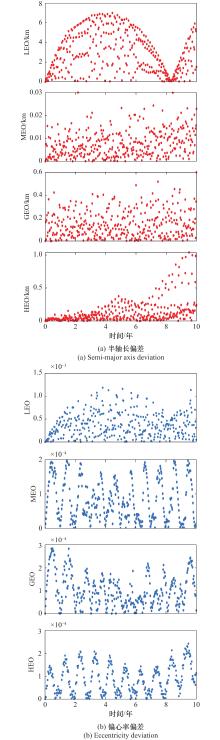
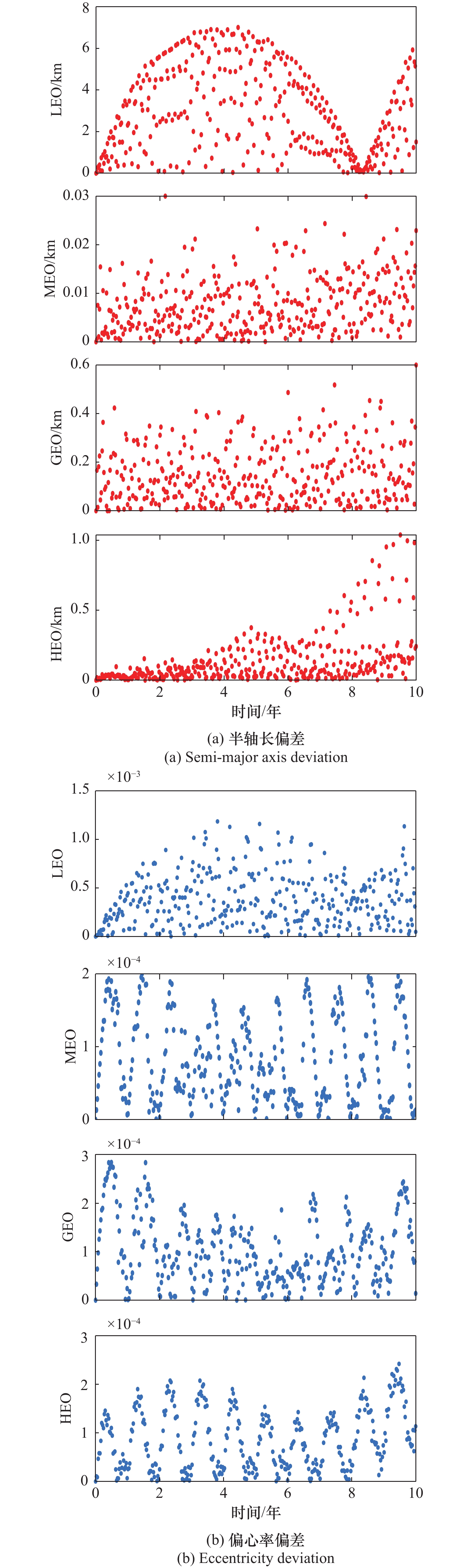
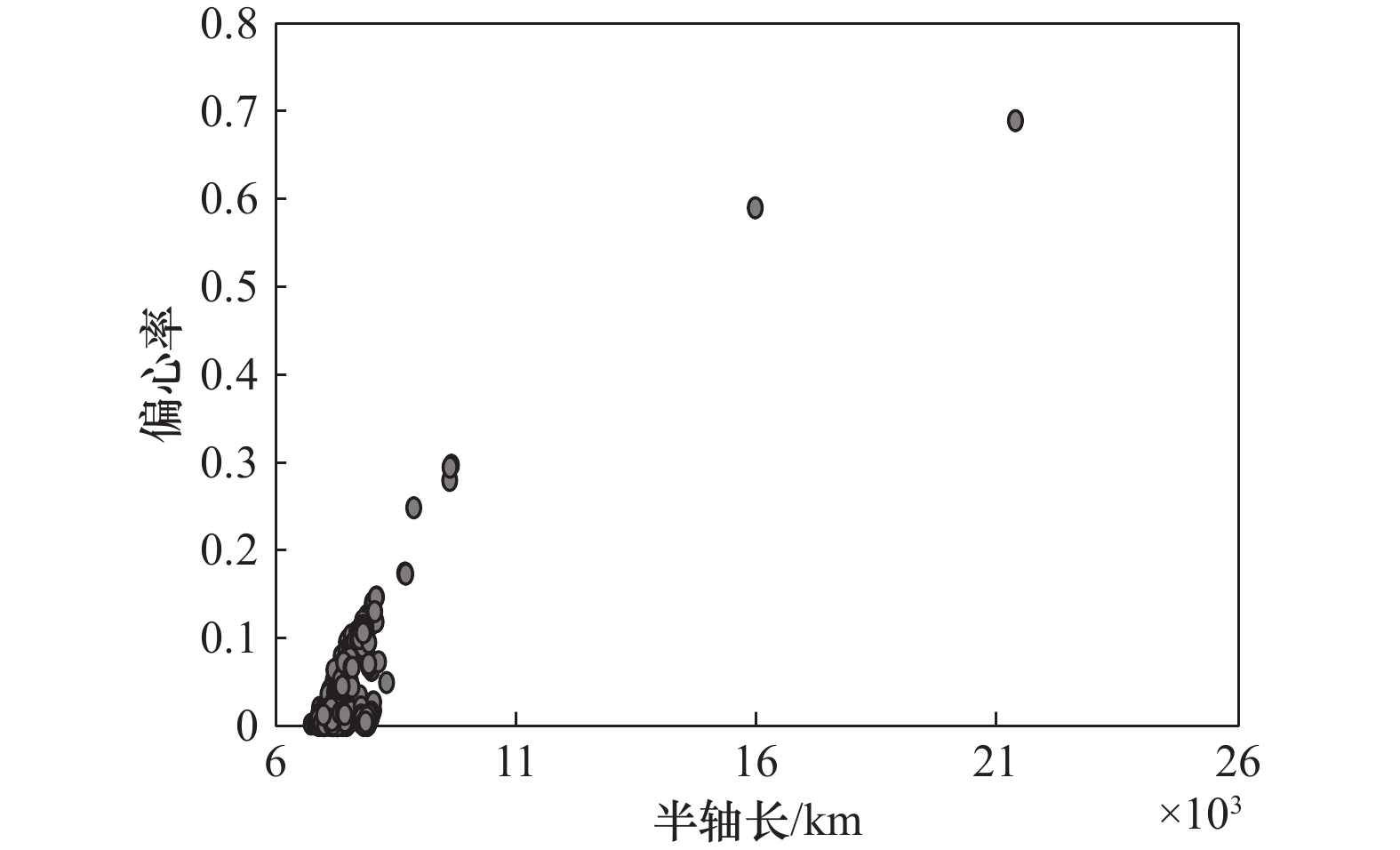
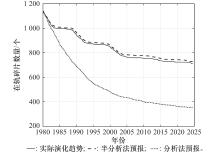
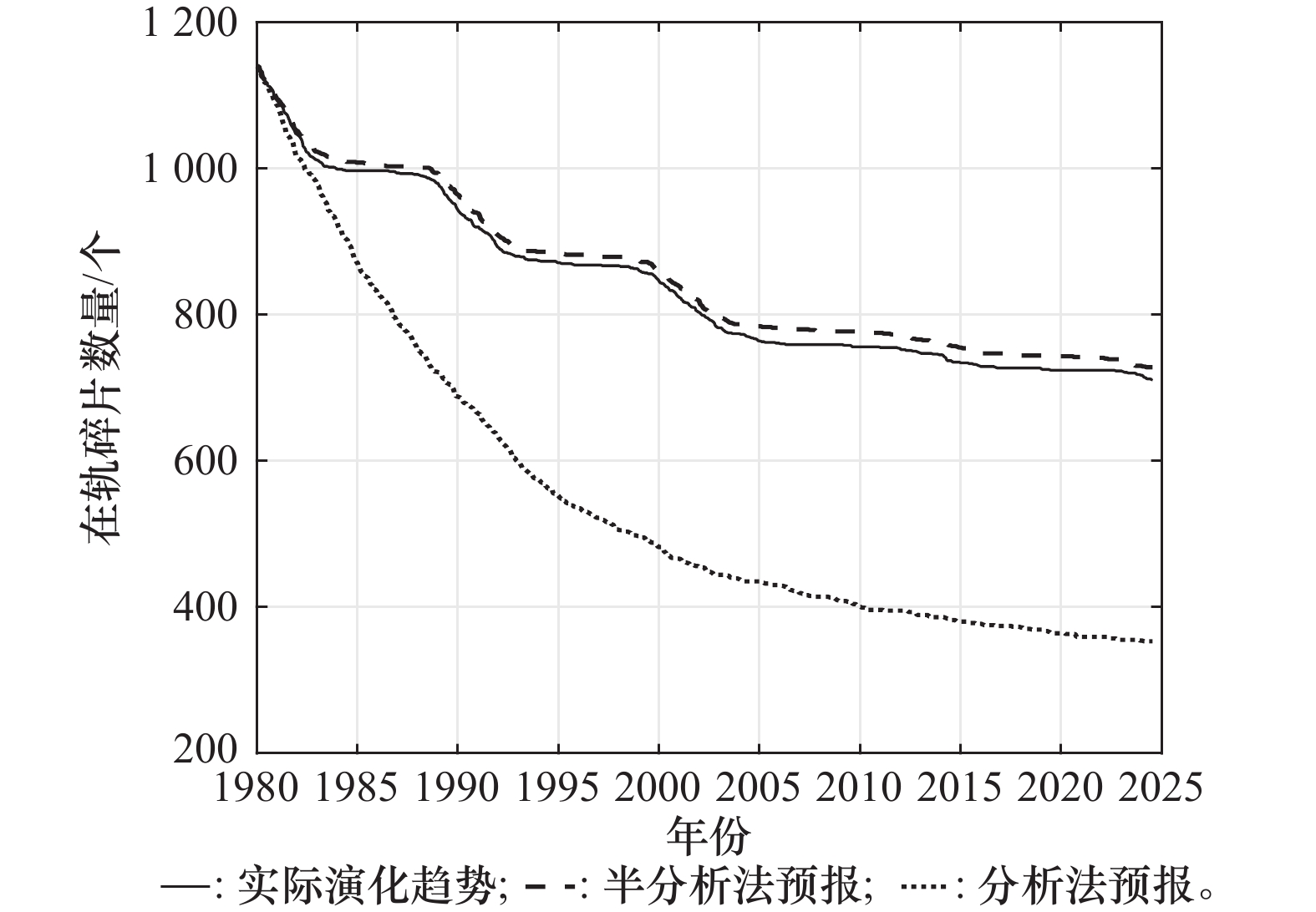
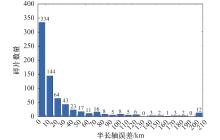
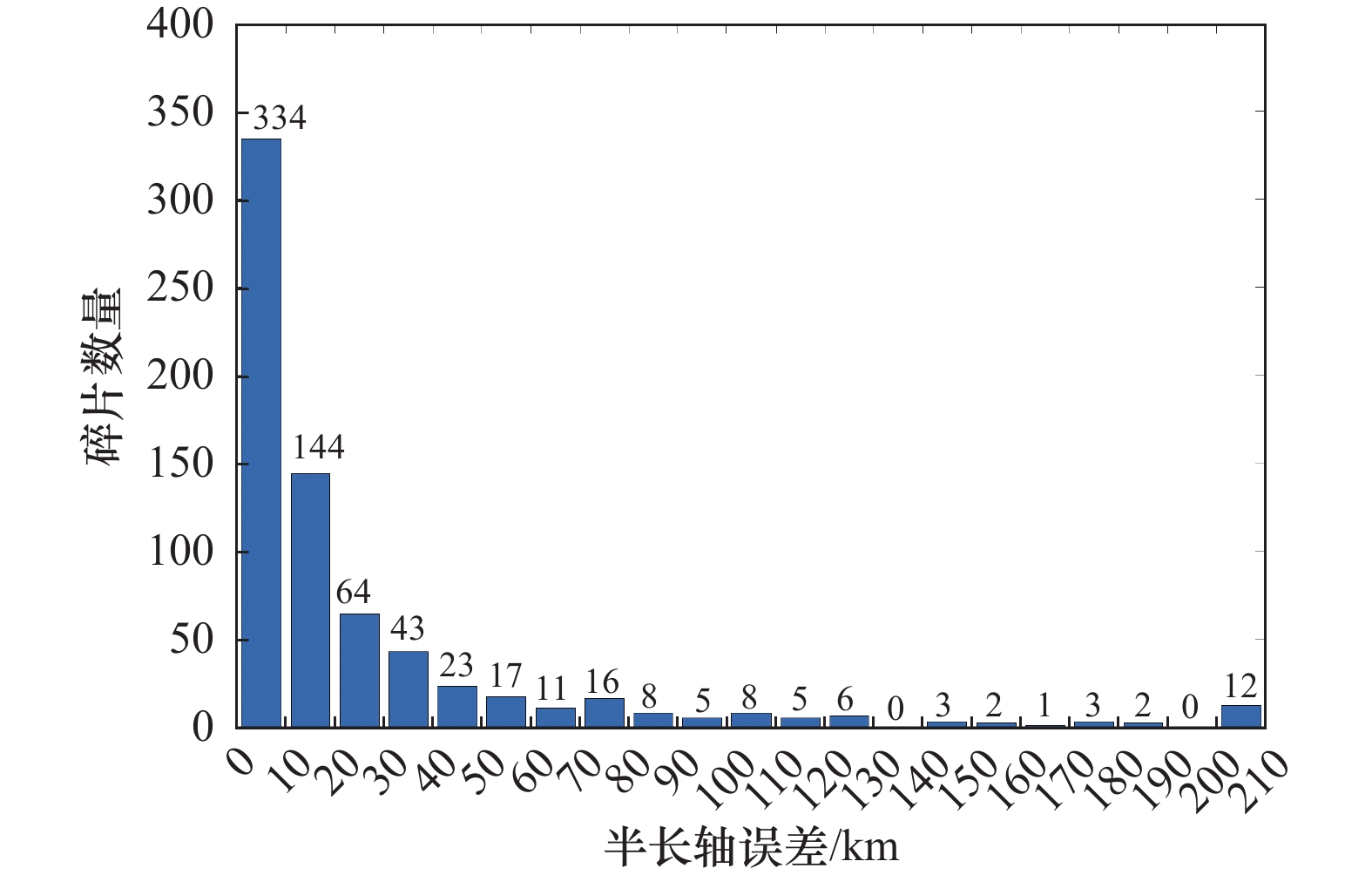
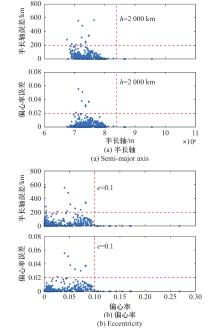
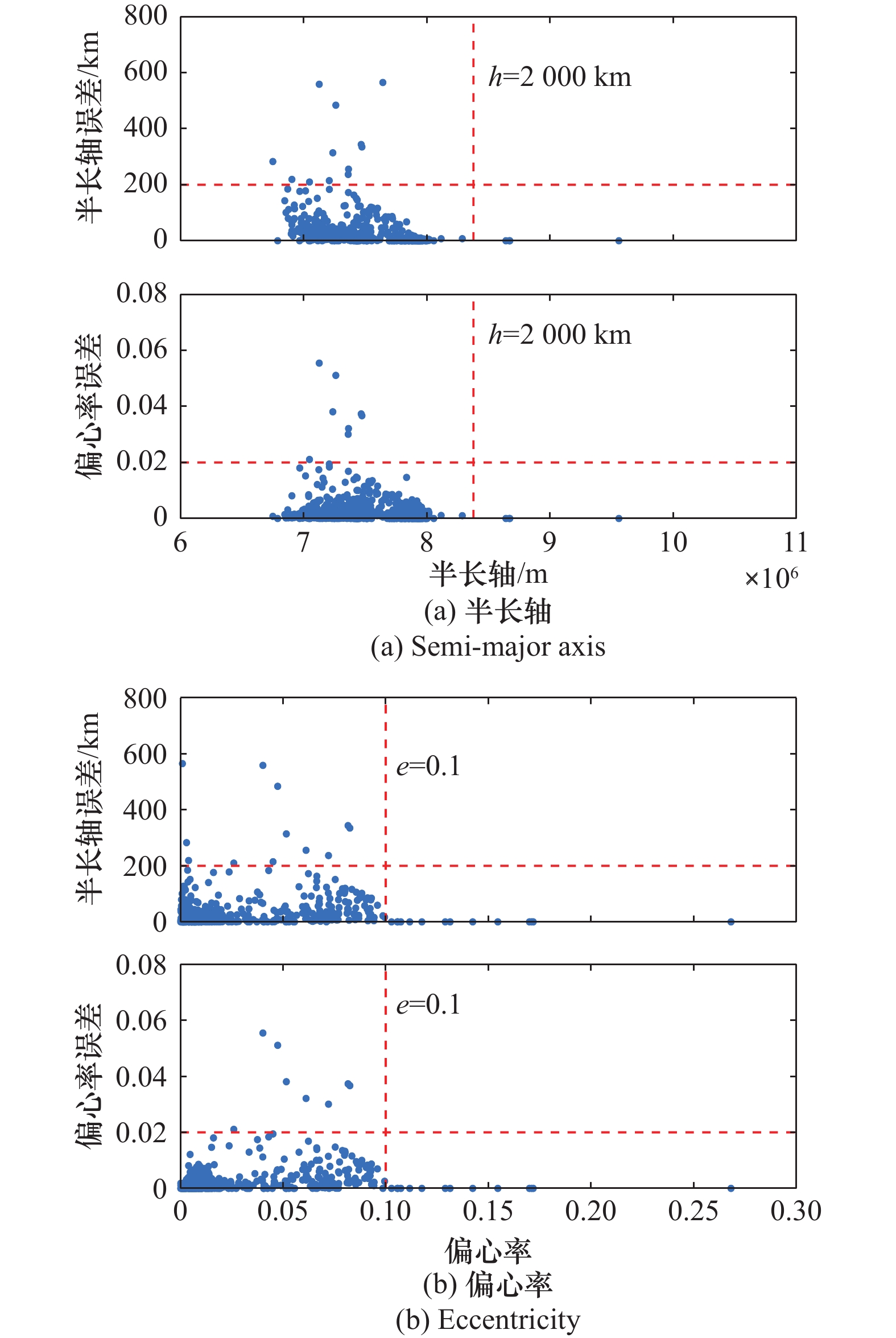
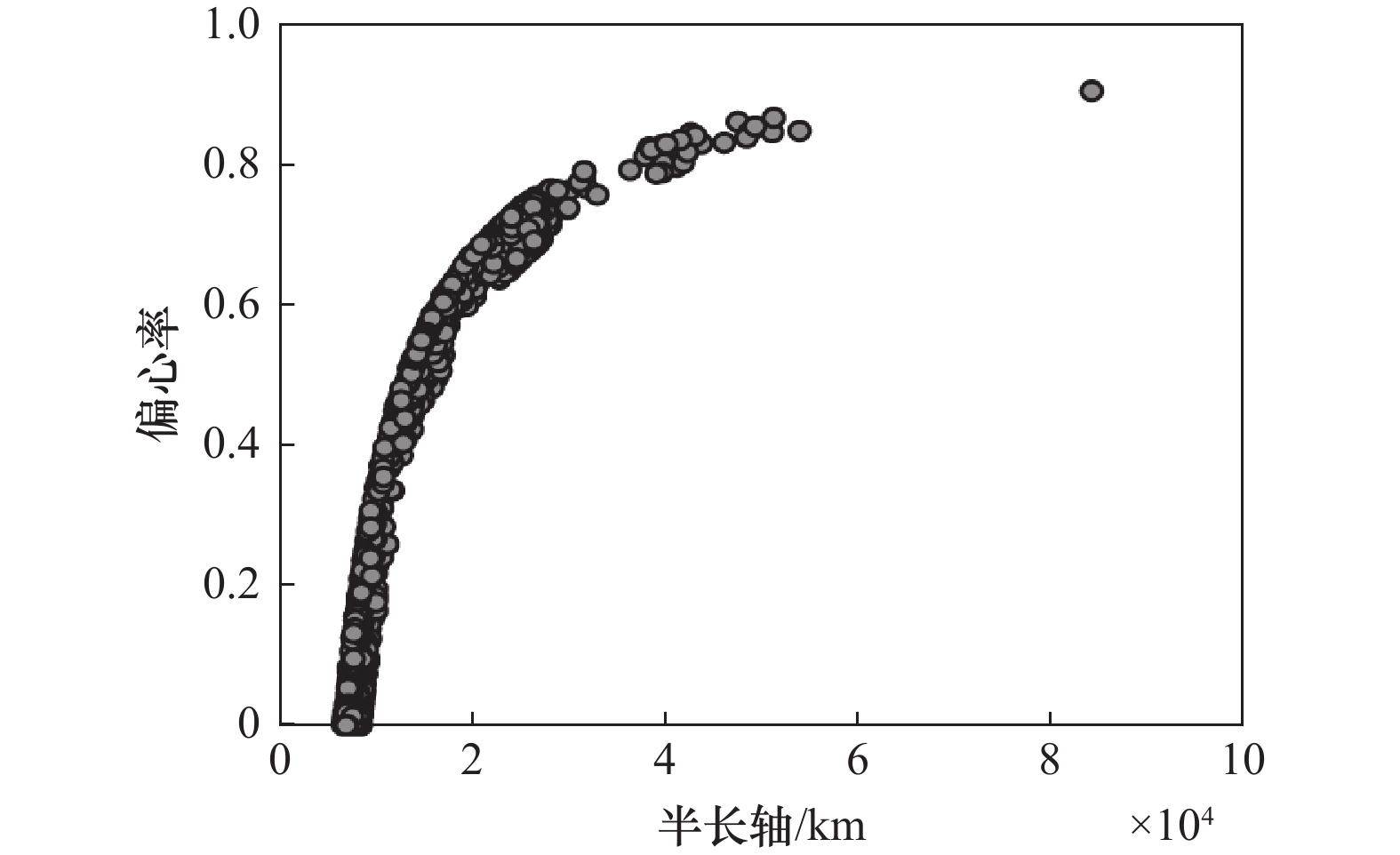
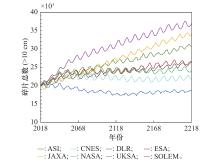
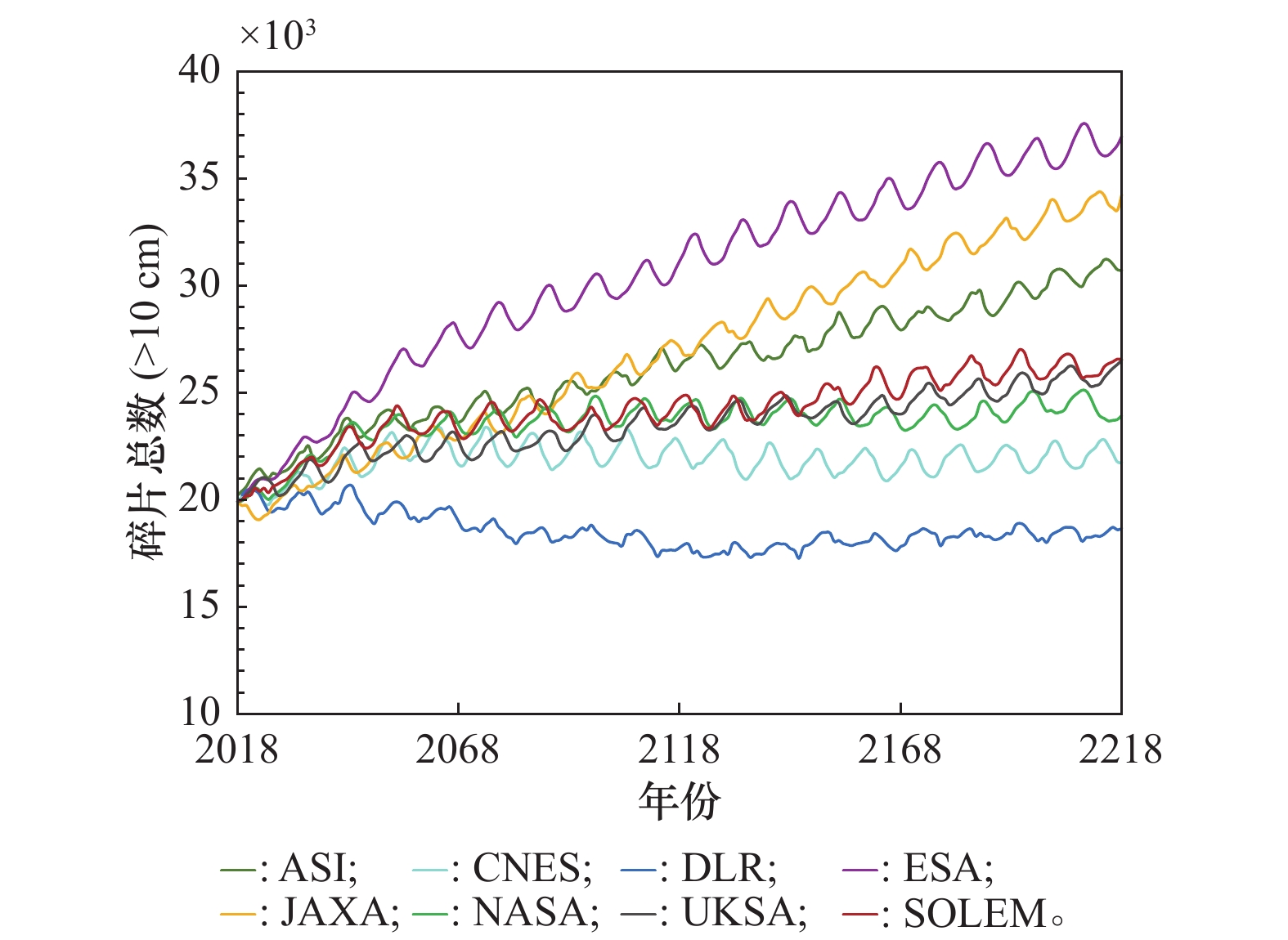
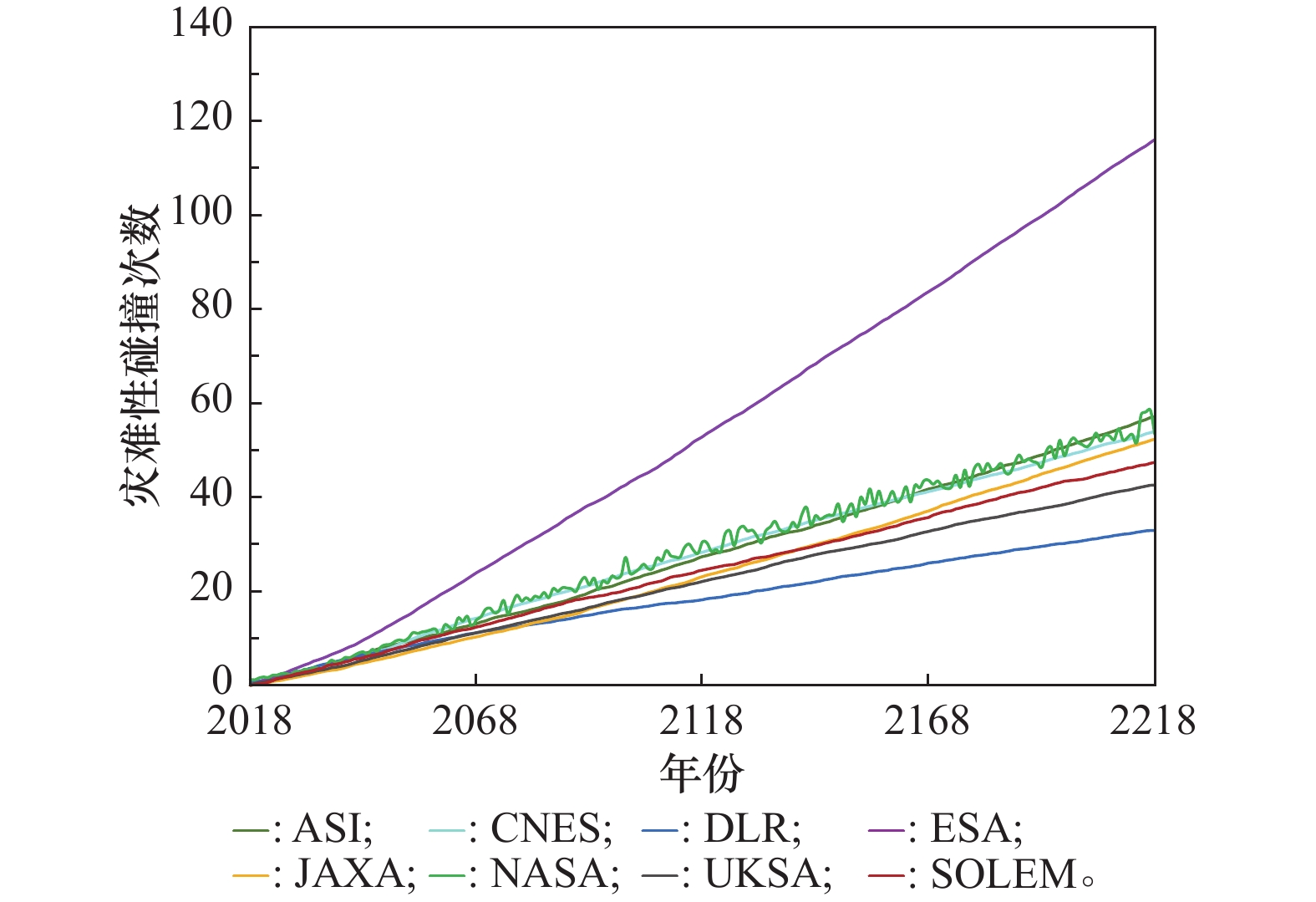
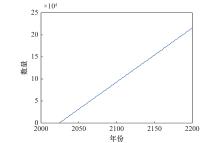
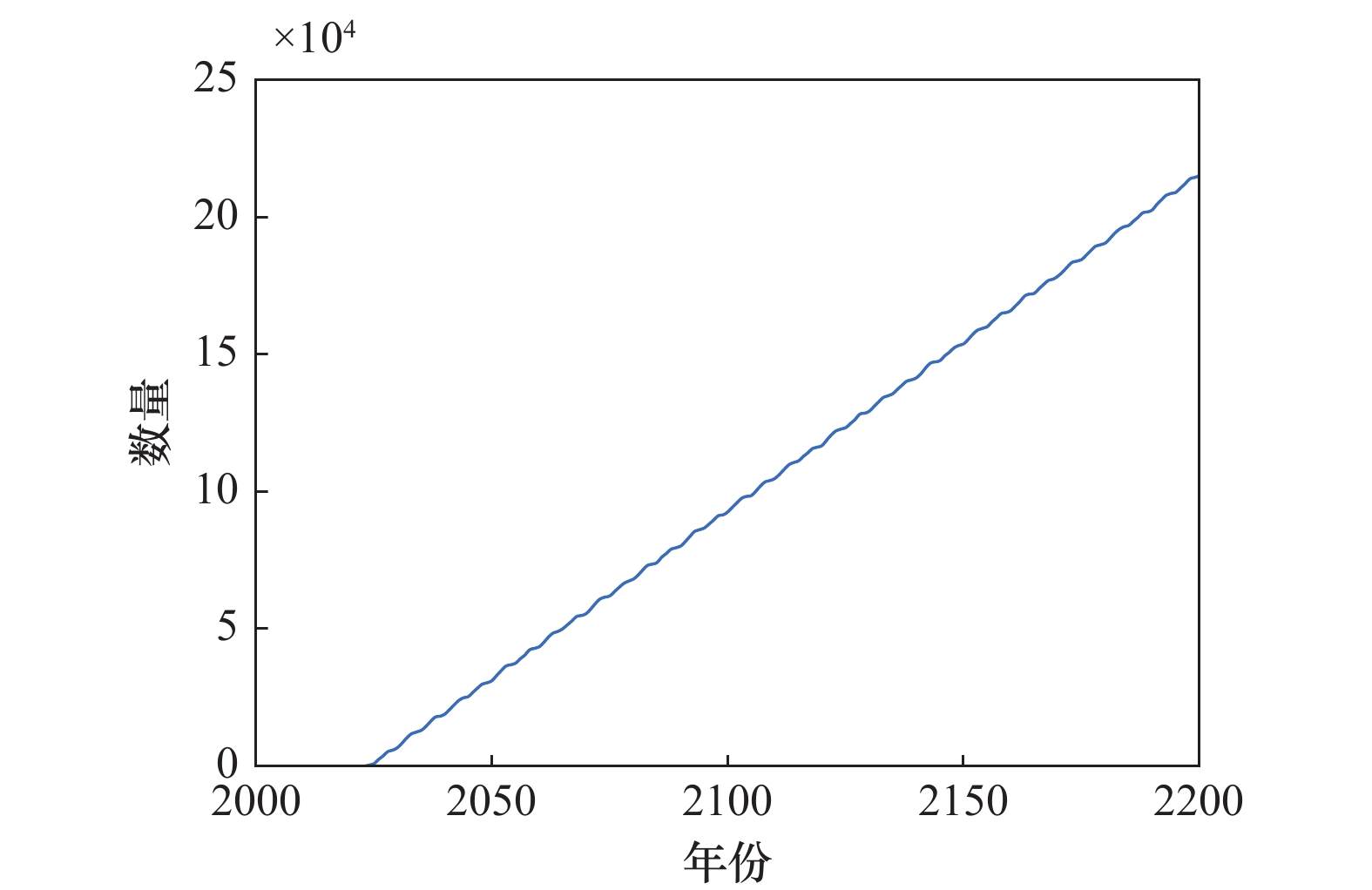
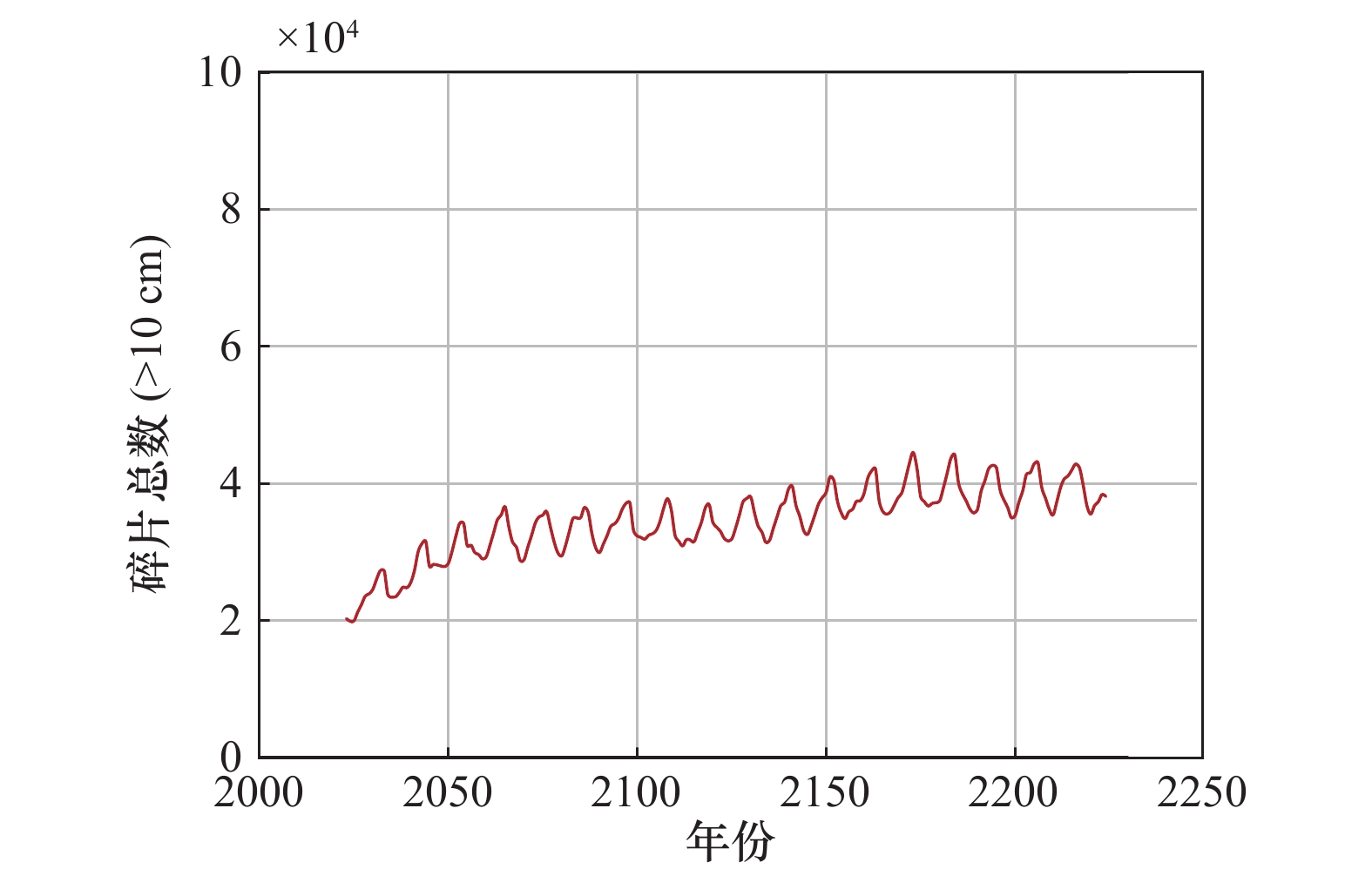
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (9): 3031-3040.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.09.24
• Guidance, Navigation and Control • Previous Articles
Modified SOLEM model based on semi-analytical method and long-term evolution analysis of space debris
Fengchun ZHENG1, Yao ZHANG1,2,*, Jing LIU1,2, Qingbo GAN1,2, Haowen CHENG1,2, Jingshi TANG3
- 1. National Astronomical Observatories,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
2. School of Astronomy and Space Science,University of Chinese Academy of Sciences,Beijing 100101,China
3. School of Astronomy and Space Science,Nanjing University,Nanjing 210023,China
-
Received:2024-08-08Online:2025-09-25Published:2025-09-16 -
Contact:Yao ZHANG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Fengchun ZHENG, Yao ZHANG, Jing LIU, Qingbo GAN, Haowen CHENG, Jingshi TANG. Modified SOLEM model based on semi-analytical method and long-term evolution analysis of space debris[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(9): 3031-3040.
share this article
| 1 | European Space Agency Space Debris Office. ESA’s annual space environment report[R]. Darmstadt: European Space Agency, 2024. |
| 2 | Space Forces-Space. The satellite situation report[EB/OL]. [2024-08-01]. https: //www.space-track.org/#ssr. |
| 3 | ROSSI A, ANSELMO L, PARDINI C, et al. The new space debris mitigation (SDM 4.0) long term evolution code[C]//Proc. of the 5th European Conference on Space Debris, 2009. |
| 4 | DOLADO-PEREZ J C, DI-COSTANZO R, REVELIN B. Introducing MEDEE-a new orbital debris evolutionary model[C]//Proc. of the 6th European Conference on Space Debris, 2013. |
| 5 | BENDISCH J, WEGENER P, REX D. The long-term evolution of debris orbits in view of spatial object accumulation[C]//Proc. of the 2nd European Conference on Space Debris, 1997. |
| 6 |
WALKER R, MARTIN C E, STOKES P H, et al. Analysis of the effectiveness of space debris mitigation measures using the DELTA model[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2001, 28 (9): 1437- 1445.
doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(01)00445-8 |
| 7 |
HARADA R, KAWAMOTO S, HANADA T. Assessments of the impacts of orbital fragmentations using the near-earth orbital debris environment evolutionary model (NEODEEM)[J]. Journal of Space Safety Engineering, 2024, 11 (3): 395- 402.
doi: 10.1016/j.jsse.2024.07.008 |
| 8 |
LIOU J C, HALL D T, KRISKO P H, et al. LEGEND-a three-dimensional LEO-to-GEO debris evolutionary model[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2004, 34 (5): 981- 986.
doi: 10.1016/j.asr.2003.02.027 |
| 9 | LEWIS H G, SWINERD G, WILLIAMS N, et al. DAMAGE: a dedicated GEO debris model framework[C]//Proc. of the 3rd European Conference on Space Debris, 2001. |
| 10 | 王大为, 汤靖师, 刘林, 等. 半分析方法在地球卫星100 yr尺度长期预报中的性能评估[J]. 天文学报, 2017, 58 (1): 20- 45. |
| WANG D W, TANG J S, LIU L, et al. The assessment of the semi-analytical method in the 100-year orbit prediction of earth satellites[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 2017, 58 (1): 20- 45. | |
| 11 | KOZAI Y. The motion of a close earth satellite[J]. The Astronomical Journal, 1959, 64 (8): 367- 377. |
| 12 | 刘林. 卫星轨道力学算法[M]. 南京: 南京大学出版社, 2019. |
| LIU L. Algorithms for satellite orbital dynamics[M]. Nanjing: Nanjing University Press, 2019. | |
| 13 | 吴连大, 王昌彬, 童傅. 人造卫星二阶摄动理论的半分析、半数值方法[J]. 天文学报, 1978, 19 (2): 131- 151. |
| WU L D, WANG C B, TONG F. A new semi-analytical and semi-numerical method for computation of the second order perturbation of artificial Earth satellites[J]. Acta Astronomica Sinica, 1978, 19 (2): 131- 151. | |
| 14 | CEFOLA P J. Equinoctial orbit elements-application to artificial satellite orbits[C]//Proc. of the Astrodynamics Conference, 1972. |
| 15 | CEFOLA P J, FOLCIK Z, DI-COSTANZO R, et al. Revisiting the DSST standalone orbit propagator[C]//Proc. of the Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, 2014. |
| 16 | OBRIEN R T, SANG J Z. Semi-analytic satellite theory using the method of multiple scales[C]//Proc. of the Astrodynamics Specialist Conference and Exhibit, 2004. |
| 17 |
WANG Y, LUO X H, XU X J. Long-term evolution and lifetime analysis of geostationary transfer orbits with solar radiation pressure[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2020, 175, 405- 420.
doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2020.06.007 |
| 18 | LUO X H, WANG Y. Long-term orbital lifetime prediction of highly eccentric orbits: a statistical approach[J]. Journal of Spacecraft and Rockets, 2023, 60 (6): 1712- 1723. |
| 19 | CAZABONNE B, CEFOLA P J. Towards accurate orbit determination using semi-analytical satellite theory[C]//Proc. of the 31st AAS/AIAA Space Flight Mechanics Meeting, 2021. |
| 20 |
SUN P, COLOMBO C, TRISOLINI M, et al. Comparison of continuity equation and Gaussian mixture model for long-term density propagation using semi-analytical methods[J]. Celestial Mechanics and Dynamical Astronomy, 2022, 134, 22.
doi: 10.1007/s10569-022-10066-8 |
| 21 | KHATRI Y, SCHEERES D J. Near-earth semi-analytical uncertainty propagation toolkit for conjunction analysis[C]//Proc. of the Advanced Maui Optical and Space Surveillance Technologies Conference, 2023. |
| 22 |
DUTT P, ANILKUMAR A K. Orbit propagation using semi-analytical theory and its applications in space debris field[J]. Astrophysics and Space Science, 2017, 362 (2): 35.
doi: 10.1007/s10509-017-3008-0 |
| 23 | LIOU J C, ANILKUMAR A K, VIRGILI B B, et al. Stability of the future LEO environment-an IADC comparison study[C]//Proc. of the 6th European Conference on Space Debris, 2013. |
| 24 |
VAN-DER-HA J C. Long-term evolution of near-geostationary orbits[J]. Journal of Guidance, 1986, 9 (3): 363- 370.
doi: 10.2514/3.20115 |
| 25 | MORAND V, DOLADO-PEREZ J C, FRAYSSE H, et al. Semi-analytical computation of partial derivatives and transition matrix using STELA software[C]//Proc. of the 6th European Conference on Space Debris, 2013. |
| 26 |
XAVIER J R, RAM K S. Prediction of satellite orbits contraction due to diurnally varying oblate atmosphere and altitude-dependent scale height using KS canonical elements[J]. Planetary and Space Science, 2009, 57 (11): 1312- 1320.
doi: 10.1016/j.pss.2009.05.007 |
| 27 | WANG X W, LIU J. An introduction to a new space debris evolution model: SOLEM[J]. Advances in Astronomy, 2019, 2019, 2738276. |
| 28 | 沈丹. 空间碎片碰撞预警置信度和长期演化建模影响因素研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2020. |
| SHEN D. Research on confidence level of space debris collision warning and factors in long-term evolution model[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2020. | |
| 29 | 王晓伟. 空间碎片环境长期演化模型与减缓清除策略分析研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2019. |
| WANG X W. Space debris environment long-term evolution model and mitigation and remediation strategies analysis[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Sciences, 2019. | |
| 30 |
JOHNSON N L, KRISKO P H, LIOU J C, et al. NASA’s new breakup model of EVOLVE 4.0[J]. Advances in Space Research, 2001, 28 (9): 1377- 1384.
doi: 10.1016/S0273-1177(01)00423-9 |
| 31 | Inter-Agency Space Debris Coordination Committee. IADC report on the status of the space debris environment[EB/OL]. [2024-08-01]. https://www.iadc-home.org/documents_public. |
| [1] | Enhui WU, Jing LIU, Xu YANG. Minimum orbital intersection distance based space index [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(11): 3784-3791. |
| [2] | Dawei LI, Jing LIU, Xiyan PENG, Yao ZHANG, Yanhao XIE. Initial orbit determination for a near-circular orbit of space debris with space-based short-arcs method and experiment [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2601-2611. |
| [3] | Huachao WANG, Jing LIU, Haowen CHENG, Xiyan PENG. Fast star map recognition algorithm based on fuzzy decision [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1447-1453. |
| [4] | Dan SHEN, Jing LIU. Analysis of the impact of large LEO constellation deployment on the space debris environment [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(9): 2041-2051. |
| [5] | Zhitao YANG, Jing LIU, Lin LIU. Improved method of orbit analytical solution and its application [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(2): 427-433. |
| [6] | WANG Weijie, LI Yiyong, LUO Wen, ZHANG Feizhou, ZHANG Jiang. Mission analysis on removal of space debris with spacebased laser [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2019, 41(6): 1374-1382. |
| [7] | AN Kai. Space debris positioning technology based on stereo vision [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(9): 1841-1845. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||