Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (1): 41-51.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.01.05
• Electronic Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Ship multiple-object tracking model in remote sensing scene based on inertial prediction
Chaofan PAN1, Runsheng LI1,*, Qing HU2, Quanfu BAO3, Yongqiang BAO4
- 1. School of Data and Target Engineering, University of Information Engineering, Zhengzhou 450001, China
2. Unit 61191 of the PLA, Hangzhou 310000, China
3. Unit 95806 of the PLA, Beijing 100076, China
4. Beijing Aerospace Remote Sensing International Technology Development Co. LTD, Beijing 100076, China
-
Received:2023-03-07Online:2025-01-21Published:2025-01-25 -
Contact:Runsheng LI
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Chaofan PAN, Runsheng LI, Qing HU, Quanfu BAO, Yongqiang BAO. Ship multiple-object tracking model in remote sensing scene based on inertial prediction[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(1): 41-51.
share this article
Table 2
SMOT information statistics"
| 数据集 | 视频序列数目 | 轨迹数目 | 真值框数目 | 帧数 | 分辨率 | 目标类别 |
| 训练集 | 12 | 299 | 107 940 | 1 000~1 300 | 800×800 | 1: Air. 2: Was. 3: Tar 4: Oth. 5: Aus. 6: Whi. 7: San. 8: New. 9: Tic. 10: Bur. 11: Per. 12: Lew. 13: Sup. 14: Kai. 15: Hop. 16: Mer. 17: Fre. 18: Ind. 19: Ave. 20: Sub. |
| 验证集 | 3 | 64 | 30 051 | 1 000~1 300 | 800×800 | |
| 测试集 | 5 | 107 | 44 661 | 1 000~1 300 | 800×800 |
Table 3
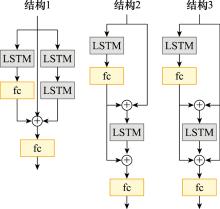
Influence of different tracker structure and hidden layer width"
| ResLSTM | 隐藏层宽度 | MOTA↑/% | MOTP↑/% | IDF1↑/% | IDs↓ | MT↑/% | Frag↓ | Size↓/kB |
| 结构1 | 32 | 60.4 | 79.9 | 64.3 | 162 | 45.2 | 981 | 159 |
| 64 | 59.9 | 79.8 | 62.7 | 179 | 46.9 | 1 002 | 483 | |
| 128 | 59.9 | 79.9 | 63.1 | 185 | 48.1 | 980 | 1 709 | |
| 256 | 59.7 | 79.9 | 63.4 | 173 | 43.3 | 996 | 6 463 | |
| 512 | 59.8 | 79.8 | 62.8 | 172 | 44.5 | 995 | 25 187 | |
| 结构2 | 32 | 53.0 | 80.1 | 56.6 | 281 | 37.2 | 1 227 | 440 |
| 64 | 53.4 | 79.3 | 56.9 | 299 | 38.9 | 1 254 | 1 362 | |
| 128 | 54.9 | 79.9 | 59.8 | 238 | 39.9 | 1 236 | 4 934 | |
| 256 | 55.0 | 79.9 | 59.2 | 253 | 41.8 | 1 202 | 18 990 | |
| 512 | 56.8 | 79.8 | 61.9 | 213 | 43.3 | 1 141 | 74 750 | |
| 结构3 | 32 | 60.9 | 79.8 | 65.3 | 161 | 46.9 | 985 | 94 |
| 64 | 61.2 | 79.8 | 65.7 | 163 | 48.8 | 977 | 253 | |
| 128 | 59.7 | 79.9 | 64.1 | 173 | 44.0 | 990 | 858 | |
| 256 | 59.4 | 79.9 | 63.4 | 183 | 44.0 | 1 028 | 3 220 | |
| 512 | 59.8 | 79.8 | 63.6 | 186 | 45.2 | 1 007 | 12 552 |
Table 4
Influence of each module on the tracing result"
| 方法 | ResLSTM | ACM | MOTA↑/% | MOTP↑/% | IDF1↑/% | IDs↓ | MT↑/% | ML↓/% | Frag↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | FPS↑ |
| 基线模型 | √ | - | 57.3 | 80.2 | 58.5 | 226 | 35.6 | 8.5 | 1 490 | 3 235 | 15 868 | 14.0 |
| √ | - | 59.2 | 79.6 | 62.6 | 190 | 45.6 | 6.1 | 1 020 | 4 625 | 13 614 | 14.2 | |
| √ | √ | 58.2 | 80.3 | 60.5 | 186 | 36.5 | 9.3 | 1 463 | 3 064 | 15 665 | 14.4 | |
| 本文方法 | √ | √ | 61.2 | 79.8 | 65.7 | 163 | 48.8 | 6.1 | 977 | 4 054 | 13 371 | 14.1 |
Table 5
Performance comparison on video sequence test set"
| 方法 | MOTA↑/% | IDF1↑/% | IDs↓ | MT↑/% | ML↓/% | Frag↓ | FP↓ | FN↓ | FPS↑ |
| SORT[ | 54.8 | 42.8 | 811 | 34.4 | 11.6 | 1 144 | 2 766 | 16 925 | 43.1 |
| ByteTrack[ | 55.4 | 44.0 | 730 | 38.5 | 10.7 | 1 076 | 4 007 | 15 461 | 40.8 |
| DeepSORT[ | 57.3 | 58.5 | 226 | 35.6 | 8.5 | 1 490 | 3 235 | 15 868 | 14.0 |
| IPMOT | 61.2 | 65.7 | 163 | 48.8 | 6.1 | 977 | 4 054 | 13 371 | 14.1 |
| 1 | BOLME D S, BEVERIDGE J R, DRAPER B A, et al. Visual object tracking using adaptive correlation filters[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Computer Society Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2010: 2544-2550. |
| 2 | HENRIQUES J F, CASEIRO R, MARTINS P, et al. Exploiting the circulant structure of tracking-by-detection with kernels[C]// Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2012: 702-715. |
| 3 | HENRIQUES J F , CASEIRO R , MARTINS P , et al. High-speed tracking with kernelized correlation filters[J]. IEEE Trans. on Pattern Analysis & Machine Intelligence, 2015, 37 (3):583-596. |
| 4 | KIANI G H, FAGG A, LUCEY S. Learning background-aware correlation filters for visual tracking[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, 2017: 1135-1143. |
| 5 | LI Y, ZHU J K. A scale adaptive kernel correlation filter tracker with feature intergration[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2014: 254-265. |
| 6 | YUN S D, CHOI J W, YOO Y J, et al. Action-decision networks for visual tracking with deep reinforcement learning[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2017: 2711-2720. |
| 7 | 刘志强, 任世恒. 复杂场景下基于OSA改进的多目标跟踪算法研究[J]. 信息技术, 2022, (4): 123- 129. |
| LIU Z Q , REN S H . Research on multi-target tracking algorithm based on improved OSA in complex scenes[J]. Information Technology, 2022, (4): 123- 129. | |
| 8 | 王彬彬. 基于SVM与Meanshift跟踪算法的运动视频目标跟踪[J]. 现代电子技术, 2022, 45 (1): 56- 60. |
| WANG B B . Moving video object tracking based on SVM and meanshift tracking algorithm[J]. Modern Electronics Technique, 2022, 45 (1): 56- 60. | |
| 9 | 张文利, 辛宜桃, 杨堃, 等. 基于改进的Transformer加Anchor-free网络的多目标跟踪算法[J]. 测控技术, 2022, 41 (2): 20- 28. |
| ZHANG W L , XIN Y T , YANG K , et al. Improved Transformer plus Anchor-free network based on multi-object tracking algorithm[J]. Measurement & Control Technology, 2022, 41 (2): 20- 28. | |
| 10 | BEWLEY A, GE Z, OTT L, et al. Simple online and realtime tracking[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2016: 3464-3468. |
| 11 | WOJKE N, BEWLEY A, PAULUS D. Simple online and realtime tracking with a deep association metric[C]//Proc. of the IEEE International Conference on Image Processing, 2017: 3645-3649. |
| 12 | ZHANG Y F, SUN P Z, JIANG Y, et al. ByteTrack: multi-object tracking by associating every detection box[EB/OL]. [2023-01-07]. https://arXivpreprintarXiv:2110.06864, 2021. |
| 13 | WANG Z D, ZHENG L, LIU Y X, et al. Towards real-time multi-object tracking[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 107-122. |
| 14 | ZHANG Y F, WANG C Y, WANG X G, et al. A simple baseline for multi-object tracking[EB/OL]. [2023-01-07]. https://arXivpreprintarXiv:2004.01888. |
| 15 | PENG J L, WANG C G, WAN F B, et al. Chained-tracker: chaining paired attentive regression results for end-to-end joint multiple-object detection and tracking[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 145-161. |
| 16 | ZHOU X Y, KOLTUN V, KRÄHENBVHL P. Tracking objects as points[C]//Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2020: 474-490. |
| 17 | SUN P Z, JIANG Y, ZHANG R F, et al. Transtrack: multiple object tracking with transformer[EB/OL]. [2023-01-07]. https://arXivpreprintarXiv:2012.15460, 2020. |
| 18 | MEINHARDT T, KIRILLOV A, LEAL-TAIXE L, et al. Trackformer: multi-object tracking with transformers[C]//Proc. of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2022: 8844-8854. |
| 19 | ZENG F G, DONG B, ZHANG Y, et al. Motr: end-to-end multiple-object tracking with transformer[EB/OL]. [2023-01-07]. https://arXivpreprintarXiv:2105.03247, 2021. |
| 20 | VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N, et al. Attention is all you need[C]//Proc. of the Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems, 2017. |
| 21 | SHI X J, CHEN Z R, WANG H, et al. Convolutional LSTM network: a machine learning approach for precipitation nowcasting[C]//Proc. of the 28th International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems, 2015: 802-810. |
| 22 | KALMAN R E . A new approach to linear filtering and prediction problems[J]. Journal of Basic Engineering, 1960, 82 (D): 35- 45. |
| 23 | ZAREMBA W, SUTSKEVER I, VINYALS O. Recurrent neural network regularization[EB/OL]. [2023-01-07]. https://arXivpreprintarXiv:1409.2329, 2014. |
| 24 | HE K M, ZHANG X Y, REN S Q, et al. Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2016: 770-778. |
| 25 | BALDUZZI D, FREAN M, LEARY L, et al. The shattered gradients problem: if resnets are the answer, then what is the question?[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Machine Learning, 2017: 342-350. |
| 26 | LECUN Y , BOTTOU L , BENGIO Y , et al. Gradient-based learning applied to document recognition[J]. Proceedings of the IEEE, 1998, 86 (11): 2278- 2324. |
| 27 | ZHANG F , WANG X Y , ZHOU S L , et al. Arbitrary-oriented ship detection through center-head point extraction[J]. IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2021, 60 (1): 5612414. |
| 28 | BERNARDIN K , STIEFELHAGEN R . Evaluating multiple object tracking performance: the clear mot metrics[J]. EURASIP Journal on Image and Video Processing, 2008, 246309. |
| 29 | RISTANI E, SOLERA F, ZOU R S, et al. Performance mea-sures and a data set for multi-target, multi-camera tracking[C]// Proc. of the European Conference on Computer Vision, 2016: 17-35. |
| 30 | LI Y, HUANG C, NEVATIA R. Learning to associate: hybridboosted multi-target tracker for crowded scene[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, 2009: 2953-2960. |
| [1] | Hongmeng CHEN, Jun LI, Jing LIU, Wei HUANG, Yingjie ZHANG, Yan CHEN, Yaobing LU. SAR-ISAR hybrid imaging method for sea surface ship target based on Radon time-frequency analysis [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(1): 109-116. |
| [2] | Qian CHENG, Jia LI, Juan DU. Ship target detection algorithm of optical remote sensing image based on YOLOv5 [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(5): 1270-1276. |
| [3] | Runlin LI, Huanxin ZOU, Xu CAO, Fei CHENG, Shitian HE, Meilin LI. Multi-direction remote sensing ship detection based on center point and semantic information [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1772-1781. |
| [4] | Chaofan PAN, Runsheng LI, Yan XU, Qing HU, Chaoyang NIU, Wei LIU. Ship detection of optical remote sensing images based on aware vectors [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3631-3640. |
| [5] | Yu LEI, Xiangguang LENG, Xiaoyan ZHOU, Zhongzhen SUN, Kefeng JI. Recognition method of ship target in complex SAR image based on improved ResNet network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3652-3660. |
| [6] | Xiaoya JIA, Hongqiao WANG, Yadan YANG, Zhongma CUI, Bin XIONG. Anchor free SAR image ship target detection method based on the YOLO framework [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3703-3709. |
| [7] | Yonggang LI, Weigang ZHU, Qiongnan HUANG, Yuntao LI, Yonghua HE. Near-shore ship target detection with SAR images in complex background [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3096-3103. |
| [8] | ZHAO Zhiguo, XIAO Hui. Approach to correct ionospheric phase perturbation based on Toeplitz matrix [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2017, 39(5): 1024-1029. |
| [9] | GUO Shao-jun, SHEN Tong-sheng, XU Jian, MA Xin-xing. Detection of multi-ship targets at sea based on ObjectNess BING [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2016, 38(1): 14-20. |
| [10] | ZHAO Zhiguo, XIAO Hui. Spread Doppler clutter suppression approach in FRFT field for hybrid skysurfacewave radars [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2014, 36(12): 2411-2416. |
| [11] | ZHAO Zhi-guo, CHEN Jian-wen, BAO Zheng. Modified adaptive ocean clutter suppression approach in OTHR [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(5): 909-914. |
| [12] | YU Ding-feng,CHEN Qian,YAO Jing-jing,HE Si-yuan,ZHU Guo-qiang,HU Wei-dong. Simulation of HRRP characteristics for maritime ship targets [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2010, 32(12): 2552-2556. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||