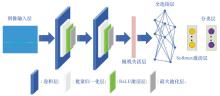
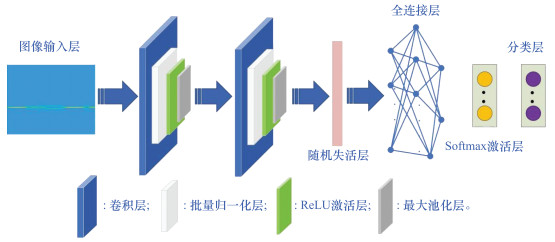
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (6): 1833-1842.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.06.12
• Sensors and Signal Processing • Previous Articles Next Articles
Unknown radar modulation mode recognition algorithm based on DBO-DAOD
Benhui ZHANG1, Songtao LIU2,*, Yulong CHAO3
- 1. Department of Warship Command, Dalian Naval Academy, Dalian 116018, China
2. Department of Information System, Dalian Naval Academy, Dalian 116018, China
3. Unit 92896 of the PLA, Dalian 116018, China
-
Received:2024-04-19Online:2025-06-25Published:2025-07-09 -
Contact:Songtao LIU
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Benhui ZHANG, Songtao LIU, Yulong CHAO. Unknown radar modulation mode recognition algorithm based on DBO-DAOD[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(6): 1833-1842.
share this article
Table 1
Signal simulation parameters of radar modulation waveform"
| 雷达调制波形 | 参数 | 取值范围 |
| Rect | fc N | U(fs/6, fs/5) U[500, 1 920] |
| LFM FMCW | fc BN | U(fs/6, fs/5) U(fs/20, fs/16) U[500, 1 920] |
| Barker | LBc fc Ncc | {7, 11, 13} U(fs/6, fs/5) U[11, 14] |
| Frank P1 | fc Ncc M | U(fs/6, fs/5) {4, 5, 6} {6, 7, 8} |
| P2 | fc Ncc M | U(fs/6, fs/5) {4, 5, 6} {6, 8} |
| P3 P4 PX Zadoff-Chu | fc Ncc m | U(fs/6, fs/5) {4, 5, 6} {39, 49, 64} |
| MFSK | fc B LBc N | U(fs/6, fs/5) U(fs/20, fs/16) {6, 10, 12} U[500, 1 920] |
Table 3
Comparison of recognition results of a single unknown radar modulation mode %"
| 波形名称 | DAOD(验证集) | DBO-DAOD(训练集) | DBO-DAOD(验证集) | |||||
| Accuracy | F-measure | Accuracy | F-measure | Accuracy | F-measure | |||
| Zadoff-Chu | 85.428 6 | 92.141 8 | 99.91±0.09 | 99.95±0.05 | 85.3±7.79 | 91.68±4.55 | ||
| Rect | 85.571 4 | 92.224 8 | 100±0 | 100±0 | 96.66±6.34 | 98.16±3.49 | ||
| Px | 85.285 7 | 92.058 6 | 91.83±2.37 | 95.09±1.29 | 95.12±3.13 | 97.15±1.66 | ||
| P4 | 85.285 7 | 92.058 6 | 92.31±2.69 | 95.56±1.53 | 87.25±4.13 | 92.91±2.14 | ||
| P3 | 85 | 91.891 9 | 91.50±6.81 | 95.41±3.67 | 86.46±7.24 | 92.40±4.20 | ||
| P2 | 98.857 1 | 99.328 9 | 99.85±0.02 | 99.91±0.01 | 97.25±2.81 | 98.34±1.73 | ||
| 平均值 | 87.57 | 93.28 | 95.90±5.10 | 97.65±2.86 | 91.34 | 95.11 | ||
Table 4
Comparison of recognition results of multiple unknown radar modulation modes"
| 开放度 | KNN | CAPLS | CD-OSR | DAOD | DBO-DAOD | |||||||||
| Accuracy | F-measure | Accuracy | F-measure | Accuracy | F-measure | Accuracy | F-measure | Accuracy | F-measure | |||||
| 0 | 86.17 | 91.01 | 93.83 | 96.35 | 0 | NaN | 99.83 | 99.90 | 100±0.0 | 100±0 | ||||
| 0.039 2 | 73.86 | 84.96 | 82.00 | 90.11 | 14.29 | NaN | 85.43 | 92.14 | 87.31±6.97 | 92.91±3.98 | ||||
| 0.074 2 | 64.62 | 78.51 | 72.62 | 84.14 | 25 | NaN | 74.88. | 85.63 | 86.52±7.17 | 91.55±4.42 | ||||
| 0.105 6 | 57.44 | 72.97 | 64.78 | 78.62 | 33.33 | NaN | 66.33 | 79.76 | 96.52±4.42 | 97.41±3.29 | ||||
| 0.134 0 | 51.70 | 68.16 | 57.70 | 73.18 | 40 | NaN | 59.70 | 74.77 | 92.15±6.50 | 93.85±3.28 | ||||
| 0.159 8 | 47.00 | 63.95 | 51.64 | 68.11 | 45.45 | NaN | 53.91 | 70.05 | 88.42±6.87 | 90.37±4.56 | ||||
| 0.183 5 | 43.08 | 60.22 | 47.67 | 64.56 | 50 | NaN | 56.00 | 69.19 | 88.68±5.05 | 89.74±3.90 | ||||
| 平均值 | 60.55 | 74.25 | 67.18 | 79.30 | 29.72 | NaN | 70.2 | 81.63 | 91.37 | 93.69 | ||||
| 1 |
张琴, 田宝玉. 通信信号调制模式的自动识别技术及发展前景[J]. 电讯技术, 2008, 48 (2): 6- 10.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893X.2008.02.002 |
|
ZHANG Q , TIAN B Y . Automatic recognition technology for communication modulation signals and its prospects[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2008, 48 (2): 6- 10.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-893X.2008.02.002 |
|
| 2 | 何正日. 雷达辐射源信号识别技术研究[D]. 西安: 西安电子科技大学, 2015. |
| HE Z R. Research on radar emitter signal recognition technology[D]. Xi'an: Xidian University, 2015. | |
| 3 |
王海英, 张群英, 成文海, 等. LPI雷达信号调制识别及参数估计研究进展[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46 (6): 1908- 1924.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.09 |
|
WANG H Y , ZHANG Q Y , CHENG W H , et al. Progress in LPI radar signal modulation recognition and parameter estimation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46 (6): 1908- 1924.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.09 |
|
| 4 | 吴斌, 袁亚博, 汪勃. 基于记忆因子的连续相位调制信号最大似然调制识别[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2016, 38 (10): 2546- 2552. |
| WU B , YUAN Y B , WANG B . Maximum likelihood modulation recognition for continuous phase modulation signals using memory factor[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2016, 38 (10): 2546- 2552. | |
| 5 |
WANG X , XU G , YAN H , et al. LPI radar signals modulation recognition based on ACDCA-ResNet[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 45168- 45180.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3270231 |
| 6 | 杨静雅, 齐彦丽, 周一青, 等. CNN-Transformer轻量级智能调制识别算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 50 (3): 40- 49. |
| YANG J Y , QI Y L , ZHOU Y Q , et al. Algorithm for recognition of lightweight intelligent modulation based on the CNN-transformer networks[J]. Journal of Xidian University(Natural Science), 2023, 50 (3): 40- 49. | |
| 7 | 邵凯, 朱苗苗. 一种信号调制识别网络的轻量化设计[J]. 电讯技术, 2023, 63 (5): 626- 632. |
| SHAO K , ZHU M M . Lightweight design of a signal modulation identification neural network[J]. Telecommunication Engineering, 2023, 63 (5): 626- 632. | |
| 8 | 孙会楠. 基于深度学习的多进制相移键控信号调制识别研究[J]. 太原学院学报(自然科学版), 2024, 42 (1): 54- 64. |
| SUN H N . Research on modulation MPSK signal based on reco-gnition of deep learning[J]. Journal of Taiyuan University(Natural Sciences), 2024, 42 (1): 54- 64. | |
| 9 |
张茜茜, 王禹, 林云, 等. 基于深度学习的自动调制识别方法综述[J]. 无线电通信技术, 2022, 48 (4): 697- 710.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.04.017 |
|
ZHANG X X , WANG Y , LIN Y , et al. A comprehensive survey of deep learning-based automatic modulation recognition methods[J]. Radio Communications Technology, 2022, 48 (4): 697- 710.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3114.2022.04.017 |
|
| 10 |
刘松涛, 赵帅, 汪慧阳. 雷达辐射源识别技术新进展[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2022, 17 (6): 523- 533.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2022.06.002 |
|
LIU S T , ZHAO S , WANG H Y . New development on the technology of radar emitter identification[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2022, 17 (6): 523- 533.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2022.06.002 |
|
| 11 | ZHEN Y , JUN Y , PEDRAM G , et al. Open set recognition in real world[J]. International Journal of Computer Vision, 2024, 132 (3): 3208- 3231. |
| 12 |
LI J J , YU Z Q , DU Z K , et al. A comprehensive survey on source-free domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Trans.on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2024, 46 (8): 5743- 5762.
doi: 10.1109/TPAMI.2024.3370978 |
| 13 | 郝云飞, 刘章孟, 郭福成, 等. 基于生成对抗网络的信号调制方式的开集识别[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41 (11): 2619- 2624. |
| HAO Y F , LIU Z M , GUO F C , et al. Open set recognition of signal modulation based on generative adversarial networks[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41 (11): 2619- 2624. | |
| 14 | 肖易寒, 李航, 于祥祯, 等. 基于MobileNetV3-SVDD的雷达信号调制方式开集识别[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2022, 43 (8): 1178- 1185. |
| XIAO Y H , LI H , YU X Z , et al. Open set recognition of radar signal modulation based on MobileNetV3-SVDD[J]. Jour nal of Harbin Engineering University, 2022, 43 (8): 1178- 1185. | |
| 15 | 秦博伟, 蒋磊, 许华, 等. 基于RE-GAN的调制信号开集识别算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45 (10): 3321- 3328. |
| QIN B W , JIANG L , XU H , et al. A open-set recognition algorithm for modulation signal based on RE-GAN[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45 (10): 3321- 3328. | |
| 16 | 卜可. 基于迁移学习的自动调制识别研究[D]. 北京: 北京邮电大学, 2021. |
| BU K. Research on transfer learning based automatic modulation classification[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2021. | |
| 17 | 徐强. 基于迁移学习的调制识别技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2021. |
| XU Q. Research on modulation recognition technology based on transfer learning[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2021. | |
| 18 |
FAN Z , LU J , LIU F , et al. Open set domain adaptation: theoretical bound and algorithm[J]. IEEE Trans.on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, 2021, 32 (10): 4309- 4322.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2020.3017213 |
| 19 | XUE J K , SHEN B . Dung beetle optimizer: a new metaheuristic algorithm for global optimization[J]. The Journal of Supercomputing, 2022, 27 (10): 7305- 7336. |
| 20 |
张本辉, 刘松涛. 未知辐射源识别技术研究进展[J]. 中国电子科学研究院学报, 2023, 18 (9): 864- 872.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2023.09.012 |
|
ZHANG B H , LIU S T . Research progress on unknown radiation source identification technology[J]. Journal of China Academy of Electronics and Information Technology, 2023, 18 (9): 864- 872.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5692.2023.09.012 |
|
| 21 | 刘星宏, 周毅, 周涛, 等. 基于自步学习的开放集领域自适应[J]. 计算机研究与发展, 2023, 60 (8): 1711- 1726. |
| LIU X H , ZHOU Y , ZHOU T , et al. Self-paced learning for open-set domain adaptation[J]. Journal of Computer Research and Development, 2023, 60 (8): 1711- 1726. | |
| 22 | BUSTO P P, GALL J. Open set domain adaptation[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 754- 763. |
| 23 | SAITO K, YAMAOTO S, USHIKU Y, et al. Open set domain adaptation by back propagation[C]//Proc. of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 156-171. |
| 24 | WANG J D, FENG W J, CHEN Y Q, et al. Visual domain adaptation with manifold embedded distribution alignment[C]//Proc. of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, 2018: 402-410. |
| 25 |
DENNIS H , DUNANT H , GETHIN W R . Gear fault diagnosis using an improved reassigned smoothed pseudo Wigner-Ville distribution[J]. Cogent Engineering, 2018, 5 (1): 1436928.
doi: 10.1080/23311916.2018.1436928 |
| 26 | 赵小川, 何灏. 深度学习理论及实践(MATLAB版)[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2021. |
| ZHAO X C , HE H . Deep learning theory and practice(MATLAB edition)[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2021. | |
| 27 |
赵帅, 刘松涛, 汪慧阳. 基于PSO-CNN的LPI雷达波形调制识别算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43 (12): 3552- 3563.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.12.17 |
|
ZHAO S , LIU S T , WANG H Y . LPI radar waveform recognition algorithm based on PSO-CNN[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43 (12): 3552- 3563.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.12.17 |
|
| 28 | WANG Q, BU P H, TOBY P B. Unifying unsupervised domain adaptation and zero-shot visual recognition[C]//Proc. of the International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, 2019. |
| 29 | GENG C X , CHEN S C . Collective decision for open set recognition[J]. IEEE Trans.on Knowledge and Data Engineering, 2020, 34 (3): 192- 204. |
| 30 | 高菲, 杨柳, 李晖. 开放集识别研究综述[J]. 南京大学学报(自然科学), 2022, 58 (1): 115- 134. |
| GAO F , YANG L , LI H . A survey on open set recognition[J]. Journal of Nanjing University(Natural Sciences), 2022, 58 (1): 115- 134. |
| [1] | Zhikang LIN, Longfei SHI, Jialei LIU, Jiazhi MA. Scintillation detection scheduling method of netted radar based on deep Q-learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(5): 1443-1452. |
| [2] | Jinwei JIA, Min GAO, Zhuangzhi HAN, Limin LIU, Yuanwei YIN. Overview of anti-information interference technology for radio proximity fuze [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 0, (): 1074-1107. |
| [3] | Jinwei JIA, Min GAO, Zhuangzhi HAN, Limin LIU, Yuanwei YIN. Overview of anti-information interference technology for radio proximity fuze [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1074-1107. |
| [4] | Fangzheng LIU, Ruiqi ZENG, Yang GONG, Zhenzhong HAN. ZC-OFDM-based radar interference integrated waveform design and processing method [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(9): 2999-3011. |
| [5] | Dongxia LI, Jiani WANG, Xiangqing PENG, Haitao LIU, Lei WANG. DME pulse interference suppression method based on cSVB algorithm [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(8): 2877-2885. |
| [6] | Pengfei YANG, Ling HE, Qian WANG, Ruidi WANG, Mingzhi ZHANG. Interference identification based on mixed signal multidomain feature and Transformer framework [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 2138-2145. |
| [7] | Zhiguo SUN, Yupeng SHA, Xiaoyan NING. Low detection probability communication technology based on NFM-BOK waveform [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(12): 4030-4039. |
| [8] | Yu LIN, Yi BU, Xianxiang YU, Guolong CUI. Joint cognitive design method of waveform and filter for multi-mainlobe jamming [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(11): 3437-3448. |
| [9] | Luwei FENG, Songtao LIU, Huazhi XU. Intelligent radar jamming decision-making method based on POMDP model [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(9): 2755-2760. |
| [10] | Husheng WANG, Baixiao CHEN, Qingzhi YE. Research on anti-chaff jamming method based on measured data [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 2010-2021. |
| [11] | Jinyang HE, Ziyang CHENG, Zhanlei LI, Zishu HE, Minghui SHA. Low Doppler sensitive waveform design method against interrupted sampling repeater jamming [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(5): 1333-1341. |
| [12] | Dong XIA, Kaixuan ZHANG, Youbao DING, Baopeng LI. Co-channel interference resistance based on agile wave form of phase encode and CFAR technology [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1210-1219. |
| [13] | Dong FU, Jing PENG, Ming MA, Feiqiang CHEN, Gang OU. GNSS time spoofing detection and discrimination based on clock bias hypothesis test [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 948-955. |
| [14] | Shuai ZHAO, Songtao LIU, Huiyang WANG. LPI radar waveform recognition algorithm based on PSO-CNN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3552-3563. |
| [15] | Jinyang HE, Ziyang CHENG, Zishu HE. Cognitive constant modulus waveform design method against interrupted sampling repeater jamming [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(9): 2448-2456. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||