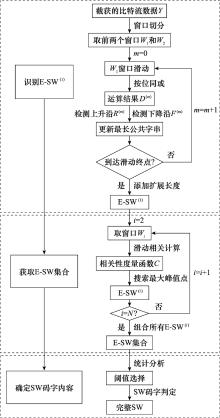
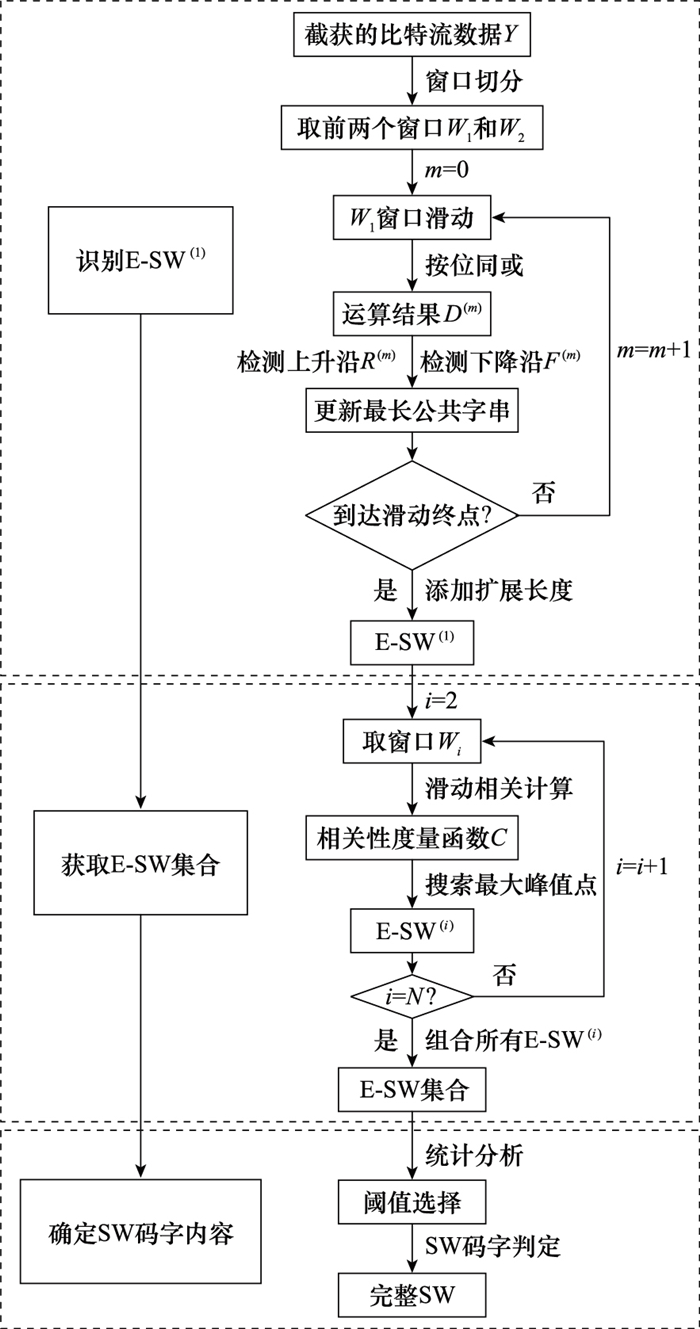
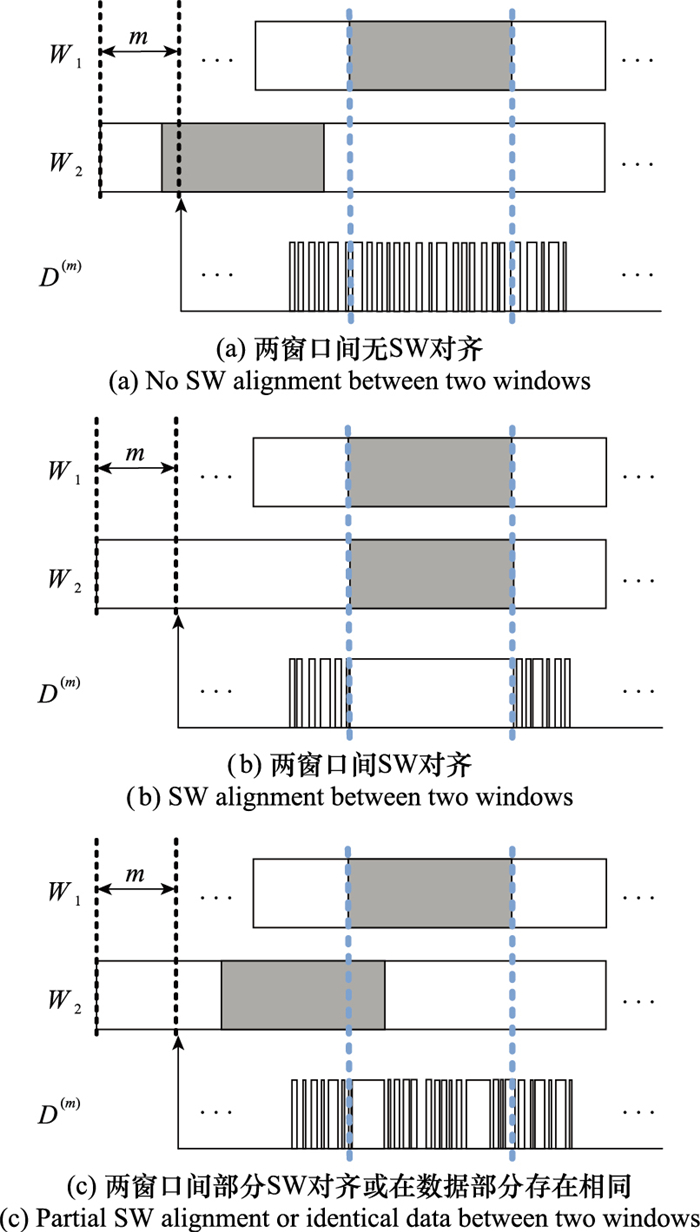
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2024, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (10): 3567-3576.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.10.33
• Communications and Networks • Previous Articles
Blind recognition algorithm for non-equal length frame synchronization word based on two window-sliding operations
Yuanqing WANG, Pengjiang HU, Jun'an YANG, Hui LIU
- Institute of Electronic Countermeasures, National University of Defense Technology, Hefei 230037, China
-
Received:2023-06-29Online:2024-09-25Published:2024-10-22 -
Contact:Jun'an YANG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Yuanqing WANG, Pengjiang HU, Jun'an YANG, Hui LIU. Blind recognition algorithm for non-equal length frame synchronization word based on two window-sliding operations[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(10): 3567-3576.
share this article
Table 2
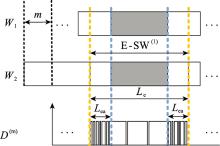
Output results of each intermediate step of the algorithm"
| 变量 | 输出结果 | 长度或维度 |
| E-SW(1) | 10111101001001000$\underline 1$1110011110001111110011100111000 | 49比特 |
| E-SW集合 |  | N维×49比特(N=63) |
| γsum(保留2位小数) | [0.59 0.54 0.48 0.60 0.46 0.49 0.44 0.540 0 0.98 0.03 0.02 1 0 0 0 0.05 1 1 0.98 0 0.02 1 0.97 1 1 0.03 0 0.02 1 1 1 1 0.98 0.98 0 0 0.98 1 0.52 0.51 0.44 0.46 0.52 0.57 0.46 0.62 0.54] | 49比特 |
| SW | 00100100001110011110001111110011 | 32比特 |
| 1 | 薛开平, 柳彬, 王劲松, 等.面向链路比特流的未知帧关联分析[J].电子与信息学报,2017,39(2):374-380. |
| XUE K P , LIU B , WANG J S , et al.Data link bit stream oriented association on unknown frame[J].Journal of Electronics & Information Technology,2017,39(2):374-380. | |
| 2 |
KIL Y S , LEE H , KIM S H , et al.Analysis of blind frame recognition and synchronization based on Sync word periodicity[J].IEEE Access,2020,8,147516-147532.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3014426 |
| 3 | PRATIK P B, KALYANKUMAR B. Non-cooperative denial of communication after synchronizing with repeating sequences[C]//Proc. of the Defense Science Research Conference and Expo, 2011. |
| 4 |
XU Y Y , ZHONG Y , HUANG Z P .An improved blind recognition algorithm of frame parameters based on self-correlation[J].Information,2019,10(2):64-72.
doi: 10.3390/info10020064 |
| 5 | 白彧, 杨晓静, 王懋.基于相关滤波和哈达玛变换的帧同步码识别[J].探测与控制学报,2011,33(3):69-72, 80. |
| BAI Y , YANG X J , WANG M .Recognition method of frame synchronization codes based on relativity filter and Hadamard transformation algorithm[J].Journal of Detection and Control,2011,33(3):69-72, 80. | |
| 6 |
SUWANSANTISUK W , CHIANI M , WIN M Z .Frame synchronization for variable-length packets[J].IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications,2008,26(1):52-69.
doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2008.080106 |
| 7 |
QIN J Y , HUANG Z P , LIU C W , et al.Novel blind recognition algorithm of frame synchronization words based on soft-decision in digital communication systems[J].PLoS ONE,2015,10(7):e0132114.
doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0132114 |
| 8 | 熊颢, 雷迎科, 吴子龙.基于码元密度检测的帧同步码盲识别算法[J].探测与控制学报,2021,43(1):73-78. |
| XIONG H , LEI Y K , WU Z L .Frame synchronization code blind recognition based on symbol density detection[J].Journal of Detection & Control,2021,43(1):73-78. | |
| 9 | 陈庆超, 王韬, 冯文博, 等.基于最长公共子串挖掘的未知链路层协议帧切割算法[J].计算机科学,2020,47(7):227-230. |
| CHEN Q C , WANG T , FENG W B , et al.Unknown link layer protocol frame segmentation algorithm based on longest common substrings mining[J].Computer Science,2020,47(7):227-230. | |
| 10 | 李永辉, 陈小莉, 吴彩凤, 等.一种非等长帧同步识别与参数提取算法[J].电子测量技术,2019,42(22):123-128. |
| LI Y H , CHEN X L , WU C F , et al.A non-equal length frame algorithm of synchronization recognition and parameter extraction[J].Electronic Measurement Technology,2019,42(22):123-128. | |
| 11 | 李歆昊, 张旻, 韩树楠.基于多重分形谱的链路层协议帧同步字盲识别[J].电子与信息学报,2017,39(7):1666-1672. |
| LI X H , ZHANG M , HAN S N .Frame synchronization word identification of link layer protocol based on multi-fractal spectrum[J].Journal of Electronics & Information Technology,2017,39(7):1666-1672. | |
| 12 | LEI Y K, CAO C H. Frame segmentation in the link layer bit stream data based on directed graph[C]//Proc. of the 12th International Conference on Communication Software and Networks, 2020: 58-62. |
| 13 | LI X H , MA T , QIAN Q S .Frame synchronization method based on association rules for CNAV-2 messages[J].Chinese Journal of Electronics,2023,32(2):295-302. |
| 14 | PAN C S, GUO Z P, YANG L, et al. Frame synchronization word identification of link layer protocol based on N-ECLAT algorithm[C]//Proc. of the 8th International Conference on Instrumentation & Measurement, Computer, Communication and Control, 2018. |
| 15 | SONG J M, KIL Y S, KIM S H. Blind frame syncword detection using deep neural networks with input linear filtering[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Information and Communication Technology Convergence, 2019: 1039-1041. |
| 16 | KIL Y S , SONG J M , KIM S H , et al.Deep learning aided blind synchronization word estimation[J].IEEE Access,2021,9,30321-30334. |
| 17 | YANG T C, HE D X, LU Z P, et al. BiLSTM-based frame synchronization for overlapped S-AIS signals: a learning empowered approach[C]//Proc. of the IEEE/CIC International Conference on Communications in China, 2023. |
| 18 | SARUNAS K , LOUISE H C , ROBERT W S .Training deep filters for physical-layer frame synchronization[J].IEEE Open Journal of the Communications Society,2022,3,1063-1075. |
| 19 | RODRIGUE I , SEBASTIEN H .On blind frame synchronization of LDPC codes[J].IEEE Communications Letters,2021,25(10):3190-3194. |
| 20 | DING X H , ZHOU K X , LI G Y , et al.Customized joint blind frame synchronization and decoding methods for analog LDPC decoder[J].IEEE Trans.on Communications,2023,72(2):756-770. |
| 21 | DING Y, HUANG Z P, LI L Q. Joint blind frame synchronization and encoder identification of LDPC codes[C]//Proc. of the 7th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing, 2022: 825-829. |
| 22 | FENG Z X , LIU Y , ZHANG S Y , et al.Polar-coding-assisted blind frame synchronization based on soft information of frozen bits[J].IEEE Communications Letters,2023,27(10):2563-2567. |
| 23 | 华博, 毛忠阳, 康家方, 等.基于非等量采样的伪码同步技术研究[J].系统工程与电子技术,2022,44(4):1401-1408. |
| HUA B , MAO Z Y , KANG J F , et al.Research on pseudo-random noise code synchronization technology based on non-commensurate sampling[J].Systems Engineering and Electronics,2022,44(4):1401-1408. | |
| 24 | ANTONIO A D , MICHELE M .Symbol-spaced feedforward techniques for blind bit synchronization and channel estimation in FSO-OOK communications[J].IEEE Trans.on Communications,2024,72(1):361-374. |
| 25 | SAMEER B , AMEER P M , DAVID K R .Synchronization techniques for underwater acoustic communications[J].International Journal of Communication Systems,2023,36(15):e5563. |
| 26 | JIN M C, ZHANG S T, HE X D, et al. Blind recognition of frame synchronization in time-code domain[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Ubiquitous Communication, 2023. |
| 27 | RODRIGUE I , SEBASTIEN H .Theoretical analysis of a map based blind frame synchronizer[J].IEEE Trans.on Wireless Communications,2009,8(11):5472-5476. |
| 28 | LIANG Y S , DINESH R , OREN E E .Sequential frame synchronization based on hypothesis testing with unknown channel state information[J].IEEE Trans.on Communications,2018,63(8):2972-2984. |
| 29 | SUI H T .Optimum frame synchronization and performance over binary symmetric channel[J].Journal of Electronics,1992,9(3):200-208. |
| 30 | RAMAMOORTHY M S , JALIHAL D , RAMAIYAN V .Optimal frame synchronization under general arrivals[J].IEEE Trans.on Communications,2018,66(11):5704-5717. |
| [1] | Yao WANG, Cong WANG, Xiang WANG, Zhitao HUANG. Non-punctured polar code parameter recognition algorithm based on soft decision [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(10): 3293-3301. |
| [2] | Jianxing LIU, Tianqi ZHANG, Haojun BAI, Shaopeng YE. Blind recognition algorithm of polar code based on information matrix estimation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 668-676. |
| [3] | Yuyuan ZHANG, Limin ZHANG, Wenjun YAN. SFBC-OFDM recognition method based on cross-correlation feature map and dilated dense convolutional neural networks [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(9): 2657-2664. |
| [4] | Zhaojun WU, Limin ZHANG, Zhaogen ZHONG. Recognition of convolutional interleaver at low SNR [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(2): 546-554. |
| [5] | Wenjun YAN, Yuyuan ZHANG, Qing LING, Keyuan YU, Kaiwen TAN, Hengyan LIU. Blind recognition algorithm of space frequency block codes based on frequency domain cross correlation sequence and peak detection [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3709-3715. |
| [6] | Yuyuan ZHNAG, Wenjun YAN, Limin ZHANG, Yuan ZHANG. Blind recognition algorithm of serial space-time block code based on convolutional neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3360-3370. |
| [7] | Tianqi ZHANG, Congcong FAN, Shengqi YU, Jiangen ZHAO. Blind recognition of orthogonal and non-orthogonal space-time block codes based on JADE and feature extraction [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(4): 933-939. |
| [8] | WANG Feng-hua XIE Hui, HUANG Zhi-tao, LIU Xiao-guang. Blind recognition of linear block code based on spectral cumulants [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2013, 35(12): 2595-2599. |
| [9] | LI Yi-bing, Ge Juan, LIN Yun. Modulation recognition using entropy features and SVM [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2012, 34(8): 1691-1695. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||