Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2021, Vol. 43 ›› Issue (7): 1928-1942.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.07.25
• Guidance, Navigation and Control • Previous Articles Next Articles
Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm with random neighborhood-based strategy and generalized opposition-based learning
Wenhai WU, Xiaofeng GUO*, Siyu ZHOU, Li GAO
- Department of Aeronautical Electric Control Engineering and Command, Naval Aviation University Qingdao Campus, Qingdao 266041, China
-
Received:2020-07-30Online:2021-06-30Published:2021-07-08 -
Contact:Xiaofeng GUO
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Wenhai WU, Xiaofeng GUO, Siyu ZHOU, Li GAO. Self-adaptive differential evolution algorithm with random neighborhood-based strategy and generalized opposition-based learning[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(7): 1928-1942.
share this article
Table 1
Benchmark functions."
| 类型 | 函数名 | 搜索域 |
| 单峰函数 | f1: Sphere | [-100, 100] |
| f2: Schwefel2.22 | [-10, 10] | |
| f3: Schwefel1.2 | [-100, 100] | |
| f4: Schwefel2.21 | [-100, 100] | |
| f5: Rosenbrock | [-30, 30] | |
| f6: Step | [-100, 100] | |
| f7: Quartic with Noise | [-1.28, 1.28] | |
| 多峰函数 | f8: Schwefel2.26 | [-500, 500] |
| f9: Rastrigin | [-5.12, 5.12] | |
| f10: Ackley | [-32, 32] | |
| f11: Griewank | [-600, 600] | |
| f12: Penalized1 | [-50, 50] | |
| f13: Penalized2 | [-50, 50] | |
| 偏移单峰函数 | f14: Shifted Sphere Function | [-100, 100] |
| f15: Shifted Schwefels Problem 1.2 | [-100, 100] | |
| f16: Schwefels Problem 1.2 with Noise in Fitness | [-100, 100] | |
| f17: Schwefels Problem 2.6 with Global Optimum on f1: Bounds | [-100, 100] | |
| f18: Shifted Rotated High Conditioned Elliptic Function | [-100, 100] | |
| 偏移多峰函数 | f19: Shifted Rosenbrocks Function Shifted | [-100, 100] |
| f20: Shifted Rotated Griewanks Function without Bounds | [0, 600] | |
| f21: Shifted Rotated Ackleys Function with Global Optimum on Bounds | [-32, 32] | |
| f22: Shifted Rastrigins Function | [-5, 5] | |
| f23: Shifted Rotated Rastrigins Function | [-5, 5] | |
| f24: Shifted Rotated Weierstrass Function | [-0.5, 0.5] | |
| f25: Schwefels Problem 2.13 | [-π, π] | |
| f26: Shifted Expanded Griewanks plus Rosenbrocks Function (F8F2) | [-3, 1] | |
| f27: Shifted Rotated Expanded Scaffers F6 Function | [-100, 100] |
Table 2
Experimental results of GOBL-RNADE and basic DE(D=30)"
| 函数 | DE/rand/1 | DE/best/1 | GOBL-RNADE |
| f1 | 1.06E-43±1.29E-43- | 2.51E+03±1.38E+03+ | 1.63E-240±0.00E+00 |
| f2 | 3.51E-24±5.53E-24+ | 5.44E+02±1.69E+02+ | 1.80E-126±6.91E-126 |
| f3 | 4.02E-11±6.35E-11+ | 4.41E+03±2.03E+03+ | 7.15E-276±0.00E+00 |
| f4 | 6.03E-02±3.32E-02+ | 1.34E+01±4.01E+00+ | 6.26E-115±2.50E-114 |
| f5 | 1.33E-01±7.28E-01+ | 6.76E+05±4.78E+05+ | 5.94E-02±1.14E-01 |
| f6 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 2.52E+03±8.58E+02+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f7 | 2.04E-01±6.32E-01+ | 4.23E-01±4.02E-01+ | 7.70E-02±2.65E-02 |
| f8 | 3.96E+00±2.16E+01+ | 4.15E+03±6.29E+02+ | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00 |
| f9 | 7.74E+01±3.01E+01+ | 9.08E+01±2.27E+01+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f10 | 3.55E-15±0.00E+00+ | 1.03E+01±1.73E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f11 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 1.99E+01±6.47E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f12 | 1.57E-32±5.57E-48- | 4.15E+03±1.22E+04+ | 1.69E-32±3.99E-33 |
| f13 | 8.84E-32±1.21E-31+ | 5.83E+05±6.29E+5+ | 2.28E-32±3.45E-32 |
| f14 | 2.13E-12±1.86E-12+ | 6.88E+00±1.56E+01+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f15 | 6.52E-11±8.60E-11+ | 5.98E-13±2.52E-13+ | 2.02E-13±6.78E-14 |
| f16 | 1.51E+06±6.17E+05+ | 3.44E+04±1.75E+04≈ | 1.94E-04±6.23E-04 |
| f17 | 3.96E+01±2.30E01+ | 9.85E-14±3.63E-14- | 6.01E-08±2.59E-07 |
| f18 | 1.38E+01±1.10E+01+ | 4.65E+08±2.73E+08+ | 1.65E-06±75.45E-06 |
| f19 | 1.94E+01±8.53E+00+ | 6.37E+02±5.38E+02+ | 1.34E+01±2.11E+01 |
| f20 | 4.63E-06±4.19E-06- | 3.72E+00±2.39E+00+ | 4.84E-03±5.83E-03 |
| f21 | 2.09E+01±4.58E-02≈ | 2.09E+01±4.41E-02≈ | 2.08E+01±1.89E-01 |
| f22 | 1.58E+02±1.79E+01+ | 7.36E+01±2.27E+01+ | 5.44E+00±2.51E+00 |
| f23 | 1.95E+02±1.31E+01+ | 1.11E+02±2.95E+01+ | 4.32E+01±1.12E+01 |
| f24 | 3.95E+01±1.07E+00+ | 1.64E+01±3.42E+00≈ | 1.96E+01±6.71E+00 |
| f25 | 1.11E+03±1.56E+03≈ | 5.77E+04±3.11E+04+ | 3.93E+03±5.44E+03 |
| f26 | 1.33E+01±4.20E+00+ | 6.54E+00±1.73E+00+ | 2.51E+00±2.29E-01 |
| f27 | 1.32E+01±1.41E-01+ | 1.19E+01±5.78E-01- | 1.29E+01±4.30E-01 |
| +/≈/- | 21/4/2 | 22/3/2 |
Table 3
Experimental results of GOBL-RNADE and basic DE(D=50)"
| 函数 | DE/rand/1 | DE/best/1 | GOBL-RNADE |
| f1 | 7.02E-44±7.68E-44+ | 1.25E+04±4.23E+03+ | 1.26E-252±0.00E+00 |
| f2 | 1.78E-27±1.35E-27+ | 7.39E+02±1.36E+02+ | 6.31E-131±3.31E-113 |
| f3 | 3.66E-11±5.20E-11+ | 1.61E+04±5.86E+03+ | 4.21E-375±0.00E+00 |
| f4 | 1.63E-02±3.76E-02+ | 4.01E+02±5.17E+00+ | 2.02E-108±6.13E-108 |
| f5 | 1.50E+00±1.10E+00- | 8.56E+06±4.34E+06+ | 3.92E+01±1.13E+00 |
| f6 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 1.20E+04±3.12E+03+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f7 | 2.11E-01±6.88E-02+ | 4.75E+00±2.32E+00+ | 8.03E-04±3.98E-04 |
| f8 | 7.90E+00±3.00E+02+ | 1.79E+02±9.04E+02+ | 8.18E-03±2.10E-02 |
| f9 | 7.24E+01±2.42E+01+ | 2.04E+02±2.39E+01+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f10 | 3.55E-15±0.00E+00+ | 1.39E+01±1.12E+00+ | 1.18E-16±6.48E-16 |
| f11 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 1.15E+02±3.21E+01+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f12 | 1.57E-32±5.56E-48- | 1.39E+06±1.36E+06+ | 1.02E-31±1.84E-31 |
| f13 | 1.34E-32±5.56E-48- | 7.30E+05±1.39E+06+ | 4.48E-32±1.85E-32 |
| f14 | 1.32E-14±2.44E-14+ | 2.57E+04±5.74E+03+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f15 | 1.67E+02±8.03E+01+ | 2.70E+04±8.56E+03+ | 1.01E-05±1.32E-05 |
| f16 | 1.42E+03±5.50E+02≈ | 4.23E+03±1.15E+04+ | 1.24E+03±8.87E+02 |
| f17 | 1.24E+03±2.84E+02- | 2.38E+04±2.56E+03+ | 2.23E+03±5.63E+02 |
| f18 | 7.51E+06±2.13E+06+ | 1.59E+08±7.47E+07+ | 2.163E+05±6.66E+04 |
| f19 | 7.95E+02±5.24E+01+ | 4.40E+09±2.03E+09+ | 7.55E+02±2.47E+01 |
| f20 | 5.11E+03±5.07E-11- | 1.22E+04±6.75E+02+ | 5.82E+03±8.61E-13 |
| f21 | 2.11E+01±2.69E-02≈ | 2.11E+01±4.25E-02≈ | 2.10E+01±2.56E-01 |
| f22 | 2.64E+02±3.87E+01+ | 4.01E+02±6.16E+01+ | 1.56E+01±5.74E+00 |
| f23 | 3.65E+02±1.56E+01+ | 4.96E+02±6.22E+01+ | 8.77E+01±2.14E+01 |
| f24 | 7.30E+01±1.87E+00+ | 4.63E+01±3.76E+00+ | 3.89E+01±1.29E+01 |
| f25 | 1.83E+04±1.32E+04+ | 1.41+06E±3.66E+05+ | 1.18E+04±1.40E+04 |
| f26 | 3.14E+01±1.40E+00+ | 2.54E+02±2.17E+02+ | 7.26E+00±4.29E-01 |
| f27 | 2.31E+01±1.62E-01+ | 2.17E+01±5.22E-01- | 2.25E+01±6.00E-01 |
| +/≈/- | 18/4/5 | 25/1/1 |
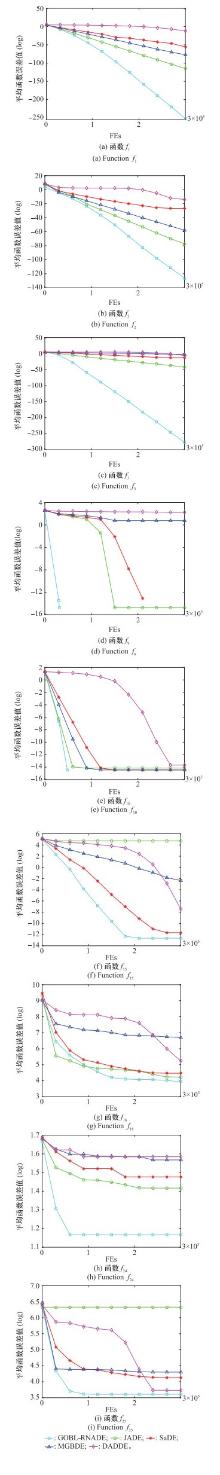
Table 4
Experimental results of GOBL-RNADE and classic DE(1)"
| 函数 | JADE | SaDE | GOBL-RNADE |
| f1 | 2.07E-157±9.50E-157+ | 3.25E-59±8.05E-59+ | 1.63E-240±0.00E+00 |
| f2 | 7.45E-78±2.05E-77+ | 3.65E-32±6.65E-32+ | 1.80E-126±6.91E-126 |
| f3 | 8.69E-44±3.38E-43+ | 1.56E-17±2.63E-17+ | 7.15E-276±0.00E+00 |
| f4 | 1.17E-27±4.43E-27+ | 5.33E-03±9.76E-03+ | 6.26E-115±2.50E-114 |
| f5 | 1.32E-01±7.27E-01+ | 3.98E-01±1.21E+00+ | 5.94E-02±1.14E-01 |
| f6 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f7 | 9.50E-02±2.57E-02+ | 1.75E-01±4.78E-02+ | 7.70E-02±2.65E-02 |
| f8 | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00≈ | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00≈ | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00 |
| f9 | 2.92E-17±3.24E-16+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f10 | 6.39E-15±1.44E-15+ | 3.55E-15±0.00E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f11 | 2.46E-04±1.35E-03+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f12 | 1.57E-32±5.56E-48- | 1.57E-32±5.56E-48- | 1.69E-32±3.99E-33 |
| f13 | 1.34E-32±5.56E-48- | 1.34E-32±5.56E-48- | 2.28E-32±3.45E-32 |
| f14 | 3.37E+02±0.00E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f15 | 5.51E+04±3.03E-11+ | 2.75E-12±1.22E-11+ | 2.02E-13±6.78E-14 |
| f16 | 1.39E+04±2.38E+03+ | 2.93E+04±1.40E+04+ | 1.94E-04±6.23E-04 |
| f17 | 5.49E-14±1.03E-14- | 3.30E-08±5.41E-08+ | 6.01E-08±2.59E-07 |
| f18 | 5.31E-01±1.37E+00+ | 3.65E+00±1.57E+01+ | 1.65E-06±75.45E-06 |
| f19 | 1.59E-06±7.23E-06- | 2.46E+02±2.27E+02+ | 1.34E+01±2.11E+01 |
| f20 | 8.20E-03±7.57E-03≈ | 1.28E-02±1.03E-02+ | 4.84E-03±5.83E-03 |
| f21 | 2.09E+01±4.48E-01+ | 2.08E+01±2.21E-01≈ | 2.08E+01±1.89E-01 |
| f22 | 1.51E-14±2.55E-14- | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00- | 5.44E+00±2.51E+00 |
| f23 | 2.44E+01±4.47E+00- | 6.62E+01±1.04E+01+ | 4.32E+01±1.12E+01 |
| f24 | 2.66E+01±1.70E+00+ | 2.83E+01±1.84E+00+ | 1.96E+01±6.71E+00 |
| f25 | 2.13E+06±1.00E-06+ | 1.02E+04±9.05E+03+ | 3.93E+03±5.44E+03 |
| f26 | 2.75E+00±1.72E-01≈ | 3.68E+00±2.98E-01+ | 2.51E+00±2.29E-01 |
| f27 | 1.23E+01±2.57E-01- | 1.28E+01±4.50E-01≈ | 1.29E+01±4.30E-01 |
| +/≈/- | 16/4/7 | 17/7/3 |
Table 5
Experimental results of GOBL-RNADE and classic DE(2)"
| 函数 | MGBDE | DADDE | GOBL-RNADE |
| f1 | 6.50E-108±1.06E-107+ | 3.37E-34±2.85E-33+ | 1.63E-240±0.00E+00 |
| f2 | 1.13E-58±1.27E-58+ | 1.63E-14±3.58E-14+ | 1.80E-126±6.91E-126 |
| f3 | 4.70E-03±4.40E-03+ | 2.87E-06±3.85E-06+ | 7.15E-276±0.00E+00 |
| f4 | 1.21E-09±5.02E-09+ | 2.79E-03±4.20E-03+ | 6.26E-115±2.50E-114 |
| f5 | 6.35E+00±1.32E+01+ | 7.37E+00±1.72E+01+ | 5.94E-02±1.14E-01 |
| f6 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f7 | 1.39E-01±3.55E-02+ | 3.98E-02±1.35E-02- | 7.70E-02±2.65E-02 |
| f8 | 8.00E+02±2.73E+02+ | 3.53E+03±2.61E+03+ | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00 |
| f9 | 1.40E+01±4.89E+00+ | 1.83E+02±1.32E+01+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f10 | 4.97E-15±1.77E-15+ | 1.77E-14±1.04E-14+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f11 | 5.00E-03±7.49E-03+ | 3.11E-03±7.36E-03+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f12 | 3.45E-03±1.89E-02+ | 1.287E-31±3.65E-31+ | 1.69E-32±3.99E-33 |
| f13 | 3.66E-04±2.00E-03+ | 5.21E-31±1.08E-30+ | 2.28E-32±3.45E-32 |
| f14 | 7.57E-15±1.96E-14≈ | 5.68E-14±0.00E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f15 | 3.50E-03±3.33E-03+ | 2.51E-07±2.48E-07+ | 2.02E-13±6.78E-14 |
| f16 | 5.02E+06±2.89E+06+ | 4.67E+05±2.81E+05+ | 1.94E-04±6.23E-04 |
| f17 | 1.26E-02±1.41E-02+ | 6.62E-03±1.06E-02+ | 6.01E-08±2.59E-07 |
| f18 | 7.73E+00±1.31E+01+ | 2.81E+00±3.51E+00+ | 1.65E-06±75.45E-06 |
| f19 | 1.32E+03±4.83E+02+ | 5.10E+00±1.04E+01- | 1.34E+01±2.11E+01 |
| f20 | 1.36E-02±1.30E-02+ | 2.05E-03±4.34E-03≈ | 4.84E-03±5.83E-03 |
| f21 | 2.09E+01±6.08E-02≈ | 2.09E+01±4.93E-02≈ | 2.08E+01±1.89E-01 |
| f22 | 1.48E+01±4.59E+00+ | 1.64E+02±1.26E+01+ | 5.44E+00±2.51E+00 |
| f23 | 1.43E+02±3.02E+01+ | 1.88E+02±1.09E+01+ | 4.32E+01±1.12E+01 |
| f24 | 3.96E+01±1.03E+00+ | 3.98E+01±9.38E-01+ | 1.96E+01±6.71E+00 |
| f25 | 1.84E+04±1.77E+04+ | 4.63E+03±3.59E+03≈ | 3.93E+03±5.44E+03 |
| f26 | 3.49E+00±2.47E+00≈ | 1.46E+01±2.32+00+ | 2.51E+00±2.29E-01 |
| f27 | 1.30E+01±2.60E-01≈ | 1.34E+01±1.86E-01+ | 1.29E+01±4.30E-01 |
| +/≈/- | 22/5/0 | 21/4/2 |
Table 6
Computation time of GOBL-RNADE and classic DE s"
| 函数 | JADE | SaDE | MGBDE | DADDE | GOBL- RNADE |
| f1 | 16.110 | 12.139 | 14.653 | 14.845 | 12.272 |
| f2 | 17.264 | 16.996 | 15.301 | 15.502 | 12.289 |
| f3 | 35.027 | 25.050 | 32.150 | 32.215 4 | 19.820 |
| f4 | 16.420 | 12.303 | 14.546 | 14.860 | 11.863 |
| f5 | 15.726 | 11.974 | 13.932 | 14.579 | 9.900 |
| f6 | 17.072 | 11.609 | 14.751 | 14.772 | 12.011 |
| f7 | 19.727 | 14.757 | 17.778 | 18.233 | 11.884 |
| f8 | 16.995 | 12.487 | 14.948 | 15.718 | 11.862 |
| f9 | 15.977 | 11.654 | 14.433 | 15.096 | 11.760 |
| f10 | 17.470 | 12.469 | 15.489 | 16.581 | 12.319 |
| f11 | 18.029 | 12.654 | 15.766 | 16.255 | 12.373 |
| f12 | 27.861 | 18.960 | 24.576 | 25.373 | 16.191 |
| f13 | 26.876 | 18.795 | 23.457 | 25.417 | 16.072 |
| f14 | 17.066 | 12.091 | 14.865 | 15.042 | 12.167 |
| f15 | 36.605 | 25.331 | 32.433 | 33.782 1 | 19.318 |
| f16 | 59.786 | 41.143 | 54.648 | 54.168 | 27.260 |
| f17 | 21.487 | 15.019 | 19.225 | 19.366 | 11.876 |
| f18 | 18.257 | 13.276 | 16.062 | 16.305 | 10.961 |
| f19 | 22.556 | 15.946 | 20.254 | 20.810 | 12.453 |
| f20 | 20.168 | 15.989 | 17.927 | 18.061 | 13.188 |
| f21 | 20.100 | 13.867 | 17.561 | 17.941 | 12.140 |
| f22 | 17.667 | 12.317 | 15.425 | 16.123 | 11.973 |
| f23 | 19.018 | 13.146 | 16.989 | 17.278 | 12.476 |
| f24 | 89.003 | 59.625 | 82.256 | 95.864 | 40.301 |
| f25 | 42.137 | 27.963 | 40.943 | 44.783 | 20.498 |
| f26 | 17.792 | 12.222 | 15.441 | 17.049 | 10.624 |
| f27 | 19.606 | 13.331 | 17.250 | 17.659 | 11.349 |
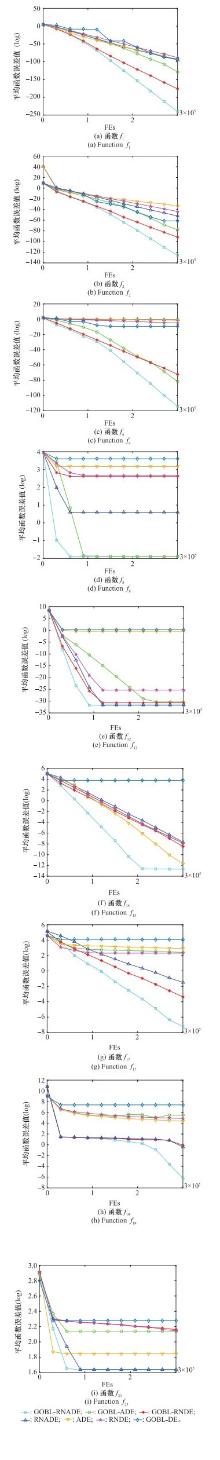
Table 8
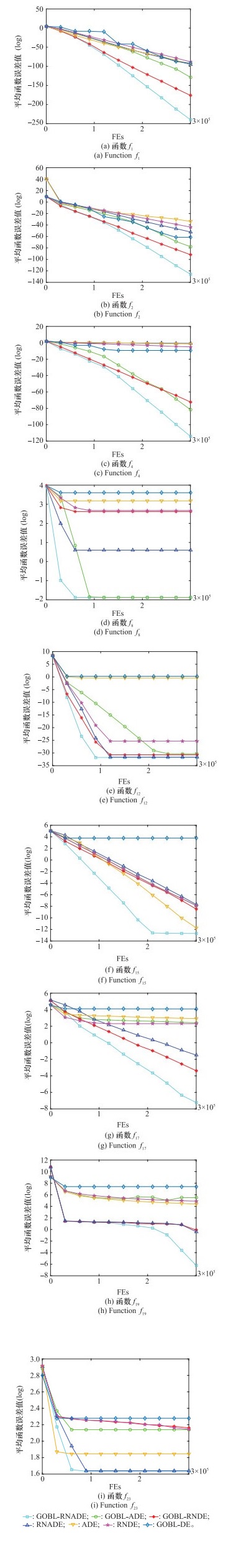
Experimental results of GOBL-RNADE and different strategies"
| 函数 | 策略 | |||
| ADE | RNDE | GOBL-DE | GOBL-RNADE | |
| f1 | 2.72E-94±1.23E-93+ | 5.25E-89±1.01E-88+ | 4.21E-71±2.30E-70+ | 1.63E-240±0.00E+00 |
| f2 | 1.94E-34±7.02E-34+ | 2.37E-44±1.83E-44+ | 3.46E-62±1.90E-61+ | 1.80E-126±6.91E-126 |
| f3 | 1.45E-21±2.76E-21+ | 9.21E-17±4.26E-16+ | 4.19E-26±2.29E-25+ | 7.15E-276±0.00E+00 |
| f4 | 3.97E-02±5.73E-02+ | 9.50E-06±1.19E-05+ | 3.83E-10±2.09E-09+ | 6.26E-115±2.50E-114 |
| f5 | 9.30E-01±1.71E+00+ | 8.09E+00±5.34E+00+ | 4.74E+05±5.39E+05+ | 5.94E-02±1.14E-01 |
| f6 | 2.90E+00±5.02E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 1.206E+03±9.55E+02+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f7 | 1.79E-01±6.99E-02+ | 1.51E-01±4.08E-02+ | 2.03E-04±1.08E-04- | 7.70E-02±2.65E-02 |
| f8 | 1.49E+03±5.13E+02+ | 4.69E+02±2.57E+02+ | 4.00E+03±6.00E+02+ | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00 |
| f9 | 3.95E+01±9.01E+00+ | 2.42E+01±2.12E+01+ | 5.13E-14±1.47E-13+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f10 | 9.06E-01±7.59E-01+ | 4.26E-15±1.44E-15+ | 1.21E-09±5.25E-09+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f11 | 1.23E-02±1.80E-02+ | 2.38E-03±4.11E-03+ | 1.02E-13±4.88E-13+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f12 | 3.67E-01±8.00E-01+ | 4.74E-26±2.59E-25+ | 1.84E+00±6.43E+00+ | 1.69E-32±3.99E-33 |
| f13 | 3.87E-01±1.50E+00+ | 3.66E-04±2.00E-03+ | 1.98E+00±4.16E+00+ | 2.28E-32±3.45E-32 |
| f14 | 5.49E-14±1.03E-14+ | 5.68E-15±1.73E-14≈ | 5.54E+03±2.32E+03+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f15 | 1.86E-12±2.53E-12+ | 1.06E-09±1.37E-09+ | 6.16E+03±2.72E+03+ | 2.02E-13±6.78E-14 |
| f16 | 9.87E+00±4.56E+01+ | 1.27E-12±5.99E-12- | 3.40E+02±6.21E+02+ | 1.94E-04±6.23E-04 |
| f17 | 8.60E+02±5.05E+02+ | 1.40E+02±4.54E-04+ | 1.23E+04±2.86E+03+ | 6.01E-08±2.59E-07 |
| f18 | 2.39E+04±1.30E+04+ | 7.80E+04±4.28E+04+ | 2.52E+07±1.54E+07+ | 1.65E-06±75.45E-06 |
| f19 | 7.01E+02±1.79E+00+ | 7.03E+02±4.41E+00+ | 4.47E+08±2.61E+08+ | 1.34E+01±2.11E+01 |
| f20 | 2.76E-02±2.01E-02+ | 1.07E-02±1.12E-02≈ | 6.71E+03±2.79E+02+ | 4.84E-03±5.83E-03 |
| f21 | 2.06E+01±3.33E-01- | 2.09E+01±4.48E-03≈ | 2.10E+01±7.91E-02+ | 2.08E+01±1.89E-01 |
| f22 | 4.05E+01±1.01E+01+ | 1.55E+01±3.58E+00+ | 1.30E+02±2.97E+01+ | 5.44E+00±2.51E+00 |
| f23 | 6.99E+01±2.01E+01+ | 1.39E+02±5.44E+01+ | 1.90E+02±4.67E+01+ | 4.32E+01±1.12E+01 |
| f24 | 2.60E+01±5.11E+00+ | 2.03E+01±1.60E+01≈ | 2.21E+01±3.28E+00+ | 1.96E+01±6.71E+00 |
| f25 | 2.01E+04±2.11E+04+ | 5.92E+03±8.45E+03≈ | 2.66E+05± 8.30E+04+ | 3.93E+03±5.44E+03 |
| f26 | 3.02E+00±7.57E-01+ | 1.06E+01±4.65E+00+ | 1.09E+01±3.49E+00+ | 2.51E+00±2.29E-01 |
| f27 | 1.27E+01±4.26E-01≈ | 1.30E+01±1.94E-01≈ | 1.23E+01±5.70E-01- | 1.29E+01±4.30E-01 |
| +/≈/- | 25/1/1 | 19/7/1 | 25/0/2 | |
Table 9
Experimental results of GOBL-RNADE and different strategies"
| 函数 | 策略 | |||
| GOBL-ADE | GOBL-RNDE | RNADE | GOBL-RNADE | |
| f1 | 5.75E-130±2.78E-129+ | 2.07E-178±0.00E+00+ | 7.06E-95±3.13E-94+ | 1.63E-240±0.00E+00 |
| f2 | 1.62E-78±8.88E-78+ | 1.58E-92±7.42E-92+ | 6.75E-53±1.59E-52+ | 1.80E-126±6.91E-126 |
| f3 | 8.88E-255±0.00E+00≈ | 4.30E-138±2.29E-137+ | 8.96E-16±1.86E-15+ | 7.15E-276±0.00E+00 |
| f4 | 2.08E-82±1.14E-81+ | 5.48E-73±1.31E-72+ | 2.24E-01±2.30E-01+ | 6.26E-115±2.50E-114 |
| f5 | 1.31E+01±1.70E+00+ | 8.81E+00±7.71E+00+ | 7.01E-01±1.24E+00≈ | 5.94E-02±1.14E-01 |
| f6 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f7 | 1.15E-03±4.68E-04- | 8.31E-02±3.80E-02≈ | 1.39E-01±4.04E-2+ | 7.70E-02±2.65E-02 |
| f8 | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00≈ | 4.17E+02±1.87E+02+ | 3.96E+00±2.16+01+ | 1.34E-02±0.00E+00 |
| f9 | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00≈ | 6.40E+00±2.77E+00+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f10 | 2.36E-16±9.01E-16≈ | 1.18E-16±6.48E-16≈ | 5.44E-15±1.80E-15+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f11 | 1.51E-16±4.22E-16+ | 9.25E-17±4.86E-16≈ | 1.31E-03±3.46E-03+ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f12 | 4.76E-31±9.80E-31+ | 1.98E-31±2.35E-31+ | 3.22E-32±2。70E-32+ | 1.69E-32±3.99E-33 |
| f13 | 1.35E-32±2.25E-34+ | 1.09E-03±3.35E-03+ | 2.45E-32±3.42E-32+ | 2.28E-32±3.45E-32 |
| f14 | 1.89E-15±1.03E-14≈ | 3.78E-15±1.96E-14≈ | 1.89E-15±1.03E-14≈ | 0.00E+00±0.00E+00 |
| f15 | 1.34E-08±1.43E-08+ | 3.35E-09±1.05E-08+ | 2.13E-08±3.86E-08+ | 2.02E-13±6.78E-14 |
| f16 | 5.51E-01±9.43E-01≈ | 8.33E+04±4.59E+04+ | 3.38E+04±1.76E+04+ | 1.94E-04±6.23E-04 |
| f17 | 2.56E+02±1.06E+02+ | 4.18E-04±8.57E-04+ | 3.23E-02±4.62E-02+ | 6.01E-08±2.59E-07 |
| f18 | 1.68E+05±1.21E+05+ | 3.18E+00±4.61E+00+ | 1.46E-01±7.29E-01+ | 1.65E-06±75.45E-06 |
| f19 | 7.09E+02±3.30E+00+ | 2.25E-05±5.90E-05- | 2.31E+02±2.11E+02+ | 1.34E+01±2.11E+01 |
| f20 | 4.17E+03±6.31E-13+ | 7.05E-03±8.61E-03≈ | 3.53E-03±5.84E-3≈ | 4.84E-03±5.83E-03 |
| f21 | 2.09E+01±1.51E-01≈ | 2.10E+01±6.35E-02+ | 2.09E+01±1.79E-01≈ | 2.08E+01±1.89E-01 |
| f22 | 1.24E+01±1.57E+01+ | 1.73E+01±4.70E+00+ | 5.17E+00±3.06E+00≈ | 5.44E+00±2.51E+00 |
| f23 | 1.38E+02±5.52E+01+ | 1.44E+02±4.91E+01+ | 4.36E+01±1.15E+01≈ | 4.32E+01±1.12E+01 |
| f24 | 1.99E+01±7.10E+00≈ | 2.11E+01±1.02E+01≈ | 2.51E+01±6.11E+00+ | 1.96E+01±6.71E+00 |
| f25 | 1.83E+04±1.62E+04+ | 6.40E+03±5.31E+03+ | 6.16E+03±6.94E+03≈ | 3.93E+03±5.44E+03 |
| f26 | 2.76E+00±1.99E-01+ | 7.53E+00±5.00E+00+ | 4.79E+00±6.74E-01+ | 2.51E+00±2.29E-01 |
| f27 | 1.32E+01±5.09E-01+ | 1.31E+01±3.18E-01≈ | 1.33E+01±3.75E-01+ | 1.29E+01±4.30E-01 |
| +/≈/- | 17/9/1 | 17/9/1 | 19/8/0 | |
| 1 |
STORN R , PRICE K . Differential evolution-a simple and efficient heuristic for global optimization over continuous spaces[J]. Journal of Global Optimization, 1997, 11 (4): 341- 359.
doi: 10.1023/A:1008202821328 |
| 2 |
ZHENG L M , ZHANG S X , ZHENG S Y , et al. Differential evolution algorithm with two-step subpopulation strategy and its application in microwave circuit designs[J]. IEEE Trans.on Industrial Information, 2016, 12 (3): 911- 923.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2016.2535347 |
| 3 |
ZHAN C J , SITU W C , YEUNG L F , et al. A parameter estimation method for biological systems modelled by ODE/DDE models using spline approximation and differential evolution algorithm[J]. IEEE/ACM Trans.on Computational Biology and Bioinformatics, 2014, 11 (6): 1066- 1076.
doi: 10.1109/TCBB.2014.2322360 |
| 4 |
ZHAO J H , XU Y , LUO F J , et al. Power system fault diagnosis based on history driven differential evolution and stochastic time domain simulation[J]. Information Sciences, 2014, 275, 13- 29.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2014.02.039 |
| 5 |
PAUL S , DAS S . Simultaneous feature selection and weighting-an evolutionary multi-objective optimization approach[J]. Pattern Recognition Letters, 2015, 65, 51- 59.
doi: 10.1016/j.patrec.2015.07.007 |
| 6 | GUO Z L , LIU G , LI D H , et al. Self-adaptive differential evolution with global neighborhood search[J]. Soft Computing, 2016, 21 (13): 3759- 3768. |
| 7 |
DAS S , MULLICK S S , SUGANTHAN P N . Recent advances in differential evolution-an updated survey[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2016, 27, 1- 30.
doi: 10.1016/j.swevo.2016.01.004 |
| 8 |
TIAN M N , GAO X B . Differential evolution with neighborhood-based adaptive evolution mechanism for numerical optimization[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 478, 422- 448.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2018.11.021 |
| 9 |
DAS S , ABRAHAM A , CHAKRABORTY U K , et al. Differential evolution using a neighborhood-based mutation operator[J]. IEEE Trans.on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13 (3): 526- 553.
doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2008.2009457 |
| 10 |
CAI Y Q , WANG J H , CHEN Y H , et al. Adaptive direction information in differential evolution for numerical optimization[J]. Soft Computing, 2016, 20 (2): 465- 494.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-014-1517-0 |
| 11 | CAI Y Q , ZHAO M , LIAO J L , et al. Neighborhood guided diff-erential evolution[J]. Soft Computing, 2016, 21 (16): 4769- 4812. |
| 12 |
LIAO J L , CAI Y Q , WANG T , et al. Cellular direction information based differential evolution for numerical optimization: an empirical study[J]. Soft Computing, 2016, 20 (7): 2801- 2827.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-015-1682-9 |
| 13 | PHAM H A, VU T C, NGUYEN B D, et al. Engineering optimization using an improved epsilon differential evolution with directional mutation and nearest neighbor comparison[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Advances in Computational Mechanics, 2018: 201-216. |
| 14 | AI-DABBAGH R D , NERI F , IDRIS N , et al. Algorithmic design issues in adaptive differential evolution schemes: review and taxonomy[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2018, 43, 248- 311. |
| 15 |
DRAA A , BOUZOUBIA S , BOUKHALFA I . A sinusoidal differential evolution algorithm for numerical optimization[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 27, 99- 126.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2014.11.003 |
| 16 | VENKATAKRISHNAN G R, MAHADEVAN J, RENGARAJ R. Differential evolution with parameter adaptation strategy to economic dispatch incorporating wind[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Intelligent and Efficient Electrical Systems, 2017: 153-165. |
| 17 | ZHANG Q K, ZHANG H X, YANG B, et al. Gaussian cauchy differential evolution for global optimization[C]//Proc. of the International CCF Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018: 166-182. |
| 18 | STANOVOV V , AKHMEDOVA S , SEMENKIN E . Selective pressure strategy in differential evolution: exploitation improvement in solving global optimization problems[J]. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, 2018, 50, 100463. |
| 19 |
LU Z Q , ZHANG L L , WANG D Z . Differential evolution with improved elite archive mutation and dynamic parameter adjustment[J]. Cluster Computing, 2019, 22 (4): 9347- 9356.
doi: 10.1007/s10586-018-2163-6 |
| 20 |
ZHANG X , ZHANG X . Improving differential evolution by differential vector archive and hybrid repair method for global optimization[J]. Soft Computing, 2016, 21 (23): 7107- 7116.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-016-2253-4 |
| 21 |
WANG H , WU Z J , RAHNAMAYAN S , et al. Enhancing particle swarm optimization using generalized opposition-based learning[J]. Information Sciences, 2011, 181, 4699- 4714.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2011.03.016 |
| 22 |
RAHNAMAYAN S , TIZHOOSH H R , SALAMA M M A . Opposition versus randomness in soft computing techniques[J]. Soft Computing, 2008, 8 (2): 906- 918.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2007.07.010 |
| 23 | WANG J . Enhanced differential evolution with generalised opposition-based learning and orientation neighbourhood mining[J]. International Journal of Computing Science and Mathematics, 2015, 6 (1): 149- 162. |
| 24 | 贺毅朝, 王熙照, 刘坤起, 等. 差分演化的收敛性分析与算法改进[J]. 软件学报, 2010, 21 (5): 875- 885. |
| HE Y C , WANG X Z , LIU K Q , et al. Convergent analysis and algorithmic improvement of differential evolution[J]. Journal of Software, 2010, 21 (5): 875- 885. | |
| 25 |
WEI W H , ZHOU J L , CHEN F , et al. Constrained differential evolution using generalized opposition-based learning[J]. Soft Computing, 2016, 20 (11): 4413- 4437.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-015-2001-1 |
| 26 |
YAO X , LIU Y , LIN G M . Evolutionary programming made faster[J]. IEEE Trans.on Evolutionary Computation, 1999, 3 (2): 82- 102.
doi: 10.1109/4235.771163 |
| 27 | SUGANTHAN P N, HANSEN N, LIANG J J, et al. Problem definitions and evaluation criteria for the CEC special session on real-parameter optimization[R]. Singapore: Nanyang Technological University, 2005. |
| 28 |
CAI Y Q , WANG J H , JIAN Y . Learning-enhanced differential evolution for numerical optimization[J]. Soft Computing, 2012, 16 (2): 303- 330.
doi: 10.1007/s00500-011-0744-x |
| 29 |
ZHANG J , SANDERSON A C . JADE: adaptive differential evolution with optional external archive[J]. IEEE Trans.on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13 (5): 945- 958.
doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2009.2014613 |
| 30 |
QIN A K , HUANG V L , SUGANTHAN P N . Differential evolution algorithm with strategy adaptation for global numerical optimization[J]. IEEE Trans.on Evolutionary Computation, 2009, 13 (2): 398- 417.
doi: 10.1109/TEVC.2008.927706 |
| 31 |
WANG H , RAHNAMAYAN S , SUN H , et al. Gaussian bare-bones differential evolution[J]. IEEE Trans.on Cybernet, 2013, 43 (2): 634- 647.
doi: 10.1109/TSMCB.2012.2213808 |
| 32 | LIU J, YIN X M, GU X S. Differential evolution improved with adaptive control parameters and double mutation strategies[C]//Proc. of the Asian Simulation Conference, 2016: 186-198. |
| [1] | Mulai TAN, Dali DING, Lei XIE, Wei DING, Chenghui LYU. UCAV escape maneuvering decision based on fuzzy expert system and IDE algorithm [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1984-1993. |
| [2] | Yunxiang CHEN, Yi RAO, Zhongyi CAI, Zezhou WANG. Remaining useful lifetime prediction and economic reserve strategy of equipment components based on improved similarity [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(9): 2688-2696. |
| [3] | Wenhai WU, Xiaofeng GUO, Siyu ZHOU, Li GAO. Improved differential evolution algorithm for solving weapon-targetassignment problem [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(4): 1012-1021. |
| [4] | Jun LUO, Jianqiang LIU, Yanan PANG. Multi-threshold image segmentation of 2D Otsu based on neighborhood search JADE [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(10): 2164-2171. |
| [5] | LI Shihao, DING Yong, GAO Zhenlong. UAV air combat maneuvering decision based on intuitionistic fuzzy game theory [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(5): 1063-1070. |
| [6] | LIU Han, YIN Cheng-you, LIU Wei. Optimization and design of wideband antenna with adaptive differential evolution algorithm based on hybrid coding method [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(4): 773-777. |
| [7] | HAN Wei, SU Xi-chao, CHEN Jun-feng. Integrated maintenance support scheduling method of multi carrier aircrafts [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(4): 809-816. |
| [8] | ZHANG Rui, GAO Hui, ZHANG Tao. Hybird optimization algorithm based on quantum and differential evolution for continuous space optimization [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(6): 1288-1292. |
| [9] | LIN Lian-lei, YAN Fang, YANG Jing-li. Use of nested differential evolution algorithm to select microburst model’s parameters [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(11): 2379-2383. |
| [10] | BAO Zi-yang, CHEN Ke-song, HE Zi-shu, HAN Chun-lin. Sparse circular arrays method based on modified DE algorithm [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(3): 497-499. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||