Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 973-981.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.04.05
• Electronic Technology • Previous Articles
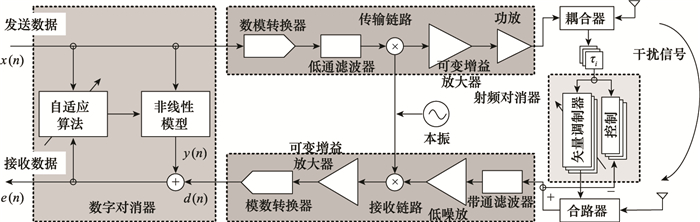
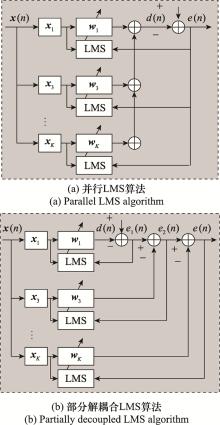
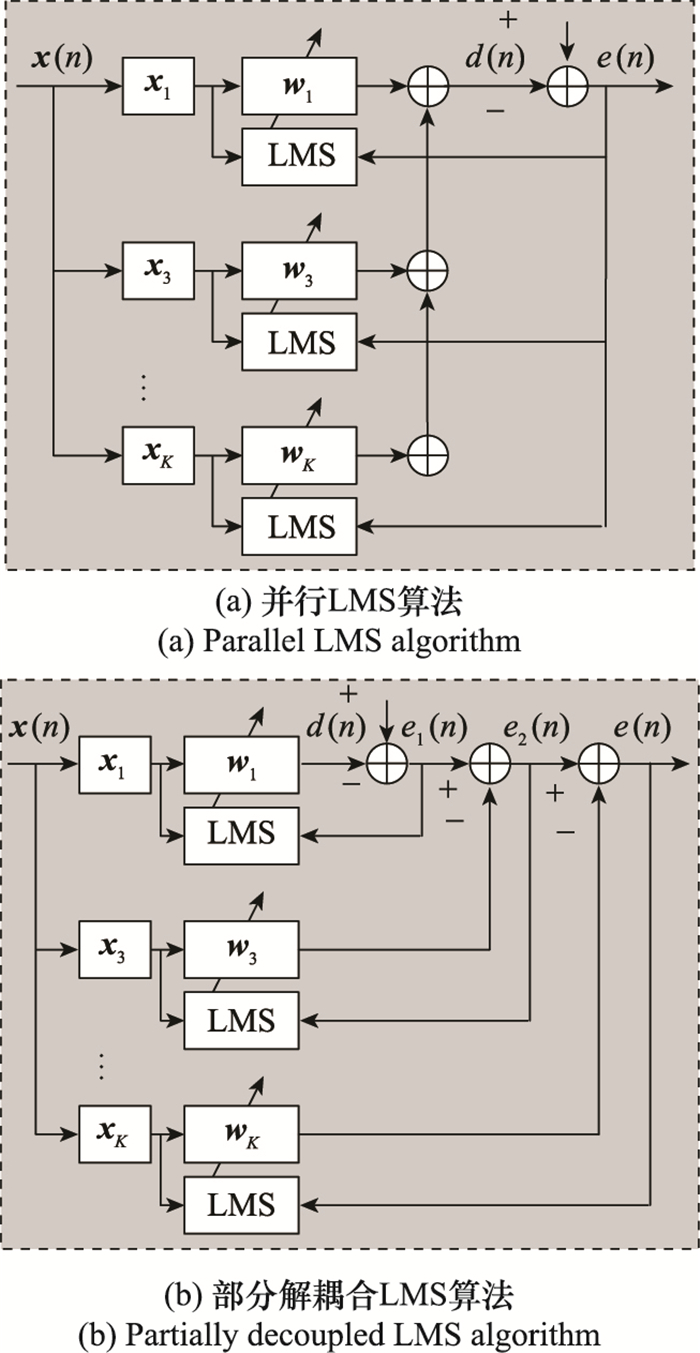
Partially decoupling based nonlinear digital interference cancellation algorithm
Zhongpu CUI, Songhu GE, Yaxing LI, Yu GUO, Jinling XING, Jin MENG
- National Key Laboratory of Science and Technology on Vessel Integrated Power System, Naval University of Engineering, Wuhan 430033, China
-
Received:2022-03-29Online:2023-03-29Published:2023-03-28 -
Contact:Songhu GE
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Zhongpu CUI, Songhu GE, Yaxing LI, Yu GUO, Jinling XING, Jin MENG. Partially decoupling based nonlinear digital interference cancellation algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(4): 973-981.
share this article
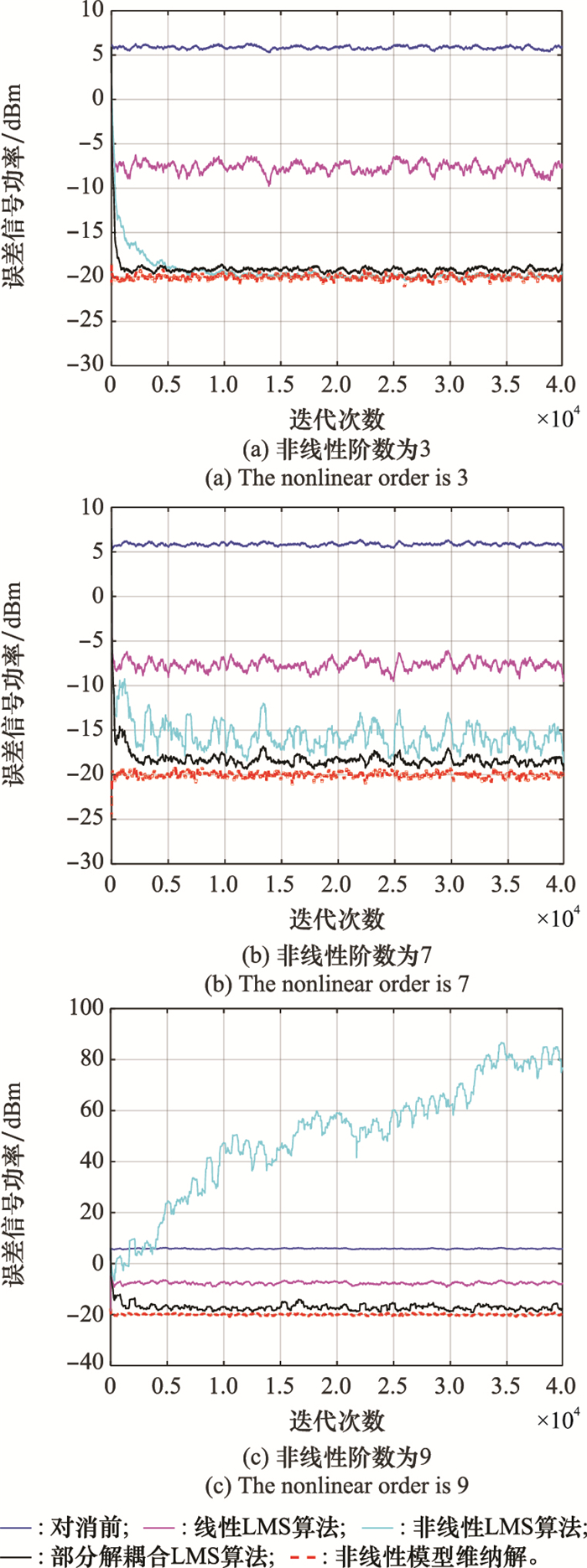
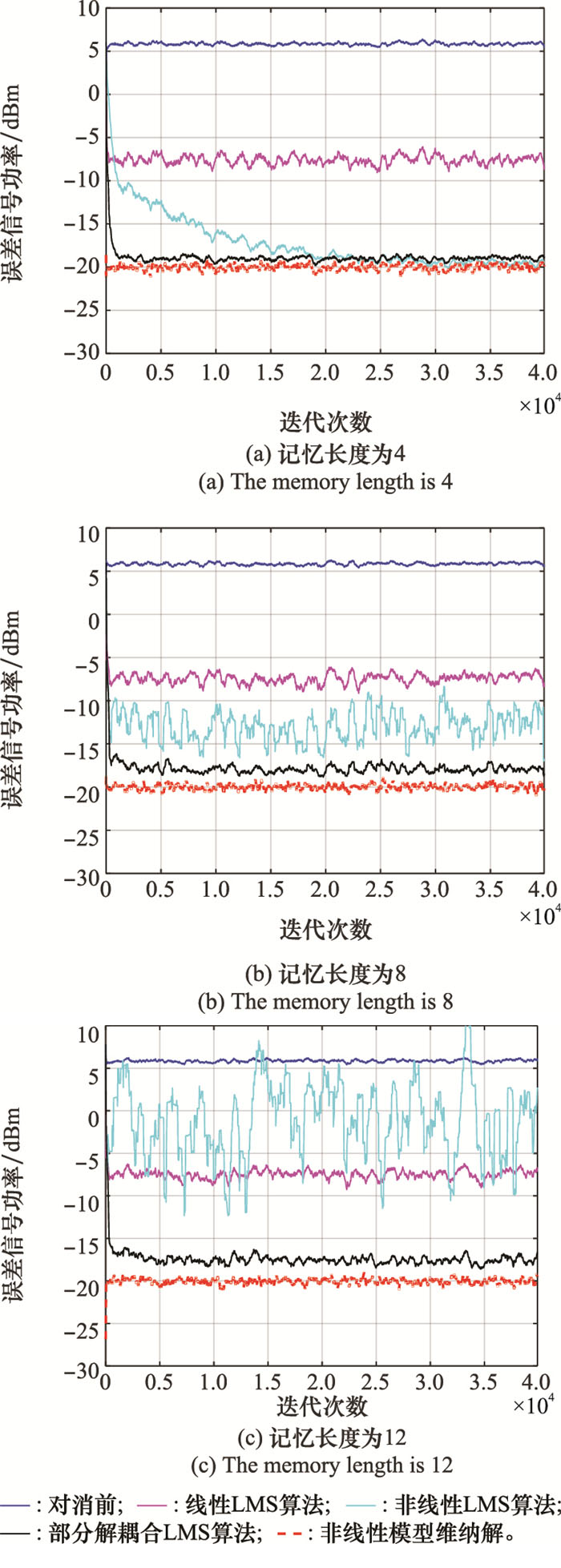
Table 1
Mean square error of three algorithms under different input interference signal ratios dBm"
| 阶次 | 线性模型维纳解 | 非线性模型维纳解 | 部分解耦合模型维纳解 | ||||||||
| 0 dB | 10 dB | 20 dB | 0 dB | 10 dB | 20 dB | 0 dB | 10 dB | 20 dB | |||
| k=1 | -19.394 1 | -16.018 1 | -7.937 4 | -19.384 1 | -16.018 1 | -7.937 4 | -19.384 1 | -16.018 1 | -7.937 4 | ||
| k=3 | -19.413 9 | -16.034 8 | -7.944 5 | -20.015 9 | -20.015 9 | -19.992 1 | -19.553 2 | -19.7116 | -19.051 1 | ||
| k=5 | -19.398 9 | -15.987 7 | -7.993 3 | -19.983 1 | -19.983 1 | -20.026 0 | -19.565 5 | -19.806 8 | -19.348 0 | ||
| k=7 | -19.383 9 | -16.009 7 | -7.985 8 | -20.019 4 | -20.019 4 | -19.983 1 | -19.555 1 | -19.884 3 | -19.408 6 | ||
| k=9 | -19.379 1 | -16.006 6 | -7.955 7 | -19.970 0 | -19.970 0 | -19.969 6 | -19.551 4 | -19.886 5 | -19.411 9 | ||
| 1 |
HE Y , ZHAO M Y , GUO W B . Performance analysis of nonlinear self-interference cancellation with timing error in full-duplex systems[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2021, 10 (5): 1075- 1078.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3057893 |
| 2 |
KENNETH E K , BRADLEY T P , JEFFREY S H . In-band full-duplex technology: techniques and systems survey[J]. IEEE Trans.on Microwave Theory and Technology, 2019, 67 (7): 3025- 3041.
doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2019.2896561 |
| 3 | SABHARWAL A , SCHNITER P . In-band full-duplex wireless: challenges and opportunities[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2014, 32 (5): 1637- 1652. |
| 4 |
LI D M , CHENG J L , VICTOR C M . Adaptive spectrum sharing for half-duplex and full-duplex cognitive radios: from the energy efficiency perspective[J]. IEEE Trans.on Communication, 2018, 66 (11): 5067- 5080.
doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2018.2843768 |
| 5 |
TONG Z , MARTIN H . Throughput analysis for full-duplex wireless networks with imperfect self-interference cancellation[J]. IEEE Trans.on Communication, 2015, 63 (11): 4490- 4500.
doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2015.2465903 |
| 6 |
LI Z , XIA Y L , PEI W J , et al. An augmented nonlinear LMS for digital self-interference cancellation in full-duplex direct-conversion transceivers[J]. IEEE Trans.on Signal Processing, 2018, 66 (15): 4065- 4078.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2846250 |
| 7 |
GE S H , XING J L , LIU Y C , et al. Dual-stage co-site RF interference canceller for wideband direct-conversion receivers using reduced observation chain[J]. IEEE Trans.on Electromagnetic Compatibility, 2020, 62 (3): 923- 932.
doi: 10.1109/TEMC.2019.2914369 |
| 8 |
DONGKYU K , HAESOON L , DAESIK H . A survey of in-band full-duplex transmission: from the perspective of PHY and MAC layers[J]. IEEE Communication Survey, 2015, 17 (4): 2017- 2046.
doi: 10.1109/COMST.2015.2403614 |
| 9 |
EVERETT E , SAHAI A , SABHARWAL A . Passive self-interference suppression for full-duplex infrastructure nodes[J]. IEEE Trans.on Wireless Communications, 2014, 13 (2): 680- 694.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2013.010214.130226 |
| 10 |
ADNAN A , PARAG K . Protocol design for enabling full-duplex operation in next generation IEEE 802.11 WLANs[J]. IEEE System Journals, 2018, 12 (4): 3438- 3449.
doi: 10.1109/JSYST.2017.2720462 |
| 11 | KRIER J, RAND I, AKYILDIZ F. Active self-interference cancellation of passband signal using gradient descent[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 24th Annual International Symposium on Personal, Indoor, and Mobile Radio Communications, 2013: 1212-1216. |
| 12 |
KAZUKI K , YUICHI M , HIDEYUKI U . Iterative nonlinear self-interference cncellation for in-band full-duplex wireless communications under mixer imbalance and amplifier nonlinearity[J]. IEEE Trans.on Wireless Communications, 2020, 19 (7): 4424- 4438.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2020.2983407 |
| 13 | CUI Z P , GE S H , LI Y X , et al. Adaptive two-dimensional orthogonalization scheme for non-linear digital canceller in full-duplex radios[J]. Electronics Letters, 2021, 58 (6): 240- 242. |
| 14 |
VOGT H , ENZNER G , SEZGIN A . State-space adaptive nonlinear self-interference cancellation for full-duplex communication[J]. IEEE Trans.on Signal Processing, 2019, 67 (11): 2810- 2825.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2019.2910490 |
| 15 |
AHMED E , ELTAWIL A . All-digital self-interference cancellation technique for full-duplex systems[J]. IEEE Trans.on Wireless Communications, 2015, 14 (7): 3519- 3532.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2015.2407876 |
| 16 | LAURI A, DANI K, VILLE S, et al. Cancellation of power amplifier induced nonlinear self-interference in full-duplex transceivers[C]//Proc. of the Asilomar Conference on Signals, Systems and Computers, 2013: 1193-1198. |
| 17 |
DING L , ZHOU G T , DENNIS R M , et al. A robust digital baseband predistorter constructed using memory polynomials[J]. IEEE Trans.on Communications, 2004, 52 (1): 159- 165.
doi: 10.1109/TCOMM.2003.822188 |
| 18 |
MAHMOUD A , LAURI A , CHANCE T , et al. Low-complexity subband digital predistortion for spurious emission suppression in noncomtiguous spectrum access[J]. IEEE Trans.on Microwave Theory and Technology, 2016, 64 (11): 3501- 3517.
doi: 10.1109/TMTT.2016.2602208 |
| 19 |
KAZUKI K , YUICHI M , HIDEYUKI U . Theoretical analysis of in-band full-duplex radios with parallel Hammerstein self-interference cancellers[J]. IEEE Trans.on Wireless Communications, 2021, 20 (10): 6772- 6786.
doi: 10.1109/TWC.2021.3076496 |
| 20 | LIU D, CHA H, WANG B B. A novel variable step length LMS algorithm based on arctangent compound function[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 5th Advanced Information Technology, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, 2021: 1691-1696. |
| 21 | ASHRAF A M, MOSTAFA M I, HESHAM F A. Performance study of adaptive filtering and noise cancellation of artifacts in ECG signals[C]//Proc. of the 17th International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology, 2015: 394-401. |
| 22 | SURYAIA R, MAMUNUR R, ZAHANGIR A. A unified analysis of the proposed wavelet transform domain LMS-algorithm for ARMA process[C]//Proc. of the 5th International Conference on Advances in Electrical Engineering, 2019: 195-200. |
| 23 | OZEN A, SOYSAL B, KAYA I. A fuzzy logic based channel estimation in Walsh-Hadamard transform employed OFDM systems[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 15th Signal Processing and Communications Applications, 2007. |
| 24 | GE S, CUI Z P, XING J L. Adaptive nonlinear digital interference cancellation with two dimensional orthogonalization for co-site radios[C]//Proc. of the IEEE MTT-S International Wireless Symposium, 2021. |
| 25 | LI Z, PEI W J, XIA Y L. Widely linear CLMS based cancellation of nonlinear self-interfereence in full-duplex direct-conversion transceivers[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing, 2018: 4329-4333. |
| 26 |
LI Z , XIA Y L , PEI W J . An augmented nonlinear LMS for digital self-interference cancellation in full-duplex direct-conversion transceivers[J]. IEEE Trans.on Signal Processing, 2018, 66 (15): 4065- 4078.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2018.2846250 |
| 27 | KORPI D, CHOI Y. Adaptive nonlinear digital self-interference cancellation for mobile inband full-duplex radio: algorithms and RF measurements[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Global Communication Conference, 2015. |
| 28 |
GRIFFITH D W , ARCE G R . Partially decoupled Volterra filters: formulation and LMS adaption[J]. IEEE Trans.on Signal Processing, 1997, 45 (6): 1485- 1494.
doi: 10.1109/78.599973 |
| 29 | ZOU Y X, CHAN S C, SANG T S. Transform domain adaptive Volterra filter algorithm based on constrained optimization[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, 1999: 219-222. |
| 30 |
GRIFFITH D W , ARCE G R . A partially decoupled RLS algorithm for Volterra filters[J]. IEEE Trans.on Signal Processing, 1999, 47 (2): 579- 582.
doi: 10.1109/78.740147 |
| 31 |
LIU Y , QUAN X , PAN W S . Digital assisted analog interference cancellation for in-band full-duplex radios[J]. IEEE Communication Letters, 2017, 21 (5): 1079- 1082.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2017.2652444 |
| [1] | Zhongyi CAI, Zezhou WANG, Xiaofeng ZHANG, Yan LI. Online prediction method of remaining useful lifetime for implicit nonlinear degradation equipment [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(6): 1410-1416. |
| [2] | LI Gongquan, LAI Tao, JIN Ke, ZHAO Yongjun. Nonlinearity phase estimation and correction of FMCW radar [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2018, 40(3): 538-545. |
| [3] | LI Fei, HU Jianbo, WANG Jianhao, WANG Tao. Adaptive Backstepping sliding mode control for a class of uncertain nonlinear systems with input constraints [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(8): 1823-1833. |
| [4] | LU Xiaodong, ZHAO Hui, ZHAO Bin, ZHOU Jun. Novel backstepping attitude control method for interception missile based on disturbance compensation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1100-1106. |
| [5] | LIU Zongcheng, CHEN Yong, DONG Xinmin, XUE Jianping, CHENG Jianfeng, WANG Zutong. Adaptive tracking control of multi-effector aircraft with actuator nonlinearity [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(2): 383-390. |
| [6] | ZENG Le-ya, XU Hua, WANG Tian-rui. Low computational complexity variable step-size CLMS algorithm based on Lorentzian function [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(5): 998-. |
| [7] | ZHANG Yong-gang, CHENG Ran, HUANG Yu-long, LI Ning. Truncated adaptive cubature particle filter [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(2): 382-391. |
| [8] | LI Fei, HU Jian-bo, WANG Jian-hao, GAO Peng. Backstepping global sliding mode control for flight attitude tracking control system with hysteretic nonlinearity [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(9): 2115-2122. |
| [9] | NING Xiao-ling, ZHANG Lin-sen, LIU Zhi-kun. Variable step size LMS equalization algorithm based on adaptive mixed power parameter in underwater acoustic channels [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(9): 2141-2147. |
| [10] | SU Rui, WANG Bin, LIU Shigang. Algorithm of memory effect and nonlinearity judgment for#br# Hammerstein channel [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(10): 2383-2390. |
| [11] | LIU Zong-cheng, DONG Xin-min, XUE Jian-ping, ZHANG Li-peng. Adaptive control for a class of nonlinear systems with uncertain actuator nonlinearity [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(1): 163-168. |
| [12] | WANG Yue, JIANG Bin, LU Ning-yun. Hybrid modeling strategy based on physical effect analysis and nonlinearity measure [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(6): 1137-1145. |
| [13] | WANG Wei, ZHAO Qing, WANG Ben, SUI Jun jie. Robust adaptive control for MEMS triaxial gyroscopewith sector input nonlinearities [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(12): 2504-2509. |
| [14] | CHEN Hui, WANG Xin-lin, LIU Bin, LI Hai-bin. Partially decoupled volterra equalizer for digital satellite channels [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(4): 847-851. |
| [15] | TIAN Fuqing, LUO Rong, LI Keyu, DING Qingxi. New variable step size LMS algorithm based on modified hyperbolic tangent function [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(9): 1758-1763. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||