Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (6): 2044-2053.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.06.22
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles
Genetic-evolutionary bi-level mission planning algorithm for multi-satellite cooperative observation
Yangyang LI, Junren LUO, Wanpeng ZHANG, Fengtao XIANG
- College of Intelligence Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
-
Received:2022-07-18Online:2024-05-25Published:2024-06-04 -
Contact:Wanpeng ZHANG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yangyang LI, Junren LUO, Wanpeng ZHANG, Fengtao XIANG. Genetic-evolutionary bi-level mission planning algorithm for multi-satellite cooperative observation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 2044-2053.
share this article
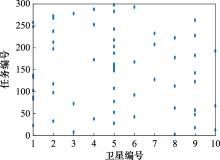
Table 3
Satellite orbit parameters"
| 卫星编号 | 半长轴/m | 离心率 | 轨道倾角/(°) | 近地点辐角/(°) | 升交点赤经/(°) | 真近点角/(°) |
| Sat1 | 7 171.393 | 0 | 96.576 | 0 | 175.72 | 0.075 |
| Sat2 | 7 171.393 | 0 | 96.576 | 0 | 145.72 | 30.075 |
| Sat3 | 7 171.393 | 0 | 96.576 | 0 | 115.72 | 60.075 |
| Sat4 | 7 171.393 | 0 | 96.576 | 0 | 85.72 | 90.075 |
| Sat5 | 7 171.393 | 0 | 96.576 | 0 | 55.72 | 120.075 |
| Sat6 | 7 171.393 | 0 | 96.576 | 0 | 25.72 | 150.075 |
| Sat7 | 7 193.589 | 0 | 98.726 | 77.105 | 107.085 | 184.637 |
| Sat8 | 6 891.852 | 0 | 97.325 | 237.611 | 333.934 | 112.26 |
| Sat9 | 6 836.068 | 0 | 97.326 | 81.466 | 76.8 | 136.42 |
| Sat10 | 7 046.723 | 0 | 98.138 | 80.162 | 178.688 | 244.539 |
Table 3
| 1 |
ZHENG Z X , GUO J , GILL E . Distributed onboard mission planning for multi-satellite systems[J]. Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, 89, 111- 122.
doi: 10.1016/j.ast.2019.03.054 |
| 2 |
XIAO Y Y , ZHANG S Y , YANG P , et al. A two-stage flow-shop scheme for the multi-satellite observation and data-downlink scheduling problem considering weather uncertainties[J]. Reliability Engineering and System Safety, 2019, 188, 263- 275.
doi: 10.1016/j.ress.2019.03.016 |
| 3 |
VALICKA C G , GARCIA D , STAID A , et al. Mixed-integer programming models for optimal constellation scheduling given cloud cover uncertainty[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2019, 275 (2): 431- 445.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2018.11.043 |
| 4 |
CHU X G , CHEN Y N , TAN Y J . An anytime branch and bound algorithm for agile earth observation satellite onboard scheduling[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2017, 60 (9): 2077- 2090.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2017.07.026 |
| 5 |
LIU Z B , FENG Z R , REN Z G . Route-reduction-based dynamic programming for large-scale satellite range scheduling problem[J]. Engineering Optimization, 2019, 51 (11): 1944- 1964.
doi: 10.1080/0305215X.2018.1558445 |
| 6 |
PELLERIN R , PERRIER N , BERTHAUT F . A survey of hybrid metaheuristics for the resource-constrained project scheduling problem[J]. European Journal of Operational Research, 2020, 280 (2): 395- 416.
doi: 10.1016/j.ejor.2019.01.063 |
| 7 | HE L , LIU X L , LAPORTE G , et al. An improved adaptive large neighborhood search algorithm for multiple agile satellites scheduling[J]. Computers & Operations Research, 2018, 100, 12- 25. |
| 8 |
WANG J J , HU X J , HE C . Reactive scheduling of multiple EOSs under cloud uncertainties: model and algorithms[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32 (1): 163- 177.
doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000015 |
| 9 |
YAO F , LI J T , CHEN Y N , et al. Task allocation strategies for cooperative task planning of multi-autonomous satellite constellation[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 63 (2): 1073- 1084.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2018.10.002 |
| 10 |
WU G H , LUO Q Z , DU X , et al. Ensemble of meta-heuristic and exact algorithm based on the divide and conquer framework for multi-satellite observation scheduling[J]. IEEE Trans.on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2022, 58 (5): 4396- 4408.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3160993 |
| 11 |
SUN H Q , XIA W , HU X X , et al. Earth observation satellite scheduling for emergency tasks[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 30 (5): 931- 945.
doi: 10.21629/JSEE.2019.05.11 |
| 12 | 陈浩, 罗棕, 杜春, 等. 一种基于Bi-GRU的卫星对地观测任务可调度性预测方法[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 48 (6): 88- 95. |
| CHEN H , LUO Z , DU C , et al. A prediction method for schedulability of satellite earth observation task based on Bi-GRU[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 48 (6): 88- 95. | |
| 13 |
PENG S , CHEN H , DU C , et al. On board observation task planning for an autonomous earth observation satellite using long short-term memory[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 65118- 65129.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2877687 |
| 14 |
WANG H J , YANG Z , ZHOU W G , et al. Online scheduling of image satellites based on neural networks and deep reinforcement learning[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2019, 32 (4): 1011- 1019.
doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2018.12.018 |
| 15 |
WANG X , WU J , SHI Z , et al. Deep reinforcement learning-based autonomous mission planning method for high and low orbit multiple agile earth observing satellites[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2022, 70 (11): 3478- 3493.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2022.08.016 |
| 16 |
HUANG Y X , MU Z C , WU S F , et al. Revising the observation satellite scheduling problem based on deep reinforcement learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2021, 13 (12): 2377.
doi: 10.3390/rs13122377 |
| 17 | DU Y H , WANG T , XIN B , et al. A data-driven parallel scheduling approach for multiple agile earth observation satellites[J]. IEEE Trans.on Evolutionary Computation, 2019, 24 (4): 679- 693. |
| 18 | 杜永浩, 邢立宁, 姚锋, 等. 航天器任务调度模型, 算法与通用求解技术综述[J]. 自动化学报, 2021, 47 (12): 2715- 2741. |
| DU Y H , XING L N , YAO F , et al. Survey on models, algorithms and general techniques for spacecraft mission scheduling[J]. Acta Automatica Sinica, 2021, 47 (12): 2715- 2741. | |
| 19 |
ZHU W M , HU X X , XIA W , et al. A two-phase genetic annealing method for integrated Earth observation satellite sche-duling problems[J]. Soft Computing, 2019, 23 (1): 181- 196.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-017-2889-8 |
| 20 |
ZHAO M , LI D C . A hierarchical parallel evolutionary algorithm of distributed and multi-threaded two-level structure for multi-satellite task planning[J]. International Journal of Automation and Control, 2020, 14 (5/6): 612- 633.
doi: 10.1504/IJAAC.2020.110075 |
| 21 |
LI Z L , LI X J . A multi-objective binary-encoding differential evolution algorithm for proactive scheduling of agile earth observation satellites[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2019, 63 (10): 3258- 3269.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2019.01.043 |
| 22 | 毛李恒, 邓清, 刘柔妮, 等. 针对多星多任务仿真调度的关键路径遗传算法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2021, 33 (1): 205- 214. |
| MAO L H , DENG Q , LIU R N , et al. CPM-GA for multi-satellite and multi-task simulation scheduling[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2021, 33 (1): 205- 214. | |
| 23 |
QI J T , GUO J J , WANG M M , et al. A cooperative autonomous scheduling approach for multiple earth observation satellites with intensive missions[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 61646- 61661.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3075059 |
| 24 | 李德仁, 丁霖, 邵振峰. 面向实时应用的遥感服务技术[J]. 遥感学报, 2021, 25 (1): 15- 24. |
| LI D R , DING L , SHAO Z F . Application-oriented real-time remote sensing service technology[J]. Journal of Remote Sensing, 2021, 25 (1): 15- 24. | |
| 25 |
WANG C , TANG J H , CHENG X H , et al. Distributed cooperative task planning algorithm for multiple satellites in delayed communication environment[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 27 (3): 619- 633.
doi: 10.1109/JSEE.2016.00066 |
| 26 |
CHANG Z X , ZHOU Z B , YAO F , et al. Observation scheduling problem for AEOS with a comprehensive task clustering[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 32 (2): 347- 364.
doi: 10.23919/JSEE.2021.000029 |
| 27 |
LI Y Q , WANG R X , YU L , et al. Satellite range scheduling with the priority constraint: an improved genetic algorithm using a station ID encoding method[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2015, 28 (3): 789- 803.
doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2015.04.012 |
| 28 |
ANGELOVA M , PENCHEVA T . Genetic operators'significance assessment in multi-population genetic algorithms[J]. International Journal of Metaheuristics, 2014, 3 (2): 162- 173.
doi: 10.1504/IJMHEUR.2014.063146 |
| 29 | 张佳唯. 面向航天侦察的任务优先级模型与算法研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2018. |
| ZHANG J W. Research on task priority model and algorithm for space reconnaissance[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2018. | |
| 30 | 于龙江, 吴限德, 毛一岚, 等. 分布式遥感卫星任务分配的合同网络算法[J]. 哈尔滨工程大学学报, 2020, 41 (7): 1059- 1065. |
| YU L J , WU X D , MAO Y L , et al. Task allocation for distributed remote sensing satellites based contract network algorithm[J]. Journal of Harbin Engineering University, 2020, 41 (7): 1059- 1065. |
| [1] | Zhiwei CHEN, Luogeng ZHANG, Xiaotong FANG, Yuan YUAN, Weiwei CUI, Hongyan DUI, Dongpao HONG. Reliability concepts, modeling, and prediction methods for weapon system of systems [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 1975-1985. |
| [2] | Ming SHI, Yuhui GAO, Gong ZHANG. Dynamic planning method based HTN for rover [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(2): 631-639. |
| [3] | Hongliang ZHAO, Yuanwen ZHANG, Leping YANG, Huan HUANG, Tian MA. Method and application analysis of remote magnetic controlling for space target [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(1): 261-270. |
| [4] | Shaobo CHEN, Jiamin YAN, Kuichen BU. Anti-intercept maneuver method of vehicle based on prediction of miss distance [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(9): 2922-2930. |
| [5] | Xingchuan LIU, Danhe CHEN, Gen XU, Wenhe LIAO. Control and strategy for satellites formation maintenance with impulsive maneuver [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(8): 2533-2545. |
| [6] | Jiaqi BAI, Yankai WANG, Hao XING. Fixed-time heterogeneous formation control of unmanned boats and quadrotor unmanned aerial vehicle [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(4): 1152-1163. |
| [7] | Qian PENG, Jianguo GUO, Zongyi GUO, Guoqing WANG. Multi-constraint multi-input interceptor integrated attitude and trajectory compound control [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(3): 806-813. |
| [8] | Dianfeng QIAO, Yan LIANG, Chaoxiong MA, Xinyu YANG, Mian WANG, Jianguo LI. Recognition and prediction of group target intention in multi-domain operations [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(11): 3403-3412. |
| [9] | Peng JIN, Kang LI. Distributed satellite resource scheduling based on improved contract network protocol [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3164-3173. |
| [10] | Tiansu LUO, Lingfeng ZHAO, Yunwen FENG, Xiaofeng XUE, Cheng LU. Super large-scale satellite constellation multi-level backup strategy based on METRIC theory [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(7): 2181-2190. |
| [11] | Juan LIU, Quanyong SU, Zheng SHI, Xianmou XUE. Optimization design and performance research on microchannel liquid cooling of phased array antenna [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1782-1788. |
| [12] | Chengfei YUE, Zhenghua XUE, Weiran YAO, Xibin CAO. Cooperative combat task allocation of multiple aerial vehicles based on the characteristic relation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1897-1906. |
| [13] | Ruiping JI, Chengyi ZHANG, Yan LIANG, Yuedong WANG. Trajectory prediction of boost-phase ballistic missile based on LSTM [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1968-1976. |
| [14] | Ning WANG, Zhe LI, Xiaolong LIANG, Yubing WANG, Yueqi HOU. Cooperative region search of UAV swarm with limited communication distance [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1615-1625. |
| [15] | Tianyang GAO, Xiaoxuan HU, Wei XIA. Constellation autonomous mission planning algorithm based on distributed co-evolution [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1600-1608. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||