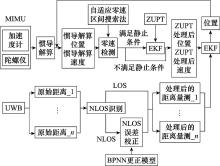
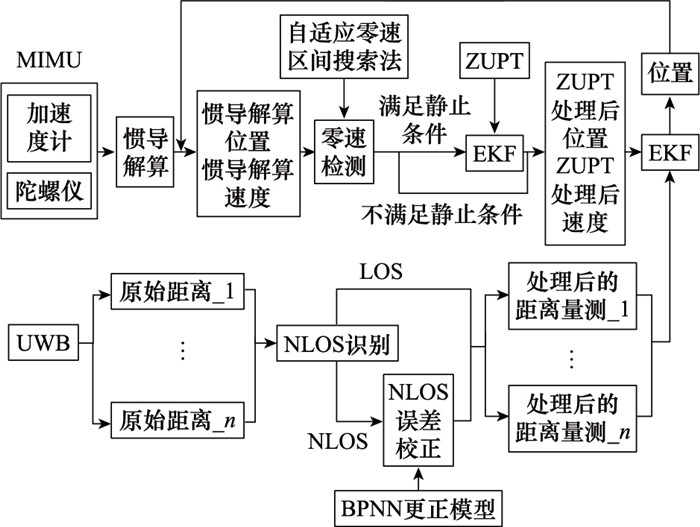
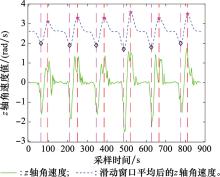
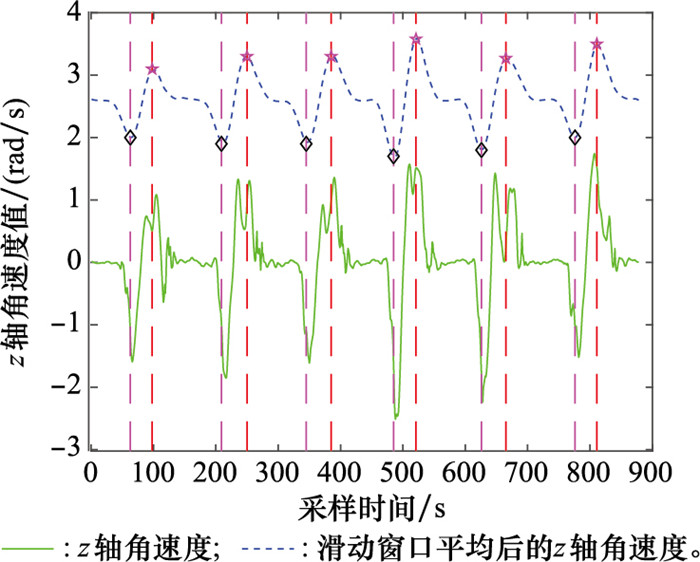
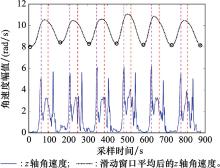
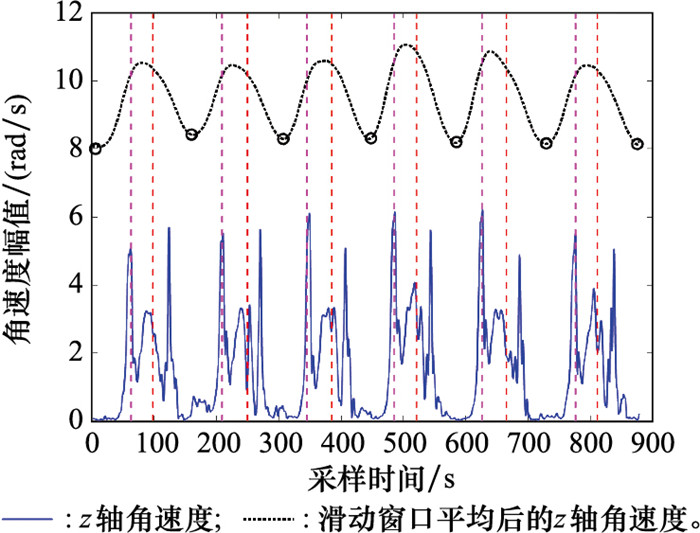
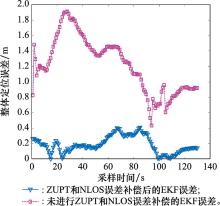
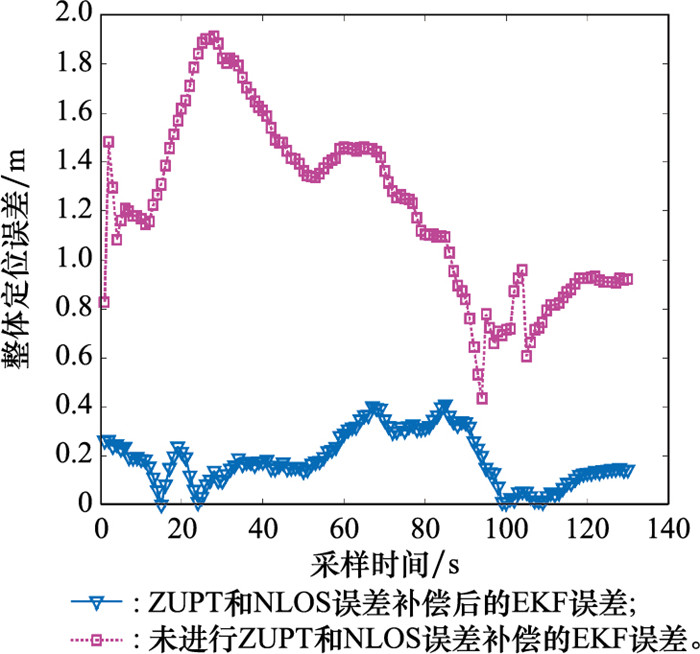
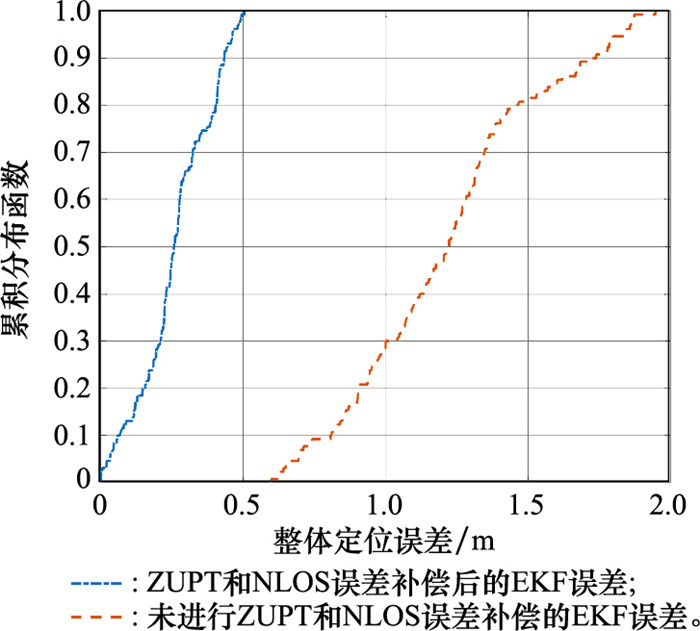
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 1300-1310.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.04.26
• Guidance, Navigation and Control • Previous Articles Next Articles
Pedestrian indoor positioning method based on INS/UWB tight integration
Yueyang BEN, Yuan HUANG, Hongdian HUANG, Qian LI
- College of Intelligent Systems Science and Engineering, Harbin Engineering University, Harbin 150001, China
-
Received:2024-03-29Online:2025-04-25Published:2025-05-28 -
Contact:Qian LI
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yueyang BEN, Yuan HUANG, Hongdian HUANG, Qian LI. Pedestrian indoor positioning method based on INS/UWB tight integration[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1300-1310.
share this article
Table 5
Statistical table of data for test sample points"
| 样本 | 点位测量数据 | BPNN预测 | ||||
| 真实距离/m | 测量距离/m | 更正前绝对误差/m | 更正后测量距离/m | 更正后绝对误差/m | ||
| A1 | 4.30 | 4.53 | 0.23 | 4.29 | 0.01 | |
| A2 | 5.30 | 5.52 | 0.22 | 5.28 | 0.02 | |
| A3 | 4.89 | 5.21 | 0.32 | 4.90 | 0.01 | |
| A4 | 3.50 | 3.68 | 0.18 | 3.53 | 0.03 | |
| A5 | 2.03 | 2.39 | 0.36 | 2.01 | 0.02 | |
| A6 | 2.11 | 2.50 | 0.39 | 2.12 | 0.01 | |
| A7 | 1.92 | 2.10 | 0.18 | 1.94 | 0.02 | |
| A8 | 4.05 | 4.28 | 0.23 | 4.08 | 0.03 | |
| A9 | 3.46 | 3.70 | 0.26 | 3.47 | 0.01 | |
| A10 | 2.59 | 2.86 | 0.27 | 2.62 | 0.03 | |
| 1 | ASHRAF I , HUR S , PARK Y . Smartphone sensor based indoor positioning: current status, opportunities, and future cha-llenges[J]. Electronics, 2024, 9 (6): 891. |
| 2 | YU Q. Indoor location methods of fire personnel based on GPS and sensor network[C]//Proc. of the 4th International Conference on Informatics Engineering & Information Science, 2022, 12161: 357-363. |
| 3 | MIAO C W , CHEN G Z , YAN C L , et al. Path planning optimization of indoor mobile robot based on adaptive ant colony algorithm[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 15, 107230. |
| 4 |
HUANG J H , JUNGINGER S , LIU H , et al. Indoor positioning systems of mobile robots: a review[J]. Robotics, 2023, 12 (2): 47.
doi: 10.3390/robotics12020047 |
| 5 |
SESYUK A , IOANNOU S , RASPOPOULOS M . A survey of 3D indoor localization systems and technologies[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22 (23): 9380.
doi: 10.3390/s22239380 |
| 6 | TEYMOURI M S, BHATTACHARYA S. Landmark-based distributed topological mapping and navigation in GPS-denied urban environments using teams of low-cost robots[EB/OL]. [2024-03-01]. https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s10458-024-09635-y. |
| 7 |
YAN J , YANG C , FAN W Y , et al. GNSS/UWB integrated positioning with robust Helmert variance component estimation[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2024, 73 (5): 2532- 2547.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2023.12.020 |
| 8 | CHIANG K W , CHANG H W , LI Y H , et al. Assessment for INS/GNSS/odometer/barometer integration in loosely-coupled and tightly-coupled scheme in a GNSS-degraded environment[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2019, 20 (6): 3057- 3069. |
| 9 |
ZHOU P , WANG H , GRAVINA R , et al. WIO-EKF: extended Kalman filtering-based Wi-Fi and inertial odometry fusion method for indoor localization[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11 (13): 23592- 23603.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3386889 |
| 10 |
JURDI R , CHEN H , ZHU Y M , et al. WhereArtThou: a WiFi-RTT-based indoor positioning system[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 41084- 41101.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3377237 |
| 11 |
NIU J W , WANG B W , SHU L , et al. ZIL: an energy-efficient indoor localization system using ZigBee radio to detect WiFi fingerprints[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2015, 33 (7): 1431- 1442.
doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2015.2430171 |
| 12 |
GUO G Y , CHEN R Z , YAN K , et al. Multi-channel and multi-RSS based BLE range estimation for indoor tracking of commercial smartphones[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23 (24): 30728- 30738.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3328711 |
| 13 | XU S H , CHEN R Z , GUO G Y , et al. Bluetooth, floor-plan, and microelectromechanical systems-assisted wide-area audio indoor localization system: apply to smartphones[J]. IEEE Trans.on Industrial Electronics, 2021, 69 (11): 11744- 11754. |
| 14 |
FAN Q G , SUN B W , AN S , et al. Performance enhancement of MEMS-based INS/UWB integration for indoor navigation applications[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2017, 17 (10): 3116- 3130.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2017.2689802 |
| 15 |
LI M G , ZHU H , YOU S Z , et al. UWB-based localization system aided with inertial sensor for underground coal mine applications[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2020, 20 (12): 6652- 6669.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2020.2976097 |
| 16 |
DE-COCK C , TANGHE E , JOSEPH W , et al. Robust IMU-based mitigation of human body shadowing in UWB indoor positioning[J]. Sensors, 2023, 23 (19): 8289.
doi: 10.3390/s23198289 |
| 17 | LIU A, LIN S W, WANG J G, et al. A method for non-line of sight identification and delay correction for UWB indoor positioning[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 17th Conference on Industrial Electronics and Applications, 2022: 9-14. |
| 18 | 李倩, 蒋正华, 孙炎, 等. 基于因子图的INS/UWB室内行人紧组合定位技术[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2022, 43 (5): 32- 45. |
| LI Q , JIANG Z H , SUN Y , et al. INS/UWB tight integrated localization technology for pedestrian indoor based on factor graph[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2022, 43 (5): 32- 45. | |
| 19 | NAHEEM K , KIM M S . A robust indoor pedestrian localization approach against human body shadowing for UWB-enabled smartphones[J]. IEEE Trans.on Instrumentation and Mea-surement, 2024, 73, 9505013. |
| 20 |
ZHANG H , WANG Q , LI Z H , et al. Research on high precision positioning method for pedestrians in indoor complex environments based on UWB/IMU[J]. Remote Sensing, 2023, 15 (14): 3555.
doi: 10.3390/rs15143555 |
| 21 | ZHU J , KIA S S . Decentralized cooperative localization with LOS and NLOS UWB inter-agent ranging[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2021, 22 (6): 5447- 5456. |
| 22 |
LI Z , DENG Z H , MENG Z D , et al. Coriolis-based heading estimation for pedestrian inertial localization based on MEMS MIMU[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2024, 11 (16): 27509- 27517.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2024.3398431 |
| 23 | GUO H M, URADZINSKI M. The usability of MTI IMU sensor data in PDR indoor positioning[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 25th International Conference on Integrated Navigation Systems, 2018. |
| 24 |
ELSANHOURY M , MAKELA P , KOLJONEN J , et al. Precision positioning for smart logistics using ultra-wideband technology-based indoor navigation: a review[J]. IEEE Access, 2022, 10, 44413- 44445.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2022.3169267 |
| 25 |
NAHEEM K , KIM M S . A low-cost foot-placed UWB and IMU fusion-based indoor pedestrian tracking system for IoT applications[J]. Sensors, 2022, 22 (21): 8160.
doi: 10.3390/s22218160 |
| 26 |
文张建, 赵立业, 沈翔. GRU-DNN改进的行人导航零速检测方法[J]. 导航定位学报, 2022, 10 (5): 97- 104.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2022.05.014 |
|
WEN Z J , ZHAO L Y , SHEN X . An improved zero-velocity detection method of pedestrian navigation based on GRU-DNN[J]. Journal of Navigation and Positioning, 2022, 10 (5): 97- 104.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4999.2022.05.014 |
|
| 27 | 陈泽, 潘献飞, 陈昶昊, 等. 一种用于足绑式行人惯性导航的区间搜索零速检测器[J]. 中国惯性技术学报, 2020, 28 (6): 709- 715. |
| CHEN Z , PAN X F , CHEN C H . A zero-velocity detector based on interval search for foot-mounted pedestrian inertial navigation[J]. Journal of Chinese Inertial Technology, 2020, 28 (6): 709- 715. | |
| 28 |
杨海, 李威, 张禾, 等. 复杂坏境下基于SINS/UWB的容错组合定位技术研究[J]. 仪器仪表学报, 2017, 38 (9): 2177- 2185.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.09.011 |
|
YANG H , LI W , ZHANG H , et al. Fault tolerant integrated positioning system based on SINS/UWB in complex environment[J]. Chinese Journal of Scientific Instrument, 2017, 38 (9): 2177- 2185.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-3087.2017.09.011 |
|
| 29 |
YUAN S W , ZHANG Y B , SHI Y T , et al. A novel ESKF based ZUPT using midpoint integration approach for indoor pedestrian navigation[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2024, 24 (7): 10920- 10932.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2024.3365979 |
| 30 |
WANG Q , FU M X , WANG J Q , et al. Free-walking: pedestrian inertial navigation based on dual foot-mounted IMU[J]. Defence Technology, 2024, 33, 573.
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2023.03.001 |
| 31 | NILSSON J O, GUPTA A K, HANDEL P. Foot-mounted inertial navigation made easy[C]// Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, 2014: 24-29. |
| 32 | WANG Y, CHERNYSHOFF A, SHKEL A M. Error analysis of ZUPT-aided pedestrian inertial navigation[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Indoor Positioning and Indoor Navigation, 2018: 206-212. |
| 33 | WANG J Y , LIU J H , XU X B , et al. A yaw correction method for pedestrian positioning using two low-cost MIMUs[J]. Mea-surement, 2023, 217, 112992. |
| 34 | 刘培原, 王坚, 盛坤鹏, 等. 非视距误差神经网络改正的超宽带定位模型研究[J]. 导航定位与授时, 2020, 7 (3): 93- 104. |
| LIU P Y , WANG J , SHENG K P , et al. Research on UWB positioning model corrected by non-line-of-sight error neural network[J]. Navigation Positioning & Timing, 2020, 7 (3): 93- 104. | |
| 35 | 李得海, 吴文坛, 马会林, 等. 室内测距型基站组网定位性能分析[J]. 武汉大学学报(信息科学版), 2025, 50 (1): 1- 10. |
| LI D H , WU W T , MA H L , et al. Positioning performance of the indoor networks of range-based reference stations[J]. Geomatics and Information Science of Wuhan University, 2025, 50 (1): 1- 10. | |
| 36 | ZHANG X D, REN M R, WANG P, et al. A new zero velocity update algorithm for the shoe-mounted personal navigation system based on IMU[C]//Proc. of the 34th Chinese Control Conference, 2015. |
| [1] | Hongde DAI, Yufeng MA, Shaowu DAI, Baidong ZHENG, Xiaoyu ZHANG. Zero velocity update algorithm for inertial pedestrian navigation based on nonlinear prediction of heading error [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(8): 2555-2561. |
| [2] | Wei GAO, Yafeng LI, Kedong WANG. Design of ultra-tightly integrated GNSS/SINS simulation platform in signal level [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(1): 184-192. |
| [3] | Jun WENG, Xiaoyun BIAN. Effect analysis and compensation of the high precision ring laser gyroscope inertial navigation system ZUPT caused by gravity disturbance [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(1): 179-183. |
| [4] | LIU Shuai, SUN Fu-ping, ZHANG Lun-dong. Research on the tight integration of ambiguity-fixed PPP and INS [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(10): 2389-2394. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||