzy analytic hierarchy process[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2019, 41 (3): 108- 111. | |
| 11 |
ATANASSOV K . Intuitionistic fuzzy sets[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 1986, 20 (1): 87- 96.
doi: 10.1016/S0165-0114(86)80034-3 |
| 12 | PAWLAK Z . Rough sets[J]. Internarial Journal of Computer and Information Sciences, 1982, 11 (2): 341- 356. |
| 13 | 范翔宇, 王红卫, 索中英. 基于粗糙集-信息熵的辐射源威胁评估方法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42 (8): 1755- 1760. |
| FAN X Y , WANG H W , SUO Z Y . Radiator threat evaluating method based on rough set and information entropy[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42 (8): 1755- 1760. | |
| 14 | 雷英杰, 路艳丽, 孔韦韦, 等. 直觉模糊粗糙集理论及应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2013. |
| LEI Y J , LU Y L , KONG W W , et al. Theory and application of intuitionistic fuzzy rough set[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2013. | |
| 15 |
WU D , YAN X B , PENG R , et al. Multi-criteria decision making based on correlation coefficient of triangular intuitionistic fuzzy numbers[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiao Tong University (Science), 2019, 24 (4): 480- 484.
doi: 10.1007/s12204-019-2098-y |
| 16 | 薛占熬, 赵丽平, 张敏, 等. 多粒度支持直觉模糊粗糙集的多属性决策方法[J]. 模式识别与人工智能, 2019, 32 (8): 677- 690. |
| XUE Z A , ZHAO L P , ZHANG M , et al. Multi-attribute decision-making method based on multi-granulation support intuitionistic fuzzy rough sets[J]. Pattern Recognition and Artificial Intelligence, 2019, 32 (8): 677- 690. | |
| 17 | 刘勇, 熊晓旋, 刘健. 优势直觉模糊粗糙集决策方法及其应用[J]. 系统管理学报, 2018, 27 (3): 538- 545, 558. |
| LIU Y , XIONG X X , LIU J . Decision making on dominant intuitionistic fuzzy rough set and its application[J]. Journal of Systems & Management, 2018, 27 (3): 538- 545, 558. | |
| 18 |
QIAN Y H , LI S Y , LIANG J Y , et al. Pessimistic rough set based decisions: a multi-granulation fusion strategy[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 264, 196- 210.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2013.12.014 |
| 19 |
ZHANG L , ZHAN J M , XU Z S . Covering-based generalized if rough sets with applications to multi-attribute decision-making[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 478, 275- 302.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.11.033 |
| 20 |
SUN B Z , MA W M , CHEN X T , et al. Heterogeneous multi-granulation fuzzy rough set-based multiple attribute group decision making with heterogeneous preference information[J]. Computers and Industrial Engineering, 2018, 122, 24- 38.
doi: 10.1016/j.cie.2018.05.034 |
| 21 |
IN F F , NI Z W , CHEN H Y , et al. Approaches to group decision making with intuitionistic fuzzy preference relations based on multiplicative consistency[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 97, 48- 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2016.01.017 |
| 22 |
SHEN F , MA X S , LI Z Y , et al. An extended intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS method based on a new distance measure with an application to credit risk evaluation[J]. Information Sciences, 2018, 428, 105- 119.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2017.10.045 |
| 23 |
HAO Z N , XU Z S , ZHAO H , et al. Novel intuitionistic fuzzy decision making models in the framework of decision field theory[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 33, 57- 70.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2016.05.001 |
| 24 | GAO Y , LI D S , ZHONG H . A novel target threat assessment method based on three-way decisions under intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making environment[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 87 (2): 103276- 103284. |
| 25 |
MENG F Y , TAN C Q , ZHANG Q . Some interval-valued intuitionistic uncertain linguistic hybrid Shapley operators[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 25 (3): 452- 463.
doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2014.00052 |
| 26 |
FAN C L , SONG Y F , LEI L , et al. New operators for aggregating intuitionistic fuzzy information with their application in decision making[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 27214- 27238.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2832206 |
| 27 | LIU P . Multiple attribute group decision making method based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy power Heronian aggregation operators[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2017, 108 (1): 199- 212. |
| 28 | LOURENZUTTI R , KROHLING R A , REFORMAT M Z . Choquet based TOPSIS and TODIM for dynamic and heterogeneous decision making with criteria interaction[J]. Information Sciences, 2017, 408 (2): 41- 69. |
| 29 | YANG Z L , LI J Q , HUANG L C , et al. Developing dynamic intuitionistic normal fuzzy aggregation operators for multi-attribute decision-making with time sequence preference[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2017, 82 (2): 344- 356. |
| 30 |
ZHOU W , XU Z S . Modeling and applying credible interval intuitionistic fuzzy reciprocal preference relations in group decision making[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28 (2): 301- 314.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.02.12 |
| [1] | Xinyu XU, Lunjun WAN, Ping CHEN, Jiangbin DAI, Zhizhou GAO. Modeling of alert patrol airspace planning in defensive counterair interception operation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1589-1599. |
| [2] | Bowen YU, Lin YU, Ming LYU, Jie ZHANG. Target threat assessment model based on M-ANFIS-PNN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3155-3163. |
| [3] | Chong JIN, Juan SUN, Yongjia WANG, Pushen CAI, Xin RONG. Threat comprehensive assessment for air defense targets based on intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS and variable weight VIKOR [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 172-180. |
| [4] | Xinping MI, Xihong CHEN, Zan LIU, Yongjin LIU, Qiang LIU. Bispectrum feature recognition of radar signal based on entropy evaluation and modal decomposition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2116-2123. |
| [5] | Yunke SUN, Zhigeng FANG, Ding CHEN. Multi-time threat assessment based on dynamic grey principal component analysis [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(3): 740-746. |
| [6] | Dongtao WEI, Xiaodong LIU, Peng LI, Yujin CHEN. Research on effectiveness evaluation method of equipment system based on node importance and improved information entropy [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3614-3623. |
| [7] | Leilei ZHANG, Long XIE, Xu GAO, Tianyu SUN, Feng ZHANG. Research on synthetic reliability assessment method for high-value ammunition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3399-3404. |
| [8] | Henglu LI, Baixiao CHEN, Yi DING, Zhaoming ZHANG. Nearest neighbor data association algorithm based on information entropy weight [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(4): 806-812. |
| [9] | Zhenshuo LEI, Songtao LIU, Yang GE, Zhenming WEN. Parameter selection and feature representation method of jamming effect online evaluation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(12): 2755-2760. |
| [10] | Xiwen TAO, Wenqi JIANG. Three-stage consensus improvement model under interval-valued intuitionistic multi-criteria group decision-making environment based on adjustment cost [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(11): 2570-2580. |
| [11] | Qiandong WANG. Fast algorithm of similarity measurement for classical trajectory [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2189-2196. |
| [12] | Guanglei MENG, Mingzhe ZHOU, Haiyin PIAO, Huimin ZHANG. Threat assessment method of dual-aircraft formation based on cooperative tactical recognition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2285-2293. |
| [13] | Chen LI, Jun'an YANG, Hui LIU. Modulation recognition algorithm based on information entropy and GA-ELM [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(1): 223-229. |
| [14] | LIANG Jialin, XIONG Wei. Capabilities assessment of the weaponry system based on combat ring [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(8): 1810-1819. |
| [15] | SUN Haiwen, XIE Xiaofang, SUN Tao, ZHANG Longjie. Threat assessment method of warships formation air defense based on DBN under the condition of small sample data missing [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1300-1308. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||