Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (3): 740-746.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.03.18
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
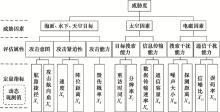
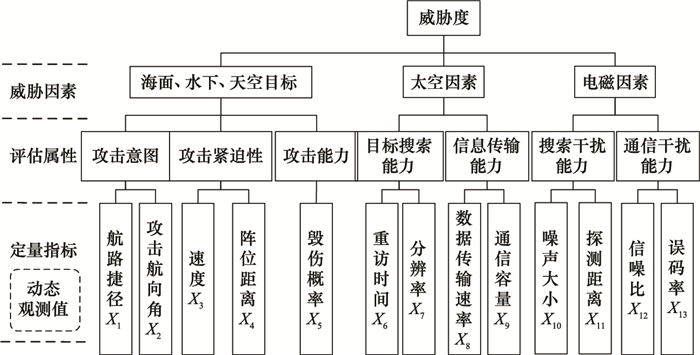
Multi-time threat assessment based on dynamic grey principal component analysis
Yunke SUN1( ), Zhigeng FANG1(
), Zhigeng FANG1( ), Ding CHEN2(
), Ding CHEN2( )
)
- 1. College of Economics and Management, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 211106, China
2. Shanghai Electro-Mechanical Engineering Institute, Shanghai 201109, China
-
Received:2020-06-05Online:2021-03-01Published:2021-03-16
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yunke SUN, Zhigeng FANG, Ding CHEN. Multi-time threat assessment based on dynamic grey principal component analysis[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(3): 740-746.
share this article
Table 1
Threat observed value"
| 指标 | A | B | C | D | |||||||||||
| 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | 1 | 2 | 3 | ||||
| 航路捷径/km | 130 | 200 | 80 | 40 | 80 | 40 | 100 | 110 | 80 | 230 | 100 | 70 | |||
| 攻击航向角/(°) | 65 | 70 | 40 | 40 | 50 | 50 | 50 | 65 | 45 | 70 | 55 | 60 | |||
| 速度/(km/h) | 200 | 180 | 25 | 25 | 80 | 35 | 50 | 55 | 60 | 150 | 105 | 180 | |||
| 阵位距离/km | 80 | 150 | 60 | 35 | 20 | 35 | 40 | 45 | 30 | 50 | 20 | 25 | |||
| 武器数量 | 2 | 1 | 3 | 4 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 2 | 4 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 重访时间/min | 3 | 2 | 3.5 | 2 | 3.5 | 4 | 3.5 | 2 | 3 | 3.5 | 2 | 3.5 | |||
| 分辨率/m | 0.5 | 1 | 2 | 0.3 | 0.9 | 0.8 | 0.6 | 0.55 | 0.6 | 1 | 0.55 | 0.6 | |||
| 传输速率/(bit/s) | 30 | 20 | 25 | 25 | 30 | 30 | 35 | 26 | 30 | 33 | 28 | 30 | |||
| 通信容量/(bit/s) | 40 | 25 | 30 | 45 | 40 | 40 | 25 | 33 | 40 | 30 | 35 | 45 | |||
| 噪声/dB | 10 | 15 | 50 | 30 | 20 | 20 | 45 | 42 | 35 | 50 | 35 | 48 | |||
| 探测距离/km | 3 | 5 | 1 | 5 | 5 | 4 | 2 | 5 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 1 | |||
| 信噪比/dB | 80 | 60 | 120 | 70 | 80 | 90 | 88 | 85 | 90 | 85 | 50 | 50 | |||
| 误码率/% | 15 | 10 | 40 | 20 | 30 | 25 | 30 | 44 | 40 | 34 | 40 | 45 | |||
Table 2
Extended grey similarity correlation degree"
| X1 | X2 | X3 | X4 | X5 | X6 | X7 | X8 | X9 | X10 | X11 | X12 | X13 | |
| X1 | 1 | 0.809 | 0.769 | 0.559 | 0.535 | 0.518 | 0.607 | 0.553 | 0.654 | 0.698 | 0.557 | 0.66 | 0.722 |
| X2 | 0.809 | 1 | 0.817 | 0.530 | 0.570 | 0.530 | 0.719 | 0.602 | 0.696 | 0.596 | 0.581 | 0.701 | 0.698 |
| X3 | 0.769 | 0.817 | 1 | 0.542 | 0.564 | 0.533 | 0.694 | 0.596 | 0.725 | 0.610 | 0.696 | 0.615 | 0.610 |
| X4 | 0.559 | 0.530 | 0.542 | 1 | 0.585 | 0.710 | 0.595 | 0.729 | 0.548 | 0.573 | 0.611 | 0.763 | 0.604 |
| X5 | 0.535 | 0.570 | 0.564 | 0.585 | 1 | 0.687 | 0.814 | 0.765 | 0.603 | 0.546 | 0.533 | 0.598 | 0.596 |
| X6 | 0.518 | 0.530 | 0.533 | 0.710 | 0.687 | 1 | 0.617 | 0.803 | 0.538 | 0.517 | 0.421 | 0.668 | 0.573 |
| X7 | 0.607 | 0.719 | 0.694 | 0.595 | 0.814 | 0.617 | 1 | 0.695 | 0.723 | 0.604 | 0.535 | 0.718 | 0.546 |
| X8 | 0.553 | 0.602 | 0.596 | 0.729 | 0.765 | 0.803 | 0.695 | 1 | 0.594 | 0.544 | 0.526 | 0.653 | 0.544 |
| X9 | 0.654 | 0.696 | 0.725 | 0.548 | 0.603 | 0.538 | 0.723 | 0.594 | 1 | 0.722 | 0.897 | 0.632 | 0.517 |
| X10 | 0.698 | 0.596 | 0.610 | 0.573 | 0.546 | 0.517 | 0.604 | 0.544 | 0.722 | 1 | 0.857 | 0.544 | 0.874 |
| X11 | 0.557 | 0.581 | 0.696 | 0.611 | 0.533 | 0.421 | 0.535 | 0.526 | 0.897 | 0.857 | 1 | 0.517 | 0.423 |
| X12 | 0.66 | 0.701 | 0.615 | 0.763 | 0.598 | 0.668 | 0.718 | 0.653 | 0.632 | 0.544 | 0.517 | 1 | 0.471 |
| X13 | 0.722 | 0.698 | 0.610 | 0.604 | 0.596 | 0.573 | 0.546 | 0.544 | 0.517 | 0.874 | 0.423 | 0.471 | 1 |
Table 3
Principal component eigenvalue and variance contribution rate of DG-PCA threat assessment"
| 主成分 | 特征值 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% |
| 1 | 8.551 3 | 64.59 | 64.59 |
| 2 | 1.148 6 | 8.67 | 73.26 |
| 3 | 0.795 7 | 6.01 | 79.27 |
| 4 | 0.725 8 | 5.48 | 84.95 |
| 5 | 0.573 3 | 4.33 | 89.08 |
| 6 | 0.361 2 | 2.73 | 91.81 |
| 7 | 0.248 5 | 1.88 | 93.69 |
| 8 | 0.203 1 | 1.53 | 95.22 |
| 9 | 0.177 4 | 1.34 | 96.56 |
| 10 | 0.141 3 | 1.07 | 97.63 |
| 11 | 0.126 5 | 0.96 | 98.59 |
| 12 | 0.120 0 | 0.91 | 99.49 |
| 13 | 0.067 2 | 0.51 | 100.00 |
Table 5
Analysis results of different PCA methods"
| 主成分 | DG-PCA | PCA | 组合KPCA | ||||||||
| 特征值 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% | 特征值 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% | 特征值 | 方差贡献率/% | 累计方差贡献率/% | |||
| 1 | 8.551 3 | 64.59 | 64.59 | 5.030 7 | 51.98 | 51.98 | 8.227 0 | 61.97 | 61.97 | ||
| 2 | 1.148 6 | 8.67 | 73.26 | 1.575 3 | 16.28 | 68.26 | 1.094 3 | 8.24 | 70.22 | ||
| 3 | 0.795 7 | 6.01 | 79.27 | 0.623 2 | 6.44 | 74.69 | 1.494 7 | 11.26 | 81.48 | ||
| 4 | 0.725 8 | 5.48 | 84.75 | 0.540 6 | 5.59 | 80.28 | 1.240 6 | 9.35 | 90.82 | ||
| 5 | 0.573 3 | 4.33 | 89.08 | 0.503 7 | 5.20 | 85.48 | 0.943 0 | 7.10 | 97.92 | ||
| 1 |
郭辉, 徐浩军, 刘凌. 基于区间数TOPSIS法的空战目标威胁评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2009, 31 (12): 2914- 2917.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.12.026 |
|
GUO H , XU H J , LIU L . Threat assessment for air combat target based on interval TOPSIS[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31 (12): 2914- 2917.
doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-506X.2009.12.026 |
|
| 2 | SAHNI M , DASS K . A method of risk analysis and threat management using AHP: an application to air defence[J]. Journal of Battlefield Technology, 2015, 18 (3): 27- 33. |
| 3 |
SUN H W , XIE X F . Threat evaluation method of warships formation air defense based on AR(p)-DITOPSIS[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30 (2): 297- 307.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.02.09 |
| 4 | GAO Y , LI D S , ZHONG H . A novel target threat assessment method based on three-way decisions under intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute decision making environment[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 87 (1): 103276. |
| 5 | 奚之飞, 徐安, 寇英信, 等. 基于改进GRA-TOPSIS的空战威胁评估[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2020, 46 (2): 388- 397. |
| XI Z F , XU A , KOU Y X , et al. Air combat threat assessment based on improved GRA-TOPSIS[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2020, 46 (2): 388- 397. | |
| 6 | LIU B , XIA H B , LONG W B , et al. Threat degree sorted of multi-protected-target in air combat platform[J]. Advances in Computer, Signals and Systems, 2016, (1): 8- 12. |
| 7 |
张浩为, 谢军伟, 葛佳昂, 等. 改进TOPSIS的多态融合直觉模糊威胁评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2018, 40 (10): 2263- 2269.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.16 |
|
ZHANG H W , XIE J W , GE J A , et al. Intuitionistic fuzzy set threat assessment based on improved TOPSIS and multiple times fusion[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40 (10): 2263- 2269.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2018.10.16 |
|
| 8 | XU X M, YANG R N. Threat assessment in air combat based on ELM neural network[C]//Proc.of the IEEE International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Computer Applications, 2019: 114-120. |
| 9 | YUE L F , YANG R N , ZUO J L , et al. Air target threat assessment based on improved moth flame optimization-gray neural network model[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering, 2019, (8): 1- 14. |
| 10 | SUN H W , XIE X F , SUN T , et al. Dynamic Bayesian network threat assessment for warship formation: a data analysis method[J]. International Journal of High Performance Systems Architecture, 2018, 8 (12): 71- 81. |
| 11 | KUMAR S , TRIPATHI B K . Modeling of threat evaluation for dynamic targets using Bayesian network approach[J]. Procedia Technology, 2016, 24 (2): 1268- 1275. |
| 12 |
KONG D P , CHANG T Q , WANG Q D , et al. A threat assessment method of group targets based on interval-valued intuitionistic fuzzy multi-attribute group decision-making[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2018, 67, 350- 369.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2018.03.015 |
| 13 |
PARTRIDGE M , CALVO R A . Fast dimensionality reduction and simple PCA[J]. Intelligent data analysis, 1998, 2 (3): 203- 214.
doi: 10.3233/IDA-1998-2304 |
| 14 |
YATA K , AOSHIMA M . Effective PCA for high-dimension, low-sample-size data with noise reduction via geometric representations[J]. Journal of Multivariate Analysis, 2012, 105 (1): 193- 215.
doi: 10.1016/j.jmva.2011.09.002 |
| 15 | YANG D , SONG G B , WANG Z G , et al. Damage detection of refractory based on principle component analysis and Gaussian mixture model[J]. Complexity, 2018, (11): 115031. |
| 16 |
YIN G Y , ZHOU S L , ZHANG W G . A threat assessment algorithm based on AHP and principal components analysis[J]. Procedia Engineering, 2011, 15, 4590- 4596.
doi: 10.1016/j.proeng.2011.08.862 |
| 17 | LIU X M, HAN Y, QIU H Z, et al. Threat evaluation in air defense based on Improved KPCA-TOPSIS[C]//Proc.of the IEEE Guidance, Navigation and Control Conference, 2018. |
| 18 | MENG F Z, FU Y S, LOU F. A network threat analysis method combined with kernel PCA and LSTM-RNN[C]//Proc.of the 10th International Conference on Advanced Computational Intelligence, 2018: 508-513. |
| 19 |
董雪, 张德平. 基于组合核主成分分析的潜艇威胁度评估模型[J]. 计算机工程, 2018, 44 (11): 46- 51.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1710-0263 |
|
DONG X , ZHANG D P . Submarine threat assessment model based on combined core principal component analysis[J]. Computer Engineering, 2018, 44 (11): 46- 51.
doi: 10.3778/j.issn.1002-8331.1710-0263 |
|
| 20 | JIANG Q C , YAN X F . Monitoring multi-mode plant-wide processes by using mutual information-based multi-block PCA, joint probability, and Bayesian inference[J]. Chemometrics and Intelligent Laboratory Systems, 2014, 136 (15): 121- 137. |
| 21 |
WANG Y W , ZHOU D H , CHEN M Y , et al. Weighted part mutual information related component analysis for quality-related process monitoring[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2020, 88, 111- 123.
doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2020.03.001 |
| 22 | 袁周, 方志耕. 灰色主成分评价模型的构建及其应用[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2016, 36 (8): 2086- 2090. |
| YUAN Z , FANG Z G . Construction and application of grey principal component evaluation model[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2016, 36 (8): 2086- 2090. | |
| 23 | 王玲玲, 方志耕. 分层构权灰色主成分评价模型及其应用[J]. 控制与决策, 2019, 34 (6): 1300- 1306. |
| WANG L L , FANG Z G . Multi-layer weighted grey principal component evaluation model and its application[J]. Control and Decision, 2019, 34 (6): 1300- 1306. | |
| 24 | 李正欣, 郭建胜, 惠晓滨, 等. 基于共同主成分的多元时间序列降维方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2013, 28 (4): 54- 59. |
| LI Z X , GUO J S , HUI X B , et al. Dimension reduction method for multivariate time series based on common principal component[J]. Control and Decision, 2013, 28 (4): 54- 59. | |
| 25 | VITANOV N K , HSFFMANN N P , WERNITZ B . Nonlinear time series analysis of vibration data from a friction brake: SSA, PCA, and MFDFA[J]. Chaos, Solitons & Fractals, 2014, 69, 90- 99. |
| 26 |
DONG Y N , QIN S J . A novel dynamic PCA algorithm for dynamic data modeling and process monitoring[J]. Journal of Process Control, 2018, 67, 1- 11.
doi: 10.1016/j.jprocont.2017.05.002 |
| 27 | SREEDHARAN J , JEE V A . Multi-objective optimization for multi-stage sequential plastic injection molding with plating process using RSM and PCA-based weighted-GRA[J]. Journal of Mechanical Engineers, 2020, 234 (5): 1014- 1030. |
| 28 |
LIU S F , XIE N M , FORREST J . Novel models of grey relational analysis based on visual angle of similarity and nearness[J]. Grey Systems: Theory and Application, 2011, 1 (1): 8- 18.
doi: 10.1108/20439371111106696 |
| 29 | 刘思峰, 杨英杰, 吴利丰. 灰色系统理论及其应用[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2014. |
| LIU S F , YANG Y J , WU L F . Grey system theory and its application[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2014. | |
| 30 | 周大镯, 姜文波, 李敏强. 一个高效的多变量时间序列聚类算法[J]. 计算机工程与应用, 2010, 46 (1): 141- 143. |
| ZHOU D Z , JIANG W B , LI M Q . An efficient clustering algorithm for multivariate time series[J]. Computer Engineering & Applications, 2010, 46 (1): 141- 143. |
| [1] | Xinyu XU, Lunjun WAN, Ping CHEN, Jiangbin DAI, Zhizhou GAO. Modeling of alert patrol airspace planning in defensive counterair interception operation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1589-1599. |
| [2] | Yingqi LU, Chengli FAN, Qiang FU, Xiaowen ZHU, Wei LI. Missile defense target threat assessment based on improved similarity measure and information entropy of IFRS [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1230-1238. |
| [3] | Bowen YU, Lin YU, Ming LYU, Jie ZHANG. Target threat assessment model based on M-ANFIS-PNN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3155-3163. |
| [4] | Chong JIN, Juan SUN, Yongjia WANG, Pushen CAI, Xin RONG. Threat comprehensive assessment for air defense targets based on intuitionistic fuzzy TOPSIS and variable weight VIKOR [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 172-180. |
| [5] | Guanglei MENG, Mingzhe ZHOU, Haiyin PIAO, Huimin ZHANG. Threat assessment method of dual-aircraft formation based on cooperative tactical recognition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2285-2293. |
| [6] | SUN Haiwen, XIE Xiaofang, SUN Tao, ZHANG Longjie. Threat assessment method of warships formation air defense based on DBN under the condition of small sample data missing [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1300-1308. |
| [7] | WANG Zhuo, ZHENG Xuehe, CHANG Xiaolan. High-speed stealth target detection algorithm based on rotating and dimension reduction [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(1): 14-20. |
| [8] | SUN Qingpeng, LI Zhanwu, CHANG Yizhe. Multi-types airplane threat assessment based on combat power field [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(9): 1993-1999. |
| [9] | XU Ximeng, YANG Rennong, FU Ying, ZHAO Yu. Target threat assessment in air combat based on ELM_AdaBoost strong predictor [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(8): 1760-1768. |
| [10] | ZHANG Ying, WANG Hongwei, CHEN You. Combined emitter threat assessment based on ICWM-RCM [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(3): 557-562. |
| [11] | OUYANG Zhihong, XUE Lei, DING Feng. Jamming target assignment method of regional electronic air defense against electrooptical precision guided weapon#br# [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(12): 2621-2628. |
| [12] | SUN Haiwen, XIE Xiaofang, SUN Tao, ZHANG Longjie. Threat assessment method of warships formation air defense based on DDBN-cloud model [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(11): 2466-. |
| [13] | ZHANG Haowei, XIE Junwei, GE Jiaang, ZHANG Zhaojian, ZONG Binfeng. Intuitionistic fuzzy set threat assessment based on improved TOPSIS and multiple times fusion#br# [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(10): 2263-2269. |
| [14] | LI Zhengxin, ZHANG Fengming, WANG Ying, TAO Qian, LI Chao. Method of missing data imputation for multivariate time series [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(1): 225-230. |
| [15] | TANG Xin, YANG Jianjun, FENG Song, REN Baoxiang. AR(p) dynamic catastrophe ranking method of target threat assessment under the loss of data [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1058-1064. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||