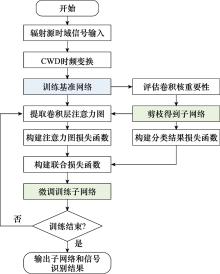
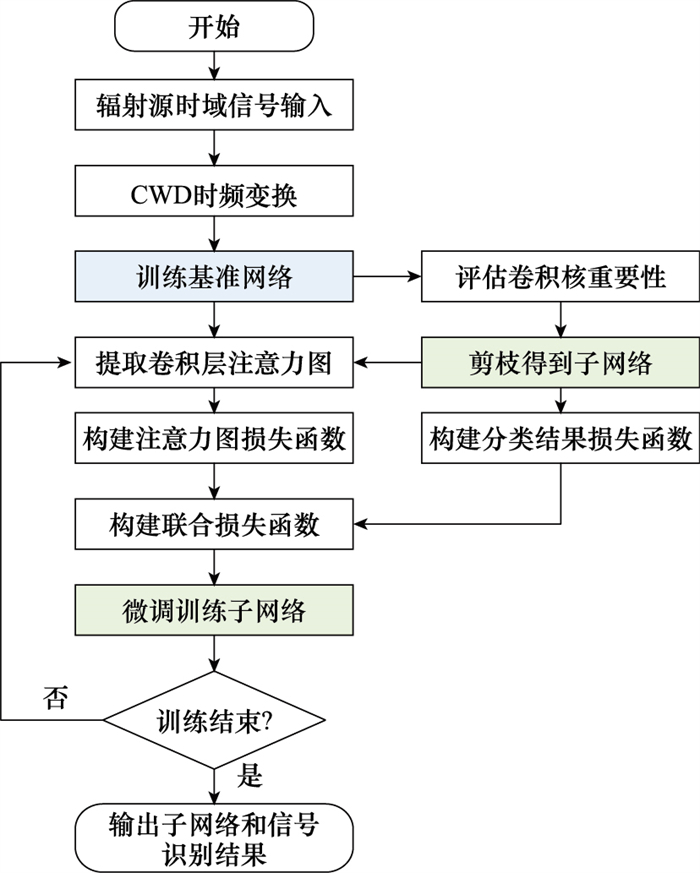
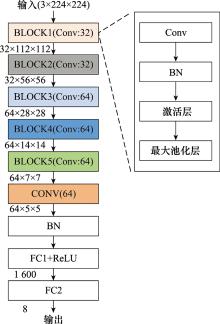
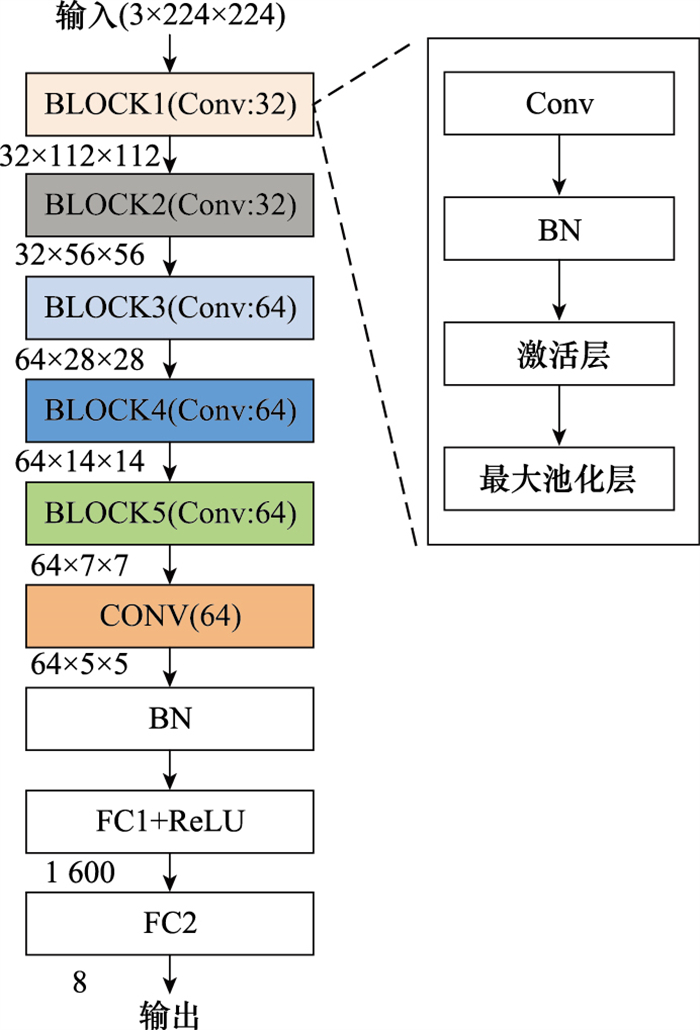
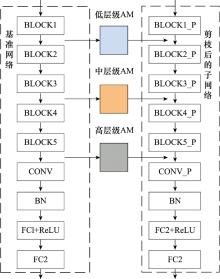
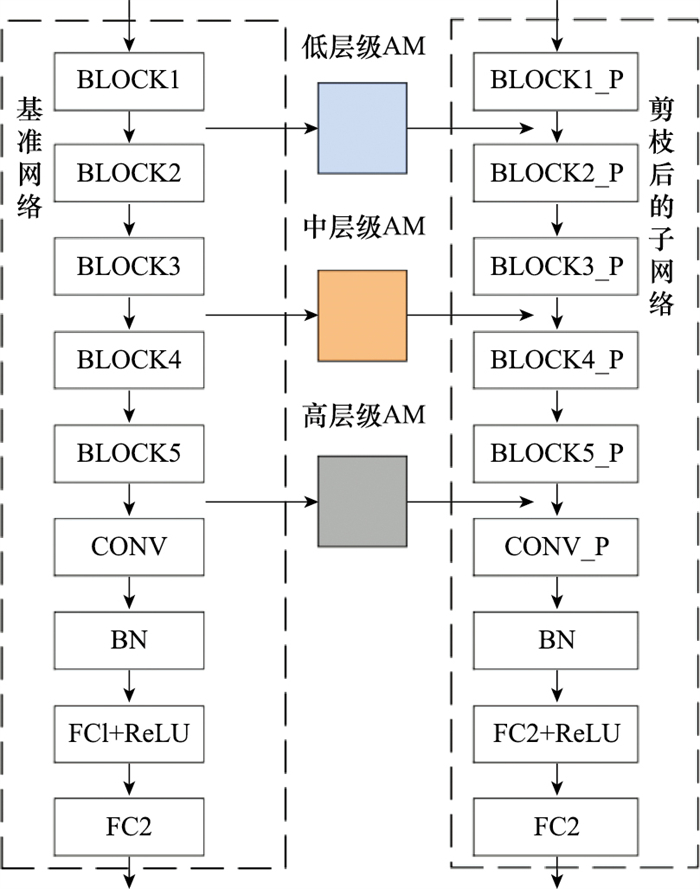
| 1 |
YANG H H , YANG X P , LIU S K , et al. Radar emitter multi-label recognition based on residual network[J]. Defence Technology, 2022, 18 (3): 410- 417.
doi: 10.1016/j.dt.2021.02.005
|
| 2 |
刘赢, 田润澜, 王晓峰. 基于深层卷积神经网络和双谱特征的雷达信号识别方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2019, 41 (9): 1998- 2005.
|
|
LIU Y , TIAN R L , WANG X F . Radar signal recognition method based on deep convolutional neural network and bispectrum feature[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41 (9): 1998- 2005.
|
| 3 |
YAO Y , WANG Z H . Radar signal recognition based on time-frequency and CNN preprocessing[J]. Journal of Detection & Control, 2018, 40 (6): 99- 105.
|
| 4 |
SHI L M , YANG C Z , WANG M L , et al. Recognition method of radar signal modulation method based on deep network[J]. Journal of Ordnance Equipment Engineering, 2021, 42 (6): 190- 193.
|
| 5 |
WANG X B, HUANG G M, ZHOU Z W, et al. Radar emitter recognition based on the short time Fourier transform and convolutional neural networks[C]//Proc. of the 10th International Congress on Image and Signal Processing, 2017.
|
| 6 |
周志文, 黄高明, 高俊, 等. 一种深度学习的雷达辐射源识别算法[J]. 西安电子科技大学学报, 2017, 44 (3): 77- 82.
|
|
ZHOU Z W , HUANG G M , GAO J , et al. Radar emitter identification algorithm based on deep learning[J]. Joumal of Xidian University, 2017, 44 (3): 77- 82.
|
| 7 |
WANG F , YANG C , HUANG S , et al. Automatic modulation classification based on joint feature and convolutional neural network[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2019, 13 (6): 998- 1003.
|
| 8 |
GAO J P , WANG X , WU R W , et al. A new modulation recognition method based on flying fish swarm algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 76689- 76706.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3079131
|
| 9 |
LIN A N , MA Z Y , HUANG Z , et al. Unknown radar waveform recognition based on transferred deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 184793- 184807.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3029192
|
| 10 |
HA P K N, VAN L D, QUANG T D. A parallel neural network-based scheme for radar emitter recognition[C]//Proc. of the 14th International Conference on Ubiquitous Information Management and Communication, 2020.
|
| 11 |
TAO S F , XIAO S , GONG S G , et al. Recognition of electromagnetic signals based on the spiking convolutional neural network[J]. Wireless Communications and Mobile Computing, 2022, 2022, 2395996.
|
| 12 |
LECUN Y , DENKER J , SOLLA S . Optimal brain damage[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 1989, 1, 598- 605.
|
| 13 |
HAN S , POOL J , TRAN J , et al. Learning both weights and connections for efficient neural network[J]. Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015, 28, 2238772.
|
| 14 |
HAN S , LIU X Y , MAO H Z , et al. EIE: efficient inference engine on compressed deep neural network[J]. ACM SIGARCH Computer Architecture News, 2016, 44 (3): 243- 254.
doi: 10.1145/3007787.3001163
|
| 15 |
HAN S, MAO H Z, DALLY W J. Deep compression: compressing deep neural networks with pruning, trained quantization and huffman coding[EB/OL]. [2024-02-22]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1510.00149.
|
| 16 |
LIU Z, LI J G, SHEN Z Q, et al. Learning efficient convolutional networks through network slimming[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference Computer Vision, 2017: 2736-2744.
|
| 17 |
LIN S H, JI R H, LI Y C, et al. Accelerating convolutional networks via global & dynamic filter pruning[C]//Proc. of the International Joint Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2018.
|
| 18 |
PAVLO M, STEPHEN T, TERO K, et al. Pruning convolutional neural networks for resource efficient inference[EB/OL]. [2024-02-22]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1611.06440.
|
| 19 |
巩凯强, 张春梅, 曾光华. 卷积神经网络模型剪枝结合张量分解压缩方法[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40 (11): 3146- 3151.
|
|
GONG K Q , ZHANG C M , ZENG G H . Convolution neural network model compression method based on pruning and tensor decomposition[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40 (11): 3146- 3151.
|
| 20 |
王忠锋, 徐志远, 宋纯贺, 等. 基于梯度的深度网络剪枝算法[J]. 计算机应用, 2020, 40 (5): 1253- 1259.
|
|
WANG Z F , XU Z Y , SONG C H , et al. Gradient-based deep network pruning algorithm[J]. Journal of Computer Applications, 2020, 40 (5): 1253- 1259.
|
| 21 |
HE Y H, LIN J, LIU Z, et al. AMC: automl for model compression and acceleration on mobile devices[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2018: 784-800.
|
| 22 |
LIU N, MA X L, XU Z Y, et al. Autocompress: an automatic DNN structured pruning framework for ultra-high compression rates[C]//Proc. of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, 2020.
|
| 23 |
LIN M B, JI R, ZHANG Y X, et al. Channel pruning via automatic structure search[EB/OL]. [2024-02-22]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2001.08565.
|
| 24 |
李屹, 魏建国, 刘贯伟. 模型剪枝算法综述[J]. 计算机与现代化, 2022 (9): 51- 59.
|
|
LI Y , WEI J G , LIU G W . Survey of model pruning algorithms[J]. Computer and Modernization, 2022 (9): 51- 59.
|
| 25 |
肖帅, 龚帅阁, 李想, 等. FPGA平台轻量化卷积神经网络辐射源信号识别方法[J]. 计算技术与自动化, 2023, 42 (4): 140- 146.
|
|
XIAO S , GONG S G , LI X , et al. Emitter signal identification method with lightweight CNN on FPGA platform[J]. Computing Technology and Automation, 2023, 42 (4): 140- 146.
|
| 26 |
SELVARAJU R R, COGSWELL M, DAS A, et al. Grad-CAM: visual explanations from deep networks via gradient-based localization[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 618-626.
|
| 27 |
ZAGORUYKO S, KOMODAKIS N. Paying more attention to attention: improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer[EB/OL]. [2024-02-22]. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.1612.03928.
|
| 28 |
LI H, KADAV A, DURDANOVIC I, et al. Pruning filters for efficient convnets[EB/O]. [2024-04-08]. https://arxiv.org/abs/1608.08710.
|
| 29 |
LIN M B, JI R R, WANG Y, et al. Hrank: filter pruning using high-rank feature map[C]//Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2020: 1529-1538.
|