Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (7): 2310-2322.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.07.15
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles
Intelligent decision-making technology for wargame by integrating three-way multiple attribute decision-making and SAC
Lisha PENG1,2, Yuxiang SUN1,*, Yufan XUE1, Xianzhong ZHOU1,3
- 1. School of Engineering Management, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, China
2. School of Information Technology & Artificial Intelligence, Zhejiang University of Finance & Economics, Hangzhou 310018, China
3. Research Center for New Technology in Intelligent Equipment, Nanjing University, Nanjing 210008, China
-
Received:2023-08-28Online:2024-06-28Published:2024-07-02 -
Contact:Yuxiang SUN
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Lisha PENG, Yuxiang SUN, Yufan XUE, Xianzhong ZHOU. Intelligent decision-making technology for wargame by integrating three-way multiple attribute decision-making and SAC[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(7): 2310-2322.
share this article
Table 2
Threat index system of tank operators in typical wargame systems"
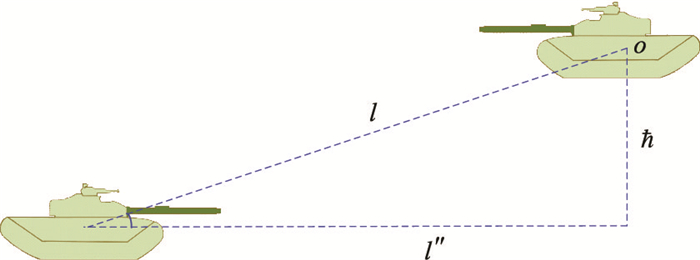
| 名称 | 类型 | 含义 | 规律(蓝方相对于红方而言) |
| 距离威胁 | 成本型 | 双方距离和夺控距离影响毁伤率和胜率 | 距离越小, 威胁越大 |
| 速度威胁 | 成本型 | 相对速度影响射程和毁伤率 | 相对速度越快, 威胁越小 |
| 角度威胁 | 综合型 | 攻击角与红方防御角共同影响毁伤率 | 攻击角越小且防御角越大时, 威胁越大 |
| 攻击能力威胁 | 效益型 | 机动能力、所携武器杀伤力、侦察能力等七要素共同影响毁伤率 | 各种能力越强, 威胁越大 |
| 防御能力威胁 | 效益型 | 装甲厚度决定其防御类和抗毁性 | 装甲越厚, 威胁越大 |
| 地形通视威胁 | 效益型 | 双方所在高程和中间高程决定蓝方能否打击到红方以及打击效果 | 观测优势越大, 威胁越大 |
| 环境指标威胁 | 效益型 | 所处环境关系到其隐蔽和机动能力 | 环境越有利于隐蔽和机动, 威胁越大 |
Table 5
Winning rates of each AI algorithm at 10 nodes in the game process"
| 局数 | TMSAC | TMPPO | M1SAC | M2SAC | M2PPO | SAC | PPO |
| 10 | 0.90 | 0.70 | 0.80 | 0.90 | 0.80 | 0.50 | 0.50 |
| 20 | 0.80 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.65 | 0.65 | 0.55 |
| 30 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.73 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.67 | 0.53 |
| 40 | 0.83 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.75 | 0.68 | 0.60 | 0.53 |
| 50 | 0.82 | 0.80 | 0.66 | 0.70 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 0.52 |
| 60 | 0.85 | 0.77 | 0.65 | 0.67 | 0.68 | 0.63 | 0.50 |
| 70 | 0.83 | 0.77 | 0.70 | 0.61 | 0.73 | 0.60 | 0.53 |
| 80 | 0.83 | 0.78 | 0.71 | 0.63 | 0.74 | 0.58 | 0.55 |
| 90 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.72 | 0.64 | 0.72 | 0.54 | 0.56 |
| 100 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.59 | 0.58 |
| 110 | 0.80 | 0.73 | 0.71 | 0.67 | 0.73 | 0.63 | 0.56 |
| 120 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.70 | 0.70 | 0.66 | 0.57 |
| 130 | 0.81 | 0.75 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 0.58 |
| 140 | 0.79 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.72 | 0.69 | 0.64 | 0.57 |
| 150 | 0.80 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.71 | 0.62 | 0.59 |
| 160 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.73 | 0.76 | 0.73 | 0.61 | 0.61 |
| 170 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.74 | 0.75 | 0.75 | 0.64 | 0.62 |
| 180 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.75 | 0.74 | 0.76 | 0.64 | 0.62 |
| 190 | 0.79 | 0.77 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.76 | 0.66 | 0.62 |
| 200 | 0.80 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.77 | 0.77 | 0.68 | 0.63 |
| 均值 | 0.81 | 0.76 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.72 | 0.62 | 0.56 |
| 1 | 李琛,黄炎焱,张永亮,等.Actor-Critic框架下的多智能体决策方法及其在兵棋上的应用[J].系统工程与电子技术,2021,43(3):755-762. |
| LIC,HUANGY Y,ZHANGY L,et al.Multi-agent decision-making method based on Actor-Critic framework and its application in wargame[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics,2021,43(3):755-762. | |
| 2 |
SILVERD,HUANGA,MADDISONC J,et al.Mastering the game of Go with deep neural networks and tree search[J].Nature,2016,529(7587):484-489.
doi: 10.1038/nature16961 |
| 3 | 胡晓峰,贺筱媛,陶九阳.AlphaGo的突破与兵棋推演的挑战[J].科技导报,2017,35(21):49-60. |
| HUX F,HEX Y,TAOJ Y.AlphaGo's breakthrough and challenges of wargaming[J].Science & Technology Review,2017,35(21):49-60. | |
| 4 | 孙宇祥,彭益辉,李斌,等.智能博弈综述: 游戏AI对作战推演的启示[J].智能科学与技术学报,2022,4(2):157-173. |
| SUNY X,PENGY H,LIB,et al.Overview of intelligent game: enlightenment of game AI to combat deduction[J].Chinese Journal of Intelligent Science and Technology,2022,4(2):157-173. | |
| 5 |
SILVERD,SCHRITTWIESERJ,SIMONYANK,et al.Mastering the game of go without human knowledge[J].Nature,2017,550(7676):354-359.
doi: 10.1038/nature24270 |
| 6 | ESPEHOLT L, SOYER H, MUNOS R, et al. IMPALA: scalable distributed deep-RL with importance weighted actor-learner architectures[C]//Proc. of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2018: 1407-1416. |
| 7 |
BARRIGAN A,STANESCUM,BESOAINF,et al.Improving RTS game AI by supervised policy learning, tactical search, and deep reinforcement learning[J].IEEE Computational Intelligence Magazine,2019,14(3):8-18.
doi: 10.1109/MCI.2019.2919363 |
| 8 | YE D H, LIU Z, SUN M F, et al. Mastering complex control in MOBA games with deep reinforcement learning[C]//Proc. of the 34th AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020, 34(4): 6672-6679. |
| 9 |
JADERBERGM,CZARNECKIW M,DUNNINGI,et al.Human-level performance in 3D multiplayer games with population-based reinforcement learning[J].Science,2019,364(6443):859-865.
doi: 10.1126/science.aau6249 |
| 10 | 尹奇跃,赵美静,倪晚成,等.兵棋推演的智能决策技术与挑战[J].自动化学报,2023,49(5):913-928. |
| YINQ Y,ZHAOM Q,NIW C,et al.Intelligent decision making technology andchallenge of wargame[J].Acta Automatica Sinica,2023,49(5):913-928. | |
| 11 |
NICOLAUM,PEREZ-LIEBANAD,O'NEI-LLM,et al.Evolutionary behavior tree approaches for navigating platform games[J].IEEE Trans.on Computational Intelligence and AI in Games,2017,9(3):227-238.
doi: 10.1109/TCIAIG.2016.2543661 |
| 12 |
NAJAM-UL-LSLAMM,ZAHRAF T,JAFRIA R,et al.Auto implementation of parallel hardware architecture for Aho-Corasick algorithm[J].Design Automation for Embbedded System,2022,26(1):29-53.
doi: 10.1007/s10617-021-09257-7 |
| 13 | 施伟,冯旸赫,程光权,等.基于深度强化学习的多机协同空战方法研究[J].自动化学报,2021,47(7):1610-1623. |
| SHIW,FENGY H,CHENGG Q,et al.Research on multi-aircraft cooperative air combat method based on deep reinforcement learning[J].Acta Automatica Sinica,2021,47(7):1610-1623. | |
| 14 |
CHENL,LIANGX X,FENGY H,et al.Online intention recognition with incomplete information based on a weighted contrastive predictive coding model in wargame[J].IEEE Trans.on Neural Networks and Learning Systems,2023,34(10):7515-7528.
doi: 10.1109/TNNLS.2022.3144171 |
| 15 | 张振,黄炎焱,张永亮,等.基于近端策略优化的作战实体博弈对抗算法[J].南京理工大学学报,2021,45(1):77-83. |
| ZHANGZ,HUANGY Y,ZHANGY L,et al.Battle entity confrontation algorithm based on proximal policy optimization[J].Journal of Nanjing University of Science and Technology,2021,45(1):77-83. | |
| 16 |
SUNY X,YUANB,ZHOUX Z,et al.Intelligent decision-making and human language communication based on deep reinforcement learning in a Wargame environment[J].IEEE Trans.on Human-Machine Systems,2023,53(1):201-214.
doi: 10.1109/THMS.2022.3225867 |
| 17 | RUEDENL V,MAYERS,BECKHK,et al.Informed machine learning: a taxonomy and survey of integrating prior knowledge into learning systems[J].IEEE Trans.on Know-ledge and Data Engineering,2021,35(1):614-633. |
| 18 |
SUNY X,YUANB,ZHANGT,et al.Research andimplementation of intelligent decision based on a priori knowledge and DQN algorithms in wargame environment[J].Electronics,2020,9(10):1668.
doi: 10.3390/electronics9101668 |
| 19 |
XUEY F,SUNY X,ZHOUJ W,et al.Multi-attribute decision-making in wargames leveraging the entropy-weight method with deep reinforcement learning[J].IEEE Trans.on Games,2024,16(1):151-161.
doi: 10.1109/TG.2023.3236065 |
| 20 | YOONP K,HWANGC L,YOONK.Multiple attribute decision making: an introduction[M].New York:Thousand Oaks Sage Publications,1995. |
| 21 |
YAOY Y.The superiority of three-way decisions in probabilistic rough set models[J].Information Sciences,2011,181(6):1080-1096.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2010.11.019 |
| 22 |
WANGW J,ZHANJ M,ZHANGC,et al.A regret-theory-based three-way decision method with a priori probability tole-rance dominance relation in fuzzy incomplete information systems[J].Information Fusion,2023,89,382-396.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2022.08.027 |
| 23 |
ZHANJ M,JIANGH B,YAOY Y.Three-way multi-attri-bute decision-making based on outranking relations[J].IEEE Trans.on Fuzzy Systems,2021,29(10):2844-2858.
doi: 10.1109/TFUZZ.2020.3007423 |
| 24 | PENG L S, ZHANG T, ZHANG X Y, et al. Threat assessment for aerial targets based on three-way multi-criteria decision making[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Networking, Sensing and Control, 2021. |
| 25 |
PENGL S,ZHOUX Z,ZHAOJ J,et al.Three-way multi-attribute decision making under incomplete mixed environments using probabilistic similarity[J].Information Science,2022,614,432-463.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2022.10.038 |
| 26 | HAARNOJA T, ZHOU A, ABBEEL P, et al. Soft Actor-Critic: off-policy maximum entropy deep reinforcement learning with a stochastic actor[C]//Proc. of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning, 2018. |
| 27 | DE JESUSJ C,KICHV A,KOLLINGA H,et al.Soft actor-critic for navigation of mobile robots[J].Journal of Intelligent & Robotic Systems,2021,102(2):31-42. |
| 28 | 杨来义,毕敬,苑海涛.基于SAC算法的移动机器人智能路径规划[J].系统仿真学报,2023,35(8):1726-1736. |
| YANGL Y,BIJ,YUANH T.Intelligent path planning for mobile robots based on soft actor-critic algorithm[J].Journal of System Simulation,2023,35(8):1726-1736. | |
| 29 | 张建东,王鼎涵,杨啟明,等.基于分层强化学习的无人机空战多维决策[J].兵工学报,2023,44(6):1547-1563. |
| ZHANGJ D,WANGD H,YANGQ M,et al.Multi-dimensional decision-making for UAV air combat based on hierarchical rein-forcement learning[J].Acta Armamentarii,2023,44(6):1547-1563. | |
| 30 | 单麒源,张智豪,张耀心,等.基于SAC算法的矿山应急救援智能车快速避障控制[J].黑龙江科技大学学报,2021,31(1):14-20. |
| SHANQ Y,ZHANGZ H,ZHANGY X,et al.High speed obstacle avoidance control of mine emergency rescue intelligent vehicle based on SAC algorithm[J].Journal of Heilongjiang University of Science and Technology,2021,31(1):14-20. | |
| 31 | 夏琳. 基于深度强化学习的海上作战仿真推演决策方法研究[D]. 北京: 中国舰船研究院, 2023. |
| XIA L. Research ondecision making method of maritime combat simulation based on deep reinforcement learning[D]. Beijing: Chinese Journal of Ship Research, 2023. | |
| 32 | 赵烨南,杜伟伟,陈铁健,等.基于集对分析的坦克多目标威胁评估方法[J].火力与指挥控制,2020,45(6):108-112. |
| ZHAOY N,DUW W,CHENT J,et al.Multi-target threat assessment method of tank based on set pair analysis[J].Fire Control & Command Control,2020,45(6):108-112. | |
| 33 | 张晓南,王德泉,杨俊峰.坦克战场目标威胁评估方法[J].指挥信息系统与技术,2015,6(1):45-48. |
| ZHANGX N,WANGD Q,YANGJ F.Battlefield target threat assessment for tank[J].Command Information System and Technology,2015,6(1):45-48. | |
| 34 | 孙宇祥,李原白,周胜,等.对抗环境下的智能兵棋系统设计及其关键技术[J].火力与指挥控制,2024,49(2):33-41. |
| SUNY X,LIY B,ZHOUS,et al.Design anel key technology of intelligent wargame system in adversary environment[J].Fire Control & Command Control,2024,49(2):33-41. |
| [1] | Mengyu ZHANG, Yajie DOU, Ziyi CHEN, Jiang JIANG, Kewei YANG, Bingfeng GE. Review of deep reinforcement learning and its applications in military field [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(4): 1297-1308. |
| [2] | Jianbin ZHOU, Jin BEN, Xinhai HUANG, Rui WANG, Xiaoyu LIANG. Construction method of extensive hexagonal wargame map and application for marching deduction [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(3): 769-776. |
| [3] | Man LIU, Hongjun ZHANG, Youwei XU, Xinliang FENG, Yufang FENG. Research on behavior decision-making of multi entities in group-level wargame [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2562-2569. |
| [4] | Li HE, Liang SHEN, Hui LI, Zhuang WANG, Wenquan TANG. Survey on policy reuse in reinforcement learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 884-899. |
| [5] | Chen LI, Yanyan HUANG, Yongliang ZHANG, Tiande CHEN. Multi-agent decision-making method based on Actor-Critic framework and its application in wargame [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(3): 755-762. |
| [6] | Kai CHENG, Gang CHEN, Xiaohan YU, Man LIU, Tianhao SHAO. Knowledge traction and data-driven wargame AI design and key technologies [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(10): 2911-2917. |
| [7] | Ke ZHANG, Wenning HAO, Xiaohan YU, Dawei JIN, Tianhao SHAO. Wargame key point reasoning method based on genetic fuzzy system [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2303-2311. |
| [8] | TAN XU, WU Junjiang, MAO Taitian, TAN Yuejin. Multi-attribute intelligent decision making method based on triangular fuzzy number hesitant intuitionistic fuzzy sets [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(4): 829-836. |
| [9] | HUANG Ru1, ZHU Yu1, ZHANG Zai-chen2. MAC contention window driven energy-saving filtering mechanism in WSN using RL [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(5): 973-979. |
| [10] | ZHANG Yuan, LIU Wen-biao, ZHANG Li-min. Situation assessment modeling for CGF based on the subjective and objective integrated weight [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(1): 85-90. |
| [11] | YANG Junqiang1,2, DU Jia2. Research on military requirement of Wargame system for planning [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(7): 1445-1447. |
| [12] | CHAI Xue,WANG Gang-lin,WU Zhe. Intelligent decision support system and its application indesign of flight control systems [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(4): 833-836. |
| [13] | MENG Guang-lei,GONG Guang-hong. Threat assessment of aerial targets based on hybrid Bayesian network [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(11): 2398-2401. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||