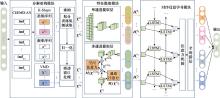
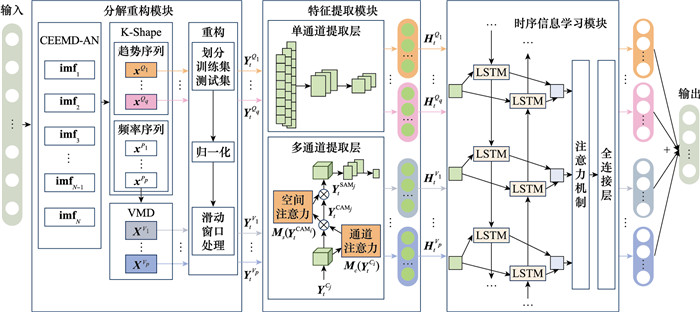
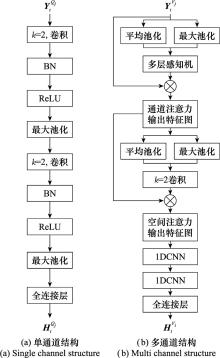
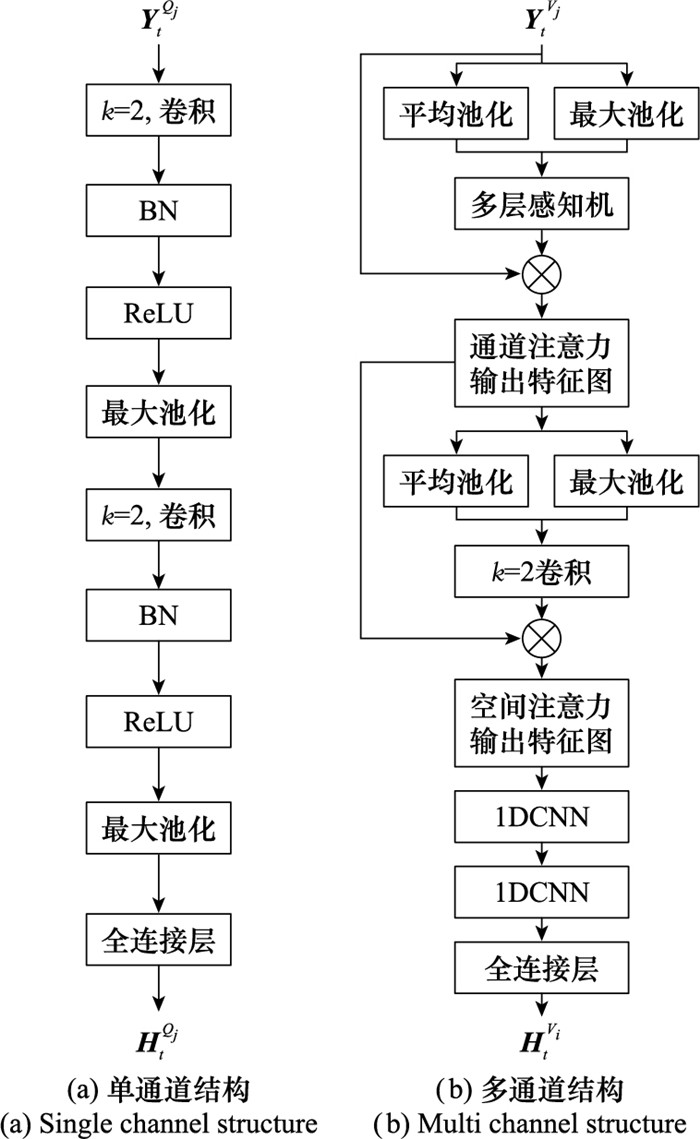
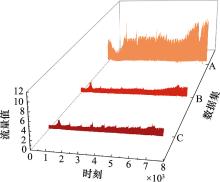
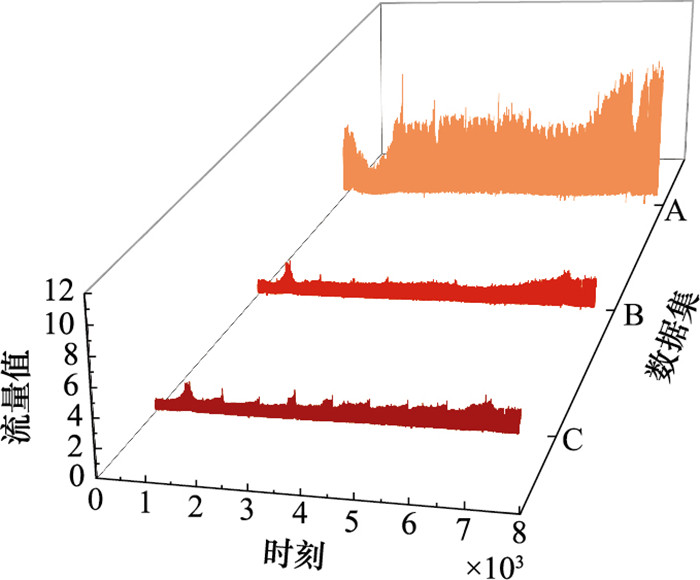
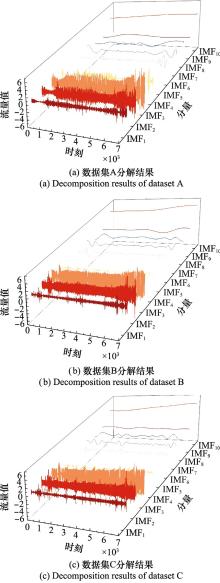
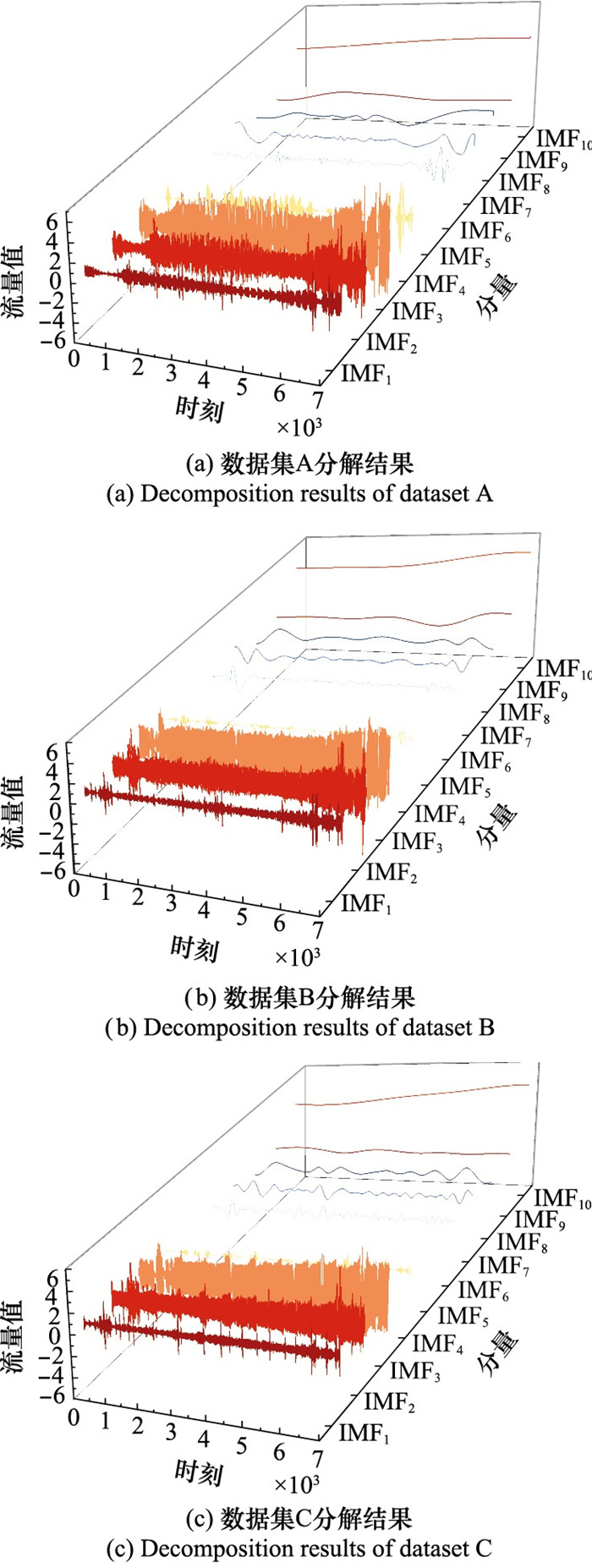
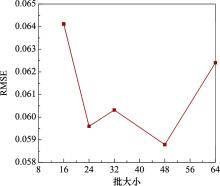
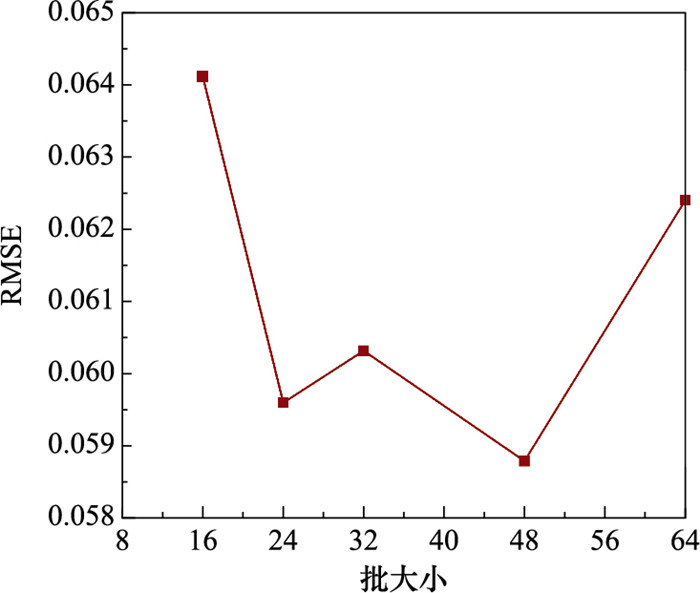
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1687-1697.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.05.31
• Communications and Networks • Previous Articles
Quadratic decomposition-based cellular traffic prediction with hybrid neural network
Amin DUAN, Zhaohui ZHANG
- School of Mathematics and Statistics, Xidian University, Xi'an 710126, China
-
Received:2024-04-12Online:2025-06-11Published:2025-06-18 -
Contact:Zhaohui ZHANG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Amin DUAN, Zhaohui ZHANG. Quadratic decomposition-based cellular traffic prediction with hybrid neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(5): 1687-1697.
share this article
Table 5
Quantitative analysis results"
| 算法 | A | B | C | ||||||||
| RMSE | MAPE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | R2 | RMSE | MAPE | R2 | |||
| ARIMA | 0.271 48 | 0.272 13 | 0.862 46 | 0.162 15 | 0.132 82 | 0.914 56 | 0.167 62 | 0.160 28 | 0.919 65 | ||
| SVR | 0.123 14 | 0.250 48 | 0.901 67 | 0.113 58 | 0.114 15 | 0.920 41 | 0.104 35 | 0.142 77 | 0.923 68 | ||
| LSTM | 0.102 21 | 0.207 09 | 0.920 41 | 0.088 42 | 0.105 24 | 0.952 65 | 0.070 20 | 0.121 34 | 0.959 87 | ||
| RCNN-ABiLSTM | 0.092 43 | 0.162 14 | 0.937 04 | 0.075 40 | 0.101 78 | 0.965 28 | 0.063 12 | 0.132 87 | 0.965 18 | ||
| ST-LSTM | 0.081 35 | 0.081 18 | 0.962 19 | 0.065 86 | 0.030 10 | 0.975 38 | 0.053 93 | 0.031 24 | 0.980 18 | ||
| CEEMDAN-TGA | 0.080 47 | 0.076 74 | 0.970 62 | 0.059 57 | 0.026 64 | 0.981 04 | 0.054 52 | 0.025 18 | 0.977 53 | ||
| 所提方法 | 0.075 72 | 0.059 12 | 0.978 47 | 0.050 14 | 0.020 96 | 0.987 60 | 0.050 51 | 0.017 88 | 0.982 60 | ||
Table 5
| 1 | Ericsson. Ericsson mobility report June 2024[R]. Stockholm: Ericsson, 2024. |
| 2 | Huawei. Communications networks 2030[R]. China: Huawei, 2024. |
| 3 | JIANG W W . Cellular traffic prediction with machine learning: a survey[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2022, 201, 117163. |
| 4 | YULE G U . Ⅶ. On a method of investigating periodicities disturbed series, with special reference to Wolfer's sunspot numbers[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A, 1927, 226 (636/646): 267- 298. |
| 5 |
TIAN M , SUN C , WU S Z . An EMD and ARMA-based network traffic prediction approach in SDN-based internet of vehicles[J]. Wireless Networks, 2021,
doi: 10.1007/s11276-021-02675-2 |
| 6 | XU F L , LIN Y Y , HUANG J X , et al. Big data driven mobile traffic understanding and forecasting: a time series approach[J]. IEEE Trans.on Services Computing, 2016, 9 (5): 796- 805. |
| 7 | WANG J. A process level network traffic prediction algorithm based on ARIMA model in smart substation[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, Communication and Computing, 2013. |
| 8 | MEHDIZADEH S , FATHIAN F , ADAMOWSKI J F . Hybrid artificial intelligence-time series models for monthly streamflow modeling[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2019, 80, 873- 887. |
| 9 |
韩驰, 熊伟. 基于改进灰狼算法优化SVR的航天侦察装备效能评估[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2021, 43 (10): 2902- 2910.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.10.25 |
|
HAN C , XIONG W . Operational effectiveness evaluation of space reconnaissance equipment based on SVR optimized by improved grey wolf optimizer[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43 (10): 2902- 2910.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2021.10.25 |
|
| 10 | 陈静, 张昭冲, 王琳凯, 等. 基于卷积长短时记忆网络的短时公交客流量预测[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36 (2): 476- 486. |
| CHEN J , ZHANG Z C , WANG L K , et al. Short-term bus passenger flow prediction based on convolutional long-short-term memory network[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36 (2): 476- 486. | |
| 11 | NIE L S, JIANG D D, YU S, et al. Network traffic prediction based on deep belief network in wireless mesh backbone networks[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference, 2017. |
| 12 | ZHANG C T , ZHANG H X , YUAN D F , et al. Citywide cellular traffic prediction based on densely connected convolutional neural networks[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2018, 22 (8): 1656- 1659. |
| 13 | ZHANG C Y, PATRAS P. Long-term mobile traffic forecasting using deep spatio-temporal neural networks[C]//Proc. of the 18th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, 2018: 231-240. |
| 14 | XU Y , YIN F , XU W J , et al. Wireless traffic prediction with scalable Gaussian process: framework, algorithms, and verification[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2019, 37 (6): 1291- 1306. |
| 15 |
闫啸家, 梁伟阁, 张钢, 等. 基于RCNN-ABiLSTM的机械设备剩余寿命预测方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45 (3): 931- 940.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.03.35 |
|
YAN X J , LIANG W G , ZHANG G , et al. Prediction method for mechanical equipment based on RCNN-ABiLSTM[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45 (3): 931- 940.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.03.35 |
|
| 16 | AGARAP A F M. A neural network architecture combining gated recurrent unit (GRU) and support vector machine (SVM) for intrusion detection in network traffic data[C]//Proc. of the 10th International Conference on Machine Learning and Computing, 2018: 26-30. |
| 17 | HUANG C W, CHIANG C T, LI Q H. A study of deep learning networks on mobile traffic forecasting[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 28th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, 2017. |
| 18 | BI J , ZHANG X , YUAN H T , et al. A hybrid prediction method for realistic network traffic with temporal convolutional network and LSTM[J]. IEEE Trans.on Automation Science and Engineering, 2021, 19 (3): 1869- 1879. |
| 19 | WANG D , BAO Y Y , WANG C M . A hybrid deep learning method based on CEEMDAN and attention mechanism for network traffic prediction[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 39651- 39663. |
| 20 |
时维国, 国明. 基于MEEMD-PE与CS-WNN模型的网络时延预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2020, 42 (1): 184- 190.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.01.25 |
|
SHI W G , GUO M . Network delay prediction based on model of modified ensemble empirical mode decomposition-permutation entropy and cuckoo search-wavelet neural network[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42 (1): 184- 190.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-506X.2020.01.25 |
|
| 21 |
薛锡瑞, 黄树彩, 韦道知, 等. 基于EMD-DESN的无人机集群航迹目的地预测[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 46 (1): 290- 299.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.01.33 |
|
XUE X R , HUANG S C , WEI D Z , et al. Destination prediction of UAV cluster trajectory based on EMD-DESN[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 46 (1): 290- 299.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.01.33 |
|
| 22 | CHANG T J , LEE T S , YANG C T , et al. A ternary-frequency cryptocurrency price prediction scheme by ensemble of clustering and reconstructing intrinsic mode functions based on CEEMDAN[J]. Expert Systems with Applications, 2023, 233, 121008. |
| 23 | WANG J Y , DAI B L , ZHANG T H , et al. A novel hybrid model of CEEMDAN-CNN-SAGU for Shanghai copper price prediction[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 25176- 25187. |
| 24 | ZHOU F T , HUANG Z H , ZHANG C H . Carbon price forecasting based on CEEMDAN and LSTM[J]. Applied Energy, 2022, 311, 118601. |
| 25 |
吴宗收, 汪立新, 沈强, 等. 基于CEEMD半球谐振陀螺输出预测方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45 (10): 3259- 3264.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.10.30 |
|
WU Z S , WANG L X , SHEN Q , et al. Output prediction method of hemispherical resonator gyro based on CEEMD[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45 (10): 3259- 3264.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.10.30 |
|
| 26 | CHEN L Y , LIU X , ZENG C , et al. Temperature prediction of seasonal frozen subgrades based on CEEMDAN-LSTM hybrid model[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22 (15): 5742. |
| 27 | 韩莹, 王乐豪, 王淑梅, 等. 宽度-深度融合时频分析的径流智能预测方法[J]. 系统仿真学报, 2024, 36 (2): 363- 372. |
| HAN Y , WANG L H , WANG S M , et al. Runoff intelligent prediction method based on broad-deep fusion time-frequency analysis[J]. Journal of System Simulation, 2024, 36 (2): 363- 372. | |
| 28 | WOO S H, PARK J C, LEE J Y, et al. Cbam: convolutional block attention module[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 3-19. |
| 29 | PAPARRIZOS J, GRAVANO L. K-shape: efficient and accur ate clustering of time series[C]//Proc. of the ACM SIGMOD International Conference on Management of Data, 2015: 1855-1870. |
| 30 | DRAGOMIRETSKIY K , ZOSSO D . Variational mode decomposition[J]. IEEE Trans.on Signal Processing, 2013, 62 (3): 531- 544. |
| 31 | GUO D , XIA X W , ZHU L , et al. Dynamic modification neural network model for short-term traffic prediction[J]. Procedia Computer Science, 2021, 187, 134- 139. |
| [1] | Lei YU, Qiuyue DENG, Liying ZHENG, Haoyu WU. Second-order progressive feature fusion network for image super-resolution reconstruction [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(2): 391-400. |
| [2] | Ran JI, Maosen XIAO, Shuo LI, Yu LIU, Zhanyi LUO, Jiawei CHENG. Research on MRTD objective testing method based on machine learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(10): 3265-3270. |
| [3] | Lei WANG, Zhiyong ZHANG, Huiqi XU, Weigui ZENG, Silei CAO. Radar emitter identification based on VMD and multi-domain joint distribution [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(8): 2479-2488. |
| [4] | Yanyan HUANG, Shaoyan GAI, Feipeng DA. Image matching algorithm based on attention mechanism of three branch spatial transformation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(11): 3363-3373. |
| [5] | Caiyun WANG, Yida WU, Jianing WANG, Lu MA, Huanyue ZHAO. SAR image target recognition based on combinatorial optimization convolutional neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2483-2487. |
| [6] | Jianyong ZHENG, Guanghui WEI. Time-frequency-energy analysis of electromagnetic signals based on multi-resolution dynamic modal decomposition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1468-1474. |
| [7] | Dong CHEN, Yanwei JU. Ship object detection SAR images based on semantic segmentation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1195-1201. |
| [8] | Jingming SUN, Shengkang YU, Jun SUN. Pose sensitivity analysis of HRRP recognition based on deep learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 802-807. |
| [9] | Hengyan LIU, Limin ZHANG, Wenjun YAN, Zhaogen ZHONG, Qing LING, Xiaojun LIANG. LDPC decoding based on WBP-CNN algorithm [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 1030-1035. |
| [10] | Kai SHAO, Miaomiao ZHU, Guangyu WANG. Modulation recognition method based on generative adversarial andconvolutional neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 1036-1043. |
| [11] | Xi ZHANG, Zhengmeng JIN, Yaqin JIANG. Total variation algorithm with depth image priors for image colorization [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 385-393. |
| [12] | Qinzhe LYU, Yinghui QUAN, Minghui SHA, Shuxian DONG, Mengdao XING. Ensemble deep learning-based intelligent classification of active jamming [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3595-3602. |
| [13] | Bo DAN, Zhequan FU, Shan GAO, Tao JIAN. Full-polarization high resolution range profile recognition technology for sea surface target based on convolutional neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 108-116. |
| [14] | Ziyan LIU, Shanshan MA, Jing LIANG, Mingcheng ZHU, Lei YUAN. Attention mechanism based CNN channel estimation algorithm in millimeter-wave massive MIMO system [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 307-312. |
| [15] | Xinping MI, Xihong CHEN, Zan LIU, Yongjin LIU, Qiang LIU. Bispectrum feature recognition of radar signal based on entropy evaluation and modal decomposition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2116-2123. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||