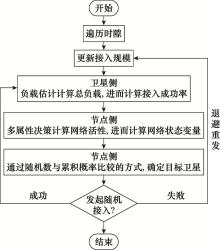
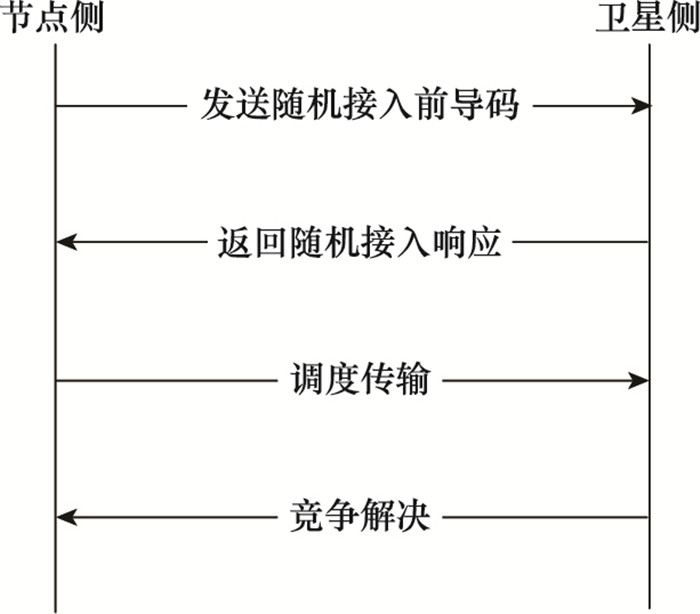
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (4): 1354-1363.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.04.34
• Communications and Networks • Previous Articles Next Articles
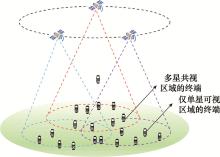
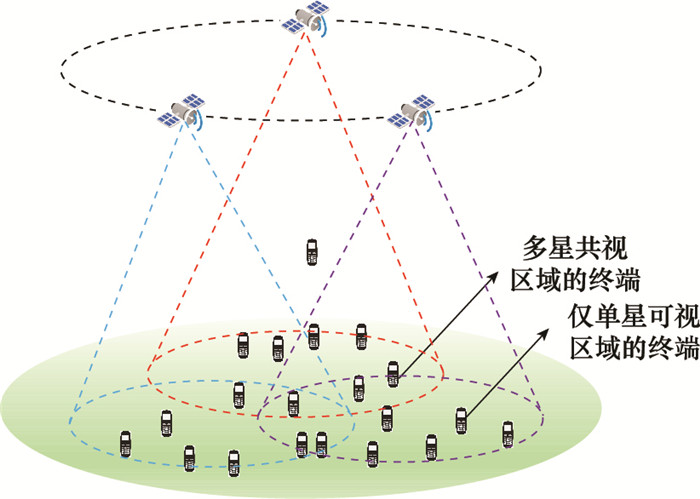
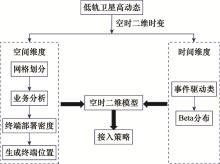
Multi-satellite load balancing algorithm based on attractor selection algorithm in low earth orbit satellite internet of things scenario
Yifan CHENG1, Tao HONG1,*, Xiaojin DING2, Gengxin ZHANG1
- 1. School of Communication and Information Engineering, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210003, China
2. School of Internet of Things, Nanjing University of Posts and Telecommunications, Nanjing 210003, China
-
Received:2021-01-11Online:2022-04-01Published:2022-04-01 -
Contact:Tao HONG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yifan CHENG, Tao HONG, Xiaojin DING, Gengxin ZHANG. Multi-satellite load balancing algorithm based on attractor selection algorithm in low earth orbit satellite internet of things scenario[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1354-1363.
share this article
| 1 |
ALANC, 沈永言. 5G世界中的卫星物联网[J]. 卫星与网络, 2018, (12): 48- 49.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-965X.2018.12.009 |
|
ALAN C , SHEN Y Y . Satellite internet of things in 5G world[J]. Satellite and Network, 2018, (12): 48- 49.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-965X.2018.12.009 |
|
| 2 |
SAGHEER A , MOHAMMED M , RIAD K , et al. A cloud-based IoT platform for precision control of soilless greenhouse cultivation[J]. Sensors, 2020, 21 (1): 223.
doi: 10.3390/s21010223 |
| 3 | MOHSENI M , JOORABIAN M , LASHKAR A A . Distribution system reconfiguration in presence of Internet of things[J]. IET Generation, Transmission & Distribution, 2020, 15 (8): 1290- 1303. |
| 4 | FAN J C , ZHANG Y , WEN W L , et al. The future of internet of things in agriculture: plant high-throughput phenotypic platform[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2020, 280 (2): 123651. |
| 5 | 沈俊, 高卫斌, 张更新. 低轨卫星物联网的发展背景、业务特点和技术挑战[J]. 电信科学, 2019, 35 (5): 113- 119. |
| SHEN J , GAO W B , ZHANG G X . Development background, service characteristics and technical challenges of low orbit satellite internet of things[J]. Telecommunication Science, 2019, 35 (5): 113- 119. | |
| 6 |
YANG D M , ZHOU Y H , HUANG W T , et al. 5G mobile communication convergence protocol architecture and key technologies in satellite internet of things system[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2021, 60 (1): 465- 476.
doi: 10.1016/j.aej.2020.09.019 |
| 7 |
WEI J Y , HAN J R , CAO S Z . Satellite IoT edge intelligent computing: a research on architecture[J]. Electronics, 2019, 8 (11): 1247.
doi: 10.3390/electronics8111247 |
| 8 | 简鑫, 曾孝平, 张力, 等. 机器类通信业务建模与流量分析[J]. 北京邮电大学学报, 2013, 36 (3): 74- 78. |
| JIAN X , ZENG X P , ZHANG L , et al. Machine communication business modeling and traffic analysis[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications, 2013, 36 (3): 74- 78. | |
| 9 | 侯世武, 谭献海. 典型物联网业务流量特性研究分析[J]. 物联网技术, 2017, 7 (6): 40- 42. 40-42, 46 |
| HOU S W , TAN X H . Research and analysis on traffic characteristics of typical Internet of things services[J]. Internet of Things Technology, 2017, 7 (6): 40- 42. 40-42, 46 | |
| 10 | RATASUK R, MANGALVEDHE N, GHOSH A, et al. Narrowband LTE-M system for M2M communication[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 80th Vehicular Technology Conference, 2014. |
| 11 | 夏海英, 曾诚, 蔡凤田, 等. 基于细胞吸引子选择机制的网络选择算法[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 42 (4): 711- 717. |
| XIA H Y , ZENG C , CAI F T , et al. Network selection algorithm based on cell attractor selection mechanism[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016, 42 (4): 711- 717. | |
| 12 | KAJIOKA S , WAKAMIYA N , MURATA M . Autonomous and adaptive resource allocation among multiple nodes and multiple applications in heterogeneous wireless networks[J]. Journal of Computer & System Sciences, 2012, 78 (6): 1673- 1685. |
| 13 | HU Z Q, LU Z M, LI Z X, et al. Adaptive network selection based on attractor selection in data offloading[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, 2016. |
| 14 | LEIBNITZ K J, WAKAMIYA N, MURATA M. Self-adaptive adhoc/sensor network routing with attractor selection[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Global Telecommunications Conference, 2006. |
| 15 | IWAI T, WAKAMIYA N, MURATA M. Error-tolerant coverage control based on bio-inspired attractor selection model for wireless sensor networks[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 10th International Conference on Computer and Information Technology, 2010: 723-729. |
| 16 |
LEIBNITZ K J , MURATA M . Attractor selection and perturbation for robust networks in fluctuating environments[J]. IEEE Network, 2010, 24 (3): 14- 18.
doi: 10.1109/MNET.2010.5464222 |
| 17 | MOTOYOSHI G , LEIBNITZ K , MURATA M . Proposal and evaluation of a future mobile network management mechanism with attractor selection[J]. EURASIP Journal on Wireless Communications and Networking, 2012, 259. |
| 18 | WU H, WEN X M, LU Z M, et al. Multi-access selection with attractor selection algorithm in heterogeneous network[C]//Proc. of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, 2015. |
| 19 |
孙建亮, 崔国刚, 周英庆. 发展我国低轨卫星通信星座系统的思考[J]. 通信技术, 2020, 53 (9): 2224- 2227.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2020.09.022 |
|
SUN J L , CUI G G , ZHOU Y Q . Thoughts on the development of China's low-orbit satellite communication constellation system[J]. Communications Technology, 2020, 53 (9): 2224- 2227.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2020.09.022 |
|
| 20 | 徐秀兰. 世界主要航线、海峡、运河的综合比较[J]. 中学地理教学参考, 2004, (4): 15- 18. |
| XU X L . Comprehensive comparison of major routes, straits and canals in the world[J]. Middle School Geography Teaching Reference, 2004, (4): 15- 18. | |
| 21 |
李毅, 侯睿, 张更新. 发展我国低轨卫星通信星座系统的思考[J]. 国际太空, 2018, (4): 62- 65.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2018.04.013 |
|
LI Y , HOU R , ZHANG G X . Thoughts on the development of China's low-orbit satellite communication constellation system[J]. International Space, 2018, (4): 62- 65.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2018.04.013 |
|
| 22 |
邢强. 低轨巨型星座的建设及其影响分析[J]. 中国航天, 2019, (12): 43- 47.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2019.12.005 |
|
XING Q . Construction of low-orbit giant constellation and its impact analysis[J]. China Aerospace Science and Technology, 2019, (12): 43- 47.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-7742.2019.12.005 |
|
| 23 |
陈东, 裴胜伟, 黄华, 等. 全球巨型低轨星座通信网络发展、特征与思考[J]. 国际太空, 2020, (4): 42- 47.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2020.04.010 |
|
CHEN D , PEI S W , HUANG H , et al. Development, characteristics and thinking of global communication network of giant low-orbit constellations[J]. International Space, 2020, (4): 42- 47.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-2366.2020.04.010 |
|
| 24 |
QU Z C , ZHANG G X , HONG T , et al. Architecture and network model of time-space uninterrupted space information network[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 27677- 27688.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2019.2902134 |
| 25 |
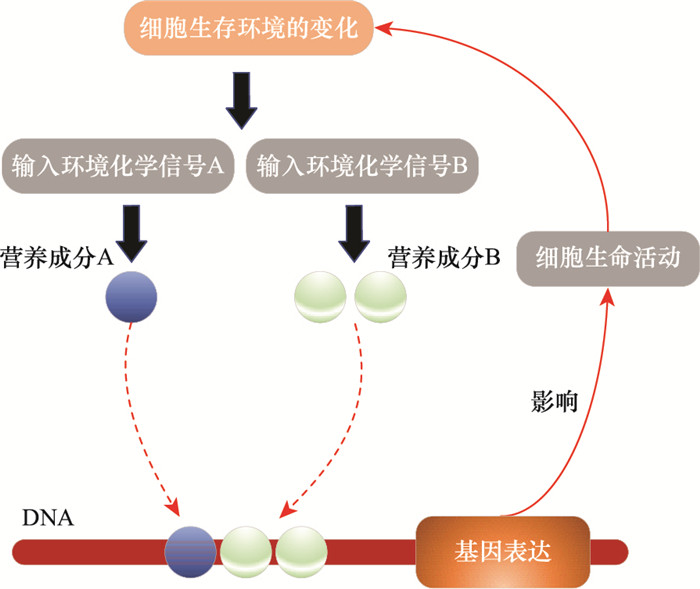
AKIKO K , ITARU U , KUNIHIKO K , et al. Adaptive response of a gene network to environmental changes by fitness-induced attractor selection[J]. PLoS ONE, 2006, 1 (1): e49- e59.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0000049 |
| 26 | WU H Q, LU Z M, LI Z X, et al. Mobile data offloading under attractor selection in heterogeneous networks[C]//Proc. of the International Symposium on Wireless Communication Systems, 2017: 164-169. |
| 27 |
WANG T C , LEE H S D . Developing a fuzzy TOPSIS approach based on subjective weights and objective weights[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2009, 36 (5): 8980- 8985.
doi: 10.1016/j.eswa.2008.11.035 |
| 28 | 3GPP Standard TR 37.868-2011. RAN improvements for machinetype communications[S]. USA: 3GPP, 2011. |
| 29 | LEE K D, SANG K, YI B. Throughput comparison of random access methods for M2M service over LTE networks[C]//Proc. of the IEEE GLOBECOM Workshops, 2011: 373-377. |
| 30 | 程一凡, 曲至诚, 张更新. 低轨卫星星座物联网业务量建模[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43 (4): 1050- 1056. |
| CHENG Y F , QU Z C , ZHANG G X . Low orbit satellite constellation Iot traffic modeling[J]. Journal of Electronics and Information Technology, 2021, 43 (4): 1050- 1056. |
| [1] | Yiqiang TANG, Xiaopeng YANG, Shengming ZHU. Low-orbit satellite channel prediction algorithm based on the hybrid CNN-BiLSTM using attention mechanism [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3863-3870. |
| [2] | Gaosai LIU, Xinglong JIANG, Huawang LI, Guang LIANG. Large-scale LEO constellation distributed routing algorithm based on location awareness [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(11): 3529-3536. |
| [3] | Jiajia HUANG, Jing LEI, Ying HUANG. Research on application of rateless code in wireless sensor network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3228-3234. |
| [4] | LIU Jinchang, HUANG Shucai, ZHAO Wei, PANG Ce, HUANG Da. Analysis on demand of anti-missile operational ability of space based infrared low orbit satellites#br# [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(8): 1777-1785. |
| [5] | HU Xiangdong, WANG Rui, HU Rong. Improved optimization algorithm of clusters maintenance for#br# sensing layer of the internet of things [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(1): 198-205. |
| [6] | WANG Juan, GUO Yu-jiang, SUN Li-juan, ZHOU Jian, HAN Chong. Load balancing algorithm for multi-traffic in double layered satellite network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(9): 2156-2161. |
| [7] |
WANG Ru-yan, ZHOU Xiao-jun, WU Da-peng.
Load balancing adaptive handover algorithm in LTE [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(9): 2156-2163. |
| [8] | LU Zhi-mao,FENG Jin-mei,FAN Dong-mei,YANG Peng,TIAN Ye. Novel partitional clustering algorithm for large data processing [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(5): 1010-1015. |
| [9] | YANG Xuan, GUO Fabin, WANG Mingzhe. Analysis of LEO constellation spatial coverage attribute based on Petri nets [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(3): 481-486. |
| [10] | MA Wu-bin, LIU Ming-xing, DENG Su, HUANG Hong-bin. Spatial resource index construction and query optimization algorithm for Internet of Things [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(1): 173-178. |
| [11] | YAO Ye, LIANG Xu-wen. Dynamic routing technique based on LEO&GEO double layered satellite network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(9): 1966-1973. |
| [12] | WANG Wei-ping, YU Wen-guang, HOU Hong-tao, LI Qun. Load balancing mechanism for parallel agent-based simulation on multi-core CPU and GPU heterogeneous platform [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(11): 2366-2373. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||