Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (2): 444-452.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.02.15
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles
Bayesian network parameter learning based on fuzzy constraints
Xinxin RU, Xiaoguang GAO, Yangyang WANG
- School of Electronic Information, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710129, China
-
Received:2022-01-24Online:2023-01-13Published:2023-02-04 -
Contact:Xiaoguang GAO
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Xinxin RU, Xiaoguang GAO, Yangyang WANG. Bayesian network parameter learning based on fuzzy constraints[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 444-452.
share this article
Table 2
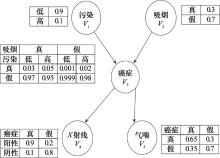
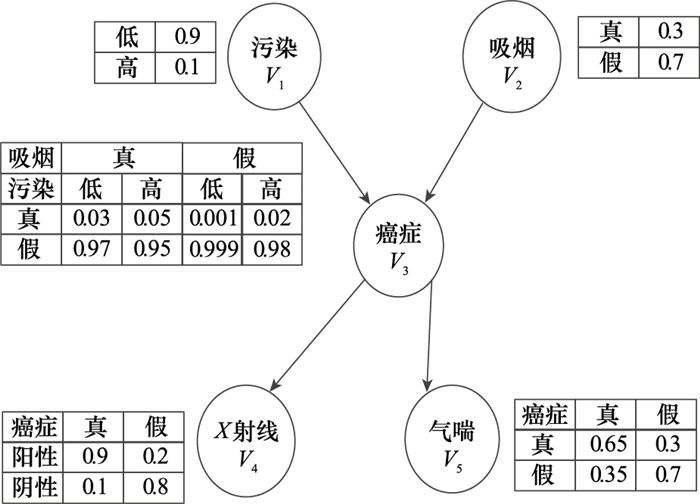
Constraints of Cancer network"
| 编号 | 约束 |
| 1 | 0.9≤P(V1=低)≤1 |
| 2 | P(V2=真)<P(V2=假) |
| 3 | 0.9≤P(V3=假|V1=低, V2=真)≤1 |
| 4 | 0.9≤P(V3=假|V1=高, V2=真)≤1 |
| 5 | 0.9≤P(V3=假|V1=低, V2=假)≤1 |
| 6 | 0.9≤P(V3=假|V1=高, V2=假)≤1 |
| 7 | 0.9≤P(V4=阳性|V3=真)≤1 |
| 8 | P(V4=阳性|V3=假)<P(V4=阴性|V3=假) |
| 9 | P(V5=真|V3=真)>P(V5=假|V3=真) |
| 10 | P(V5=真|V3=假)<P(V5=假|V3=假) |
Table 3
KL comparison of 100 samples"
| BNs | MLE | MAP | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 1.173 3±0.766 6 | 0.348 1±0.057 5 | 0.044 2±0.022 7 | 0.105 4±0.047 8 | 0.080 5±0.032 8 |
| Cancer | 0.846 7±0.744 7 | 0.844 0±0.097 4 | 0.104 2±0.035 4 | 0.052 9±0.043 1 | 0.049 8±00.000 1 |
| Sachs | 0.983 2±0.235 8 | 0.392 1±0.024 4 | 0.352 6±0.099 5 | 0.198 3±0.027 8 | 0.147 3±0.010 3 |
| Boerlage92 | 1.217 9±0.216 1 | 0.332 7±0.022 5 | 0.143 8±0.088 2 | 0.142 3±0.024 2 | 0.072 9±0.014 8 |
| Win95pts | 0.582 8±0.110 6 | 0.329 9±0.007 2 | 0.293 9±0.057 0 | 0.233 0±0.013 0 | 0.213 3±0.004 5 |
| Andes | 1.005 2±0.067 4 | 0.394 2±0.005 6 | 0.161 9±0.020 5 | 0.172 8±0.009 5 | 0.132 5±0.004 1 |
| 均值 | 0.968 2 | 0.440 2 | 0.183 4 | 0.150 8 | 0.116 1 |
Table 4
KL comparison of 300 samples"
| BNs | MLE | MAP | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.936 7±0.898 3 | 0.406 6±0.065 0 | 0.014 8±0.011 4 | 0.121 5±0.049 2 | 0.060 0±0.019 7 |
| Cancer | 0.470 2±0.442 8 | 0.416 5±0.083 4 | 0.059 9±0.032 1 | 0.036 7±0.017 9 | 0.020 6±00.001 0 |
| Sachs | 0.603 3±0.155 3 | 0.430 9±0.029 8 | 0.183 4±0.080 0 | 0.126 2±0.019 4 | 0.089 8±0.008 4 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.510 7±0.188 7 | 0.365 7±0.020 0 | 0.030 2±0.034 5 | 0.076 2±0.020 5 | 0.023 9±0.005 7 |
| Win95pts | 0.653 8±0.086 7 | 0.350 5±0.004 8 | 0.381 1±0.060 2 | 0.212 7±0.012 5 | 0.173 6±0.004 8 |
| Andes | 0.698 2±0.051 1 | 0.429 6±0.005 4 | 0.159 5±0.016 7 | 0.118 7±0.007 0 | 0.064 7±0.002 9 |
| 均值 | 0.645 5 | 0.416 7 | 0.138 2 | 0.115 3 | 0.072 1 |
Table 5
KL comparison of 500 samples"
| BNs | MLE | MAP | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.377 4±0.364 4 | 0.431 5±0.058 2 | 0.014 2±0.016 2 | 0.083 4±0.028 4 | 0.056 6±0.014 1 |
| Cancer | 0.285 2±0.302 4 | 0.179 3±0.071 6 | 0.050 1±0.031 4 | 0.030 9±0.021 8 | 0.008 0±0.000 1 |
| Sachs | 0.437 3±0.106 2 | 0.477 8±0.019 8 | 0.136 1±0.038 4 | 0.093 7±0.013 4 | 0.065 4±0.007 4 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.259 4±0.103 2 | 0.369 3±0.013 8 | 0.009 3±0.003 2 | 0.041 7±0.012 9 | 0.010 4±0.002 5 |
| Win95pts | 0.722 9±0.092 3 | 0.377 2±0.004 4 | 0.453 4±0.058 6 | 0.207 5±0.014 0 | 0.153 2±0.002 3 |
| Andes | 0.466 3±0.038 0 | 0.447 4±0.006 2 | 0.109 1±0.015 8 | 0.083 1±0.005 4 | 0.039 3±0.002 5 |
| 均值 | 0.424 8 | 0.380 5 | 0.128 7 | 0.090 1 | 0.055 5 |
Table 6
Comparison results of 100 samples with noise constraints"
| BNs | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.834 2± 0.563 1 | 0.117 0± 0.041 1 | 0.073 8± 0.041 7 |
| Cancer | 0.578 4± 0.355 7 | 0.075 3± 0.054 0 | 0.054 7± 0.040 5 |
| Sachs | 0.679 7± 0.138 5 | 0.194 3± 0.019 2 | 0.144 6± 0.008 4 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.911 8± 0.216 6 | 0.153 2± 0.029 8 | 0.075 4± 0.011 8 |
| Win95pts | 0.352 2± 0.055 6 | 0.226 4± 0.009 7 | 0.214 7± 0.004 6 |
| Andes | 0.476 9± 0.045 5 | 0.190 3± 0.009 7 | 0.133 7± 0.003 1 |
| 均值 | 0.638 9 | 0.159 4 | 0.116 2 |
Table 7
Comparison results of 300 samples with noise constraints"
| BNs | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.494 7± 0.439 7 | 0.124 3± 0.059 8 | 0.065 3± 0.017 4 |
| Cancer | 0.373 5± 0.306 9 | 0.063 8± 0.028 4 | 0.014 7± 0.016 5 |
| Sachs | 0.394 0± 0.107 9 | 0.149 5± 0.021 0 | 0.095 0± 0.010 8 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.292 1± 0.098 5 | 0.081 0± 0.018 3 | 0.031 2± 0.006 9 |
| Win95pts | 0.436 2± 0.049 3 | 0.210 6± 0.010 9 | 0.177 9± 0.004 1 |
| Andes | 0.293 2± 0.024 2 | 0.119 9± 0.008 5 | 0.068 0± 0.004 0 |
| 均值 | 0.380 6 | 0.124 9 | 0.075 4 |
Table 8
Comparison results of 500 samples with noise constraints"
| BNs | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.063 1± 0.095 5 | 0.109 0± 0.041 5 | 0.059 2± 0.019 6 |
| Cancer | 0.108 4± 0.145 4 | 0.047 6± 0.018 1 | 0.009 2± 0.006 5 |
| Sachs | 0.288 5± 0.046 6 | 0.110 3± 0.015 2 | 0.062 8± 0.009 4 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.144 1± 0.062 8 | 0.050 7± 0.009 5 | 0.016 6± 0.003 7 |
| Win95pts | 0.501 0± 0.044 2 | 0.207 0± 0.010 6 | 0.154 8± 0.002 8 |
| Andes | 0.196 7± 0.023 3 | 0.100 3± 0.006 9 | 0.040 4± 0.002 8 |
| 均值 | 0.217 0 | 0.107 5 | 0.057 2 |
Table 9
Running time of each algorithm with 100 samples s"
| BNs | MLE | MAP | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.001 7±0.000 2 | 0.001 7±0.000 3 | 1.494 4±0.024 5 | 0.002 1±0.000 1 | 0.002 8±0.000 5 |
| Cancer | 0.001 7±0.000 3 | 0.001 7±0.000 4 | 1.491 9±0.033 9 | 0.002 1±0.000 1 | 0.002 8±0.000 4 |
| Sachs | 0.015 5±0.000 7 | 0.015 5±0.000 7 | 3.840 7±0.048 5 | 0.016 4±0.001 2 | 0.037 2±0.002 5 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.011 7±0.002 2 | 0.012 1±0.001 5 | 7.383 4±0.077 3 | 0.012 5±0.000 7 | 0.024 0±0.001 7 |
| Win95pts | 0.070 5±0.004 8 | 0.072 2±0.003 9 | 23.420 1±0.362 1 | 0.089 3±0.003 7 | 0.159 4±0.007 7 |
| Andes | 0.172 7±0.016 0 | 0.174 6±0.013 5 | 77.730 0±6.792 5 | 0.197 9±0.016 0 | 0.343 2±0.031 3 |
| 均值 | 0.045 8 | 0.046 3 | 19.226 8 | 0.053 38 | 0.094 9 |
Table 10
Running time of each algorithm with 500 samples s"
| BNs | MLE | MAP | CMLE | QMAP | FMAP |
| Earthquake | 0.009 1±0.000 4 | 0.010 1±0.000 6 | 1.513 4±0.020 0 | 0.010 8±0.001 9 | 0.010 8±0.001 6 |
| Cancer | 0.008 8±0.000 3 | 0.009 0±0.000 4 | 1.479 7±0.015 1 | 0.009 9±0.000 6 | 0.010 1±0.000 3 |
| Sachs | 0.142 2±0.004 9 | 0.143 8±0.003 2 | 4.010 5±0.066 7 | 0.150 9±0.008 6 | 0.163 9±0.006 2 |
| Boerlage92 | 0.091 0±0.002 3 | 0.092 8±0.003 3 | 7.393 6±0.077 6 | 0.093 7±0.002 5 | 0.105 5±0.004 9 |
| Win95pts | 0.609 4±0.027 2 | 0.684 2±0.008 9 | 23.928 4±0.266 8 | 0.904 3±0.011 9 | 1.687 7±0.016 4 |
| Andes | 1.198 2±0.018 8 | 1.207 6±0.026 9 | 72.800 6±2.923 1 | 1.615 7±0.027 2 | 2.381 7±0.017 7 |
| 均值 | 0.052 0 | 0.055 0 | 18.521 0 | 1.792 0 | 3.966 0 |
Table 11
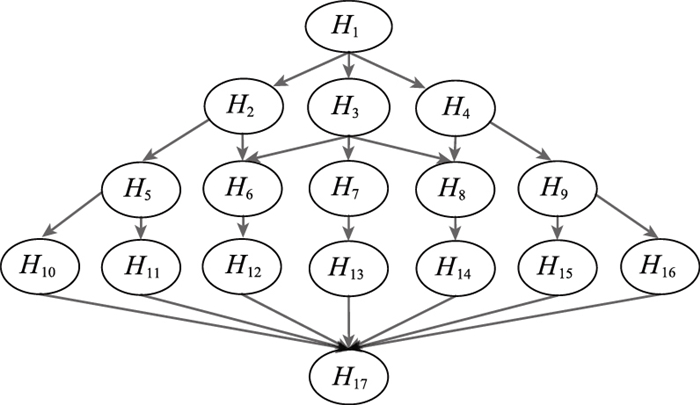
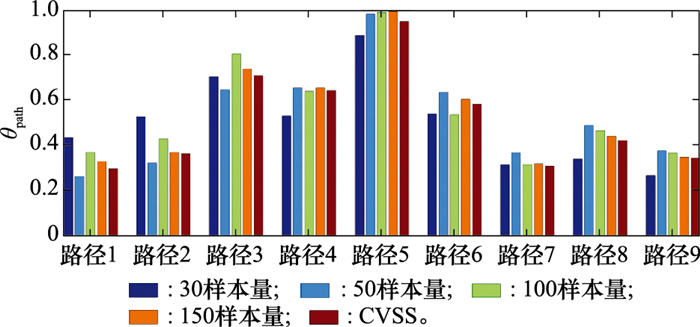
Vulnerability information and constraints"
| H | CVE | CVSS约束 |
| H2 | CVE-2018-6036 | P(H2=1|Π1=1)=0.75 |
| H3 | CVE-2017-14827 | P(H3=1|Π3=1)=0.68 |
| H4 | CVE-2017-1336 | P(H4=1|Π4=1)=0.36 |
| H5 | CVE-2017-11887 | P(H5=1|Π5=1)=0.26 |
| H6 | CVE-2019-1010156 | P(H6=1|Π6=1)=0.64 |
| H7 | CVE-2014-1761 | P(H7=1|Π7=1)=0.93 |
| H8 | CVE-2018-16844 | P(H8=1|Π8=1)=0.78 |
| H9 | CVE-2016-10627 | P(H9=1|Π9=1)=0.63 |
| H10 | CVE-2016-3454 | P(H10=1|Π10=1)=0.76 |
| H11 | CVE-2017-16375 | P(H11=1|Π11=1)=0.93 |
| H12 | CVE-2018-12498 | P(H12=1|Π12=1)=0.75 |
| H13 | CVE-2015-7994 | P(H13=1|Π13=1)=0.75 |
| H14 | CVE-2019-1010246 | P(H14=1|Π14=1)=0.55 |
| H15 | CVE-2017-8620 | P(H15=1|Π15=1)=0.93 |
| H16 | CVE-2017-11873 | P(H16=1|Π16=1)=0.76 |
| 1 | PEARL J. Probabilistic reasoning in intelligent systems: networks of plausible inference[M]. San Mateo: Morgan Kaufmann, 1988. |
| 2 |
ZHANG Y , WENG W G . Bayesian network model for buried gas pipeline failure analysis caused by corrosion and external interference[J]. Reliability Engineering System Safety, 2020, 203, 107089.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2020.107089 |
| 3 | ZHANG T Q , ZHANG T F , LI C C , et al. Complementary and alternative therapies for precancerous lesions of gastric cancer: a protocol for a Bayesian network meta analysis[J]. Medicine, 2021, 100 (2): 20249. |
| 4 |
WANG Z D , GAO X G , TAN X Y , et al. Learning Bayesian networks based on order graph with ancestral constraints[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2021, 211, 106515.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2020.106515 |
| 5 | TAN X Y , GAO X G , WANG Z D , et al. Bidirectional heuristic search to find the optimal Bayesian network structure[J]. Neurocomputing, 2020, 41 (426): 35- 46. |
| 6 |
LIU X H , GAO X G , WANG Z D , et al. Improved local search with momentum for Bayesian networks structure learning[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23 (6): 750- 769.
doi: 10.3390/e23060750 |
| 7 | 曾强, 黄政, 魏曙寰. 融合专家先验知识和单调性约束的贝叶斯网络参数学习方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42 (3): 646- 652. |
| ZENG Q , HUANG Z , WEI S H . Bayesian network parameter learning method based on expert priori knowledge and monotonic constraints[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42 (3): 646- 652. | |
| 8 | 柴慧敏, 赵昀瑶, 方敏. 利用先验正态分布贝叶斯网络参数学习[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40 (10): 2370- 2375. |
| CHAI H M , ZHAO Y Y , FANG M . Bayesian network parameter learning method based on expert priori knowledge of normal distribution[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40 (10): 2370- 2375. | |
| 9 |
PLATAS L , MEZURA M , CRUZ R , et al. Discriminative learning of Bayesian network parameters by differential evolution[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2021, 93, 244- 256.
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2020.12.026 |
| 10 |
DI R H , GAO X G , GUO Z G . Learning Bayesian network parameters under new monotonic constraints[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 28 (6): 1248- 1255.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2017.06.22 |
| 11 | COOPER G F , HERSKOVITS E . A Bayesian method for the induction of probabilistic networks from data[J]. Machine Learning, 1992, 9 (4): 309- 347. |
| 12 |
REDNER R A . Mixture densities, maximum likelihood and the EM algorithm[J]. SIAM Review, 1984, 26 (2): 195- 239.
doi: 10.1137/1026034 |
| 13 |
GAO X G , GUO Z G , REN H , et al. Learning Bayesian network parameters via minimax algorithm[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2019, 108, 62- 75.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2019.03.001 |
| 14 | CAMPOS C, TONG Y, JI Q. Constrained maximum likelihood learning of Bayesian networks for facial action recognition[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2008: 168-181. |
| 15 |
GAO X G , YANG Y , GUO Z G . Learning Bayesian networks by constrained Bayesian estimation[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30 (3): 511- 524.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.03.09 |
| 16 |
DI R H , WANG P , HE C C , et al. Constrained adjusted maximum a posteriori estimation of Bayesian network parameters[J]. Entropy, 2021, 23 (10): 1283- 1299.
doi: 10.3390/e23101283 |
| 17 |
YANG Y , GAO X G , GUO Z G , et al. Learning Bayesian networks using the constrained maximum a posteriori probability method[J]. Pattern Recognition, 2019, 91, 123- 134.
doi: 10.1016/j.patcog.2019.02.006 |
| 18 |
GUO Z G , GAO X G , REN H , et al. Learning Bayesian network parameters from small data sets: a further constrained qualitatively maximum a posteriori method[J]. International Journal of Approximate Reasoning, 2017, 91, 22- 35.
doi: 10.1016/j.ijar.2017.08.009 |
| 19 |
ROGER L , ENRIQUE S . Inductive transfer for learning Bayesian networks[J]. Machine Learning, 2010, 79 (1-2): 227- 255.
doi: 10.1007/s10994-009-5160-4 |
| 20 |
KOVACIC J . Learning parameters of Bayesian networks from datasets with systematically missing data: a meta-analytic approach[J]. Expert Systems with Application, 2020, 141, 112956.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2019.112956 |
| 21 | CHEN G J , GE Z Q . Robust Bayesian networks for low-quality data modeling and process monitoring applications[J]. Control Engineering Practice, 2020, 97 (4): 104344. |
| 22 |
YUAN P , SUN Y F , LI H , et al. Abnormal condition identification modeling method based on Bayesian network parameters transfer learning for the electro-fused magnesia smelting process[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 149764- 149775.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2947499 |
| 23 | 闫浩, 王福利, 孙钰沣, 等. 基于贝叶斯网络参数迁移学习的电熔镁炉异常工况识别[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47 (1): 197- 208. |
| YAN H , WANG F L , SUN Y F , et al. Abnormal condition identification based on Bayesian network parameters transfer learning for the electro-fused magnesia[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47 (1): 197- 208. | |
| 24 | HOU Y Y , ZHENG E R , GUO W Q , et al. Learning Bayesian network parameters with small data set: a parameter extension under constraints method[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 99, 24979- 24989. |
| 25 | ZADEH L A . Fuzzy sets[J]. Information & Control, 1965, 8 (3): 338- 353. |
| 26 | SCUTARI M. Bnlearn-an R package for Bayesian network learning and inference[EB/OL]. [2021-12-1]. http://www.bnlearn.com/bnrepository. |
| 27 | KEVIN M. Bayes net toolbox for Matlab[EB/OL]. [2021-11-1]. https://github.com/bayesnet/bnt. |
| 28 | KOLLER D . Probabilistic graphical models: principles and techniques[M]. Cambridge: MIT Press, 2009. |
| 29 | 吴晨思, 谢卫强, 姬逸潇, 等. 网络系统安全度量综述[J]. 通信学报, 2019, 40 (6): 14- 31. |
| WU C S , XIE W Q , JI Y X , et al. Survey on network system security metrics[J]. Journal on Communications, 2019, 40 (6): 14- 31. | |
| 30 | 黄克振, 连一峰, 冯登国, 等. 一种基于图模型的网络攻击溯源方法[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33 (2): 683- 698. |
| HUANG K Z , LIAN Y F , FENG D G , et al. Method of cyber attack attribution based on graph model[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33 (2): 683- 698. | |
| 31 | 符永铨, 赵辉, 王晓锋, 等. 网络行为仿真综述[J]. 软件学报, 2022, 33 (1): 274- 296. |
| FU Y Q , ZHAO H , WANG X F , et al. State-of-the-art survey on network behavior emulation[J]. Journal of Software, 2022, 33 (1): 274- 296. | |
| 32 | MELL P , SCARFONE K , ROMANOSKY S . Common vulnerability acoring system[J]. IEEE Security & Privacy, 2007, 4 (6): 85- 89. |
| [1] | Yifan LI, Huaming QIAN, Hongzhong HUANG, Tingyu ZHANG, Tudi HUANG. Reliability analysis of command and control network system based on generalized continuous time Bayesian network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3880-3886. |
| [2] | Peng WANG, Zijing SUN, Fan ZHANG, Guosong XIAO. Reliability analysis model for phased-mission system considering probabilistic common cause failures [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3887-3898. |
| [3] | Dianfeng QIAO, Yan LIANG, Chaoxiong MA, Xinyu YANG, Mian WANG, Jianguo LI. Recognition and prediction of group target intention in multi-domain operations [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(11): 3403-3412. |
| [4] | Yanzhao LIU, Zhiqiu HUANG, Guohua SHEN, Jinyong WANG, Heng XU. Behavioral decision-making methods of autonomous vehicles based on decision tree and BN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3143-3154. |
| [5] | Luda ZHAO, Bin WANG. Method of electronic countermeasure targets' list generation based on RS-DBN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(9): 2373-2382. |
| [6] | Hongzhuan CHEN, Aijia ZHAO, Tengjiao LI, Congcong CAI, Shuo CHENG, Chunli XU. Fuzzy Bayesian network inference fault diagnosis of complex equipment based on fault tree [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(5): 1248-1261. |
| [7] | Xue SUN, Zhiqiu HUANG, Guohua SHEN, Jinyong WANG, Heng XU. Behavior decision method of autonomous vehicle based on ontology and BN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(2): 452-465. |
| [8] | Changxiao ZHAO, Hao LI, Lei DONG, Peng WANG. Safety analysis and evaluation of airborne HUD system based on STPA-Bayes model [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(5): 1083-1092. |
| [9] | Qiang ZENG, Zheng HUANG, Shuhuan WEI. Bayesian network parameter learning method based on expert priori knowledge and monotonic constraints [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(3): 646-652. |
| [10] | Guanglei MENG, Mingzhe ZHOU, Haiyin PIAO, Huimin ZHANG. Threat assessment method of dual-aircraft formation based on cooperative tactical recognition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2285-2293. |
| [11] | SUN Haiwen, XIE Xiaofang, SUN Tao, ZHANG Longjie. Threat assessment method of warships formation air defense based on DBN under the condition of small sample data missing [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1300-1308. |
| [12] | LIU Jiufu, DING Xiaobin, ZHENG Rui, WANG Biao, LIU Haiyang, WANG Zhisheng. Weighted class-conditional Bayesian network classifier parameter learning of chaos quantum particle swarm [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(10): 2304-2309. |
| [13] | LI Ming, ZHANG Ren, HONG Mei, BAI Chengzu. Improved structure learning algorithm of Bayesian network based on information flow [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(6): 1385-1390. |
| [14] | GAO Xiaoguang, YE Simao, DI Ruohai, KOU Zhenchao. Bayesian network structures learning based on approach using incoporate priors method [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 790-796. |
| [15] | LAN Jie, YUAN Hongjie, XIA Jing. Improved method for dynamic fault tree analysis based on discrete time Bayesian network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(4): 948-953. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||