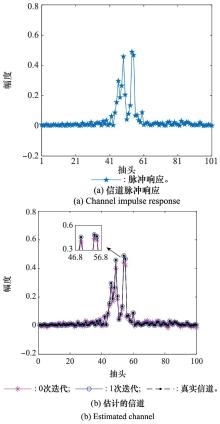
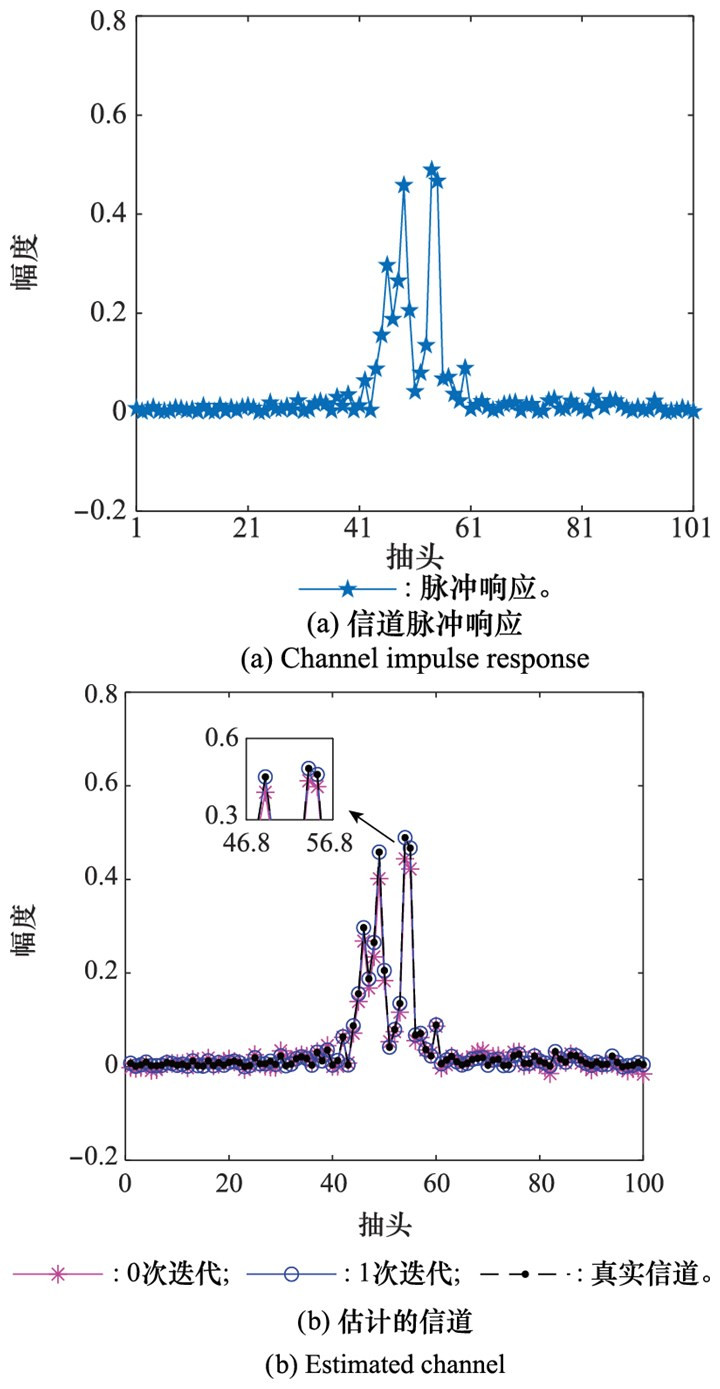
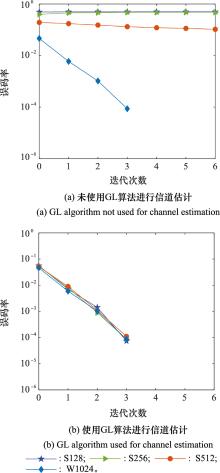
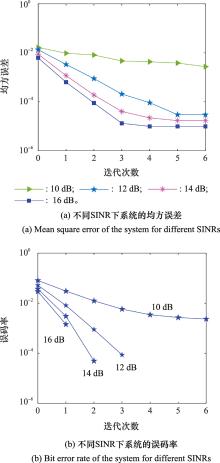
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 46 ›› Issue (1): 334-344.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.01.38
• Communications and Networks • Previous Articles
Accurate underwater acoustic channel estimation based on Gaussian likelihood
Guang YANG1,2, Peiyue QIAO1,*, Junyan LIANG1, Zhengchang QIN1, Xiaodong GONG3,4, Xiuhui NI3,4
- 1. Qingdao Technical Innovation Center for Underwater Acoustic Communication and Detection Equipment, School of Information and Control Engineering, Qingdao University of Technology, Qingdao 266525, China
2. School of Electrical and Electronics Engineering, Nanyang Technological University, Singapore 639798, Singapore
3. Institute of Oceanographic Instrumentation, Shandong Academy of Sciences, Qingdao 266318, China
4. National Technical University of Ukraine "Igor Sikorsky Kyiv Polytechnic Institute", Kyiv 03056, Ukraine
-
Received:2022-10-28Online:2023-12-28Published:2024-01-11 -
Contact:Peiyue QIAO
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Guang YANG, Peiyue QIAO, Junyan LIANG, Zhengchang QIN, Xiaodong GONG, Xiuhui NI. Accurate underwater acoustic channel estimation based on Gaussian likelihood[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 46(1): 334-344.
share this article
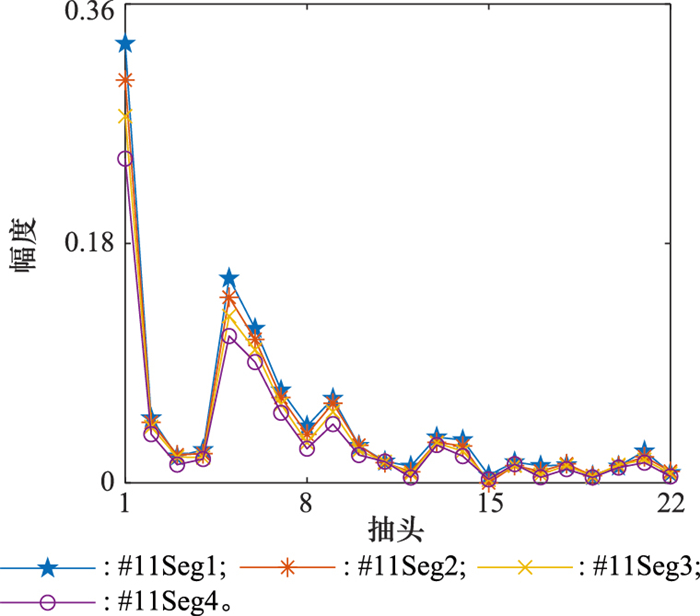
Table 1
Parameters of simulations and experiments"
| 参数 | 仿真 | 胶州湾500 m | 胶州湾5.5 km |
| 编码效率 | 1/4 | 1/8 | 1/4 |
| 功率比r | 0.25∶1 | 0.25∶1 | 0.25∶1 |
| 短块长度/sym | 256, 512 | 256 | 256 |
| CP/sym | 128 | 16 | 16 |
| 1帧, 1个数据块 | 60块, 512 bits | 16块, 256 bits | 16块, 512 bits |
| 调制方式 | - | IQ调制 | IQ调制 |
| 映射, 系统 | QPSK, 基带 | QPSK, 单载波 | QPSK, 单载波 |
| 1个数据块的时间长度/s | - | 0.27 | 0.27 |
| 1个符号的时间长度/s | - | 2.5×10-4 | 2.5×10-4 |
| 中心频率, 滤波 | - | 12 kHz, 带通 | 12 kHz, 带通 |
| 带宽/kHz | 4 | 4 | 4 |
| 采样频率/kHz | - | 96 | 96 |
| 传输速率/(bits/s) | - | 3 765 | 3 765 |
| 频带利用率/ (bps/Hz) | - | 0.94 | 0.94 |
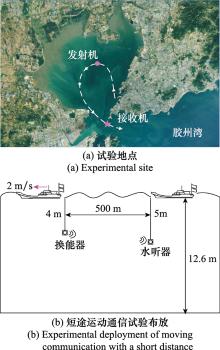
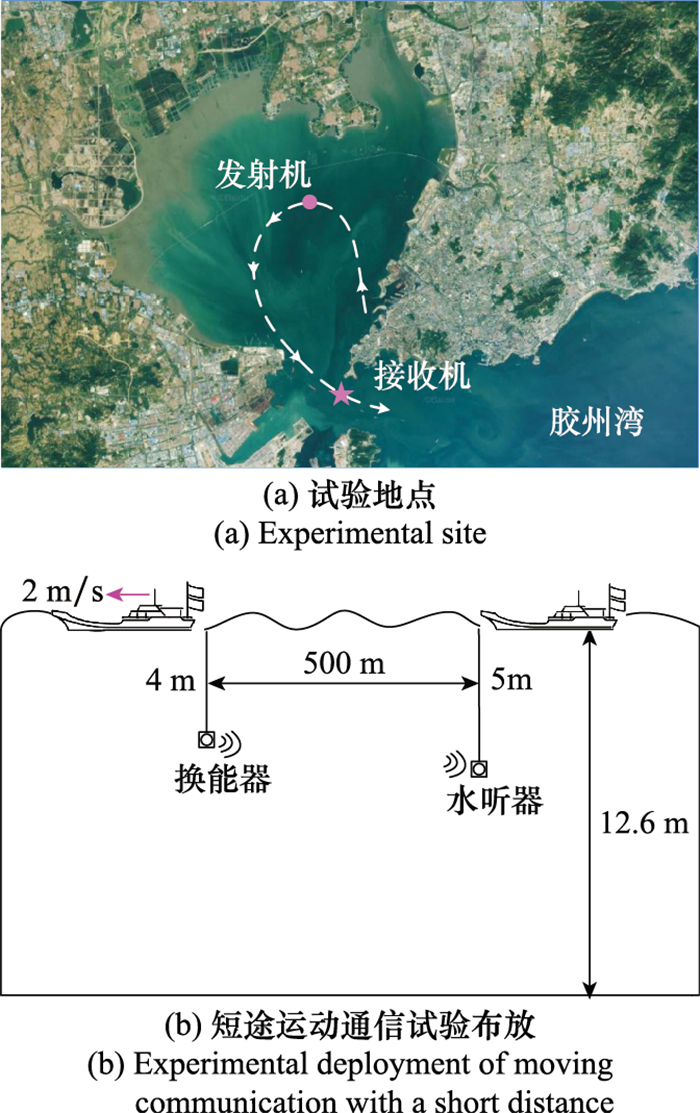
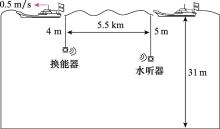
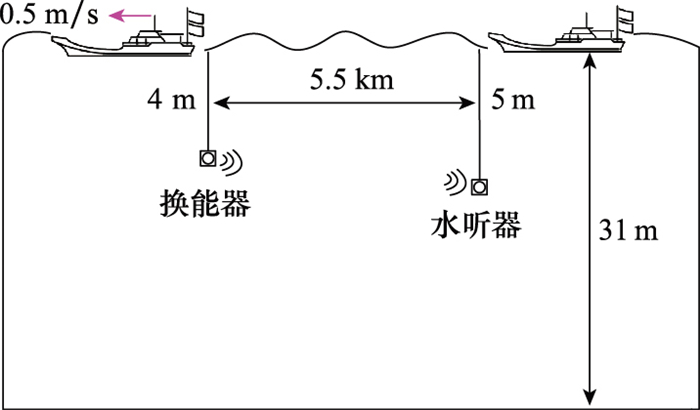
| 通信距离/m | - | 500 | 5 500 |
| 换能器深度/m | - | 4 | 4 |
| 水听器深度/m | - | 5 | 5 |
| 相对速度/(m/s) | - | 2 | 0.5 |
| SINR/dB | 9~12 | 14 | 14 |
Table 3
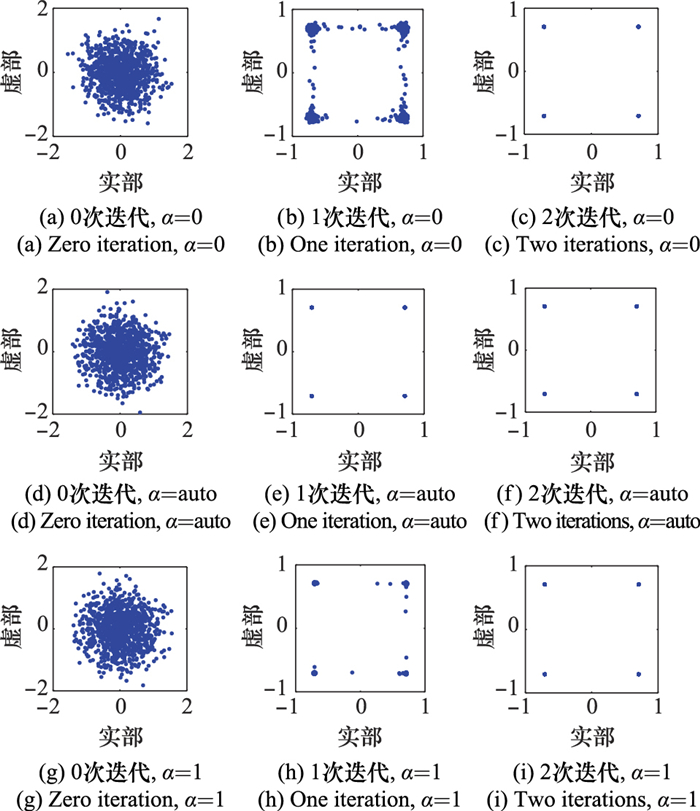
Bit error rate performance of GL algorithm with different correlation coefficients (the communication distance is about 500 m, and the relative speed is about 2 m/s)"
| 块编号 | α=auto | α=0 | α=1 | |||||
| 迭代次数 | 迭代次数 | 迭代次数 | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 2 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 6 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 7 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 8 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 10 | 0 | 0 | 3.6% | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 11.2% | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 8.8% | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 14.4% | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 0.4% | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 18.0% | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 16 | 13.6% | 0 | 30.8% | 26.0% | 14.0% | 0 | ||
| 均值 | 0.9% | 0 | 5.5% | 1.6% | 0.9% | 0 | ||
Table 4
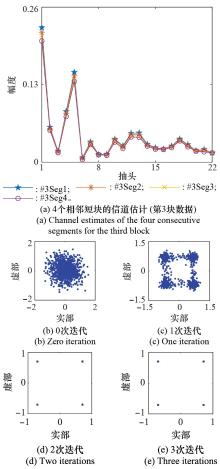
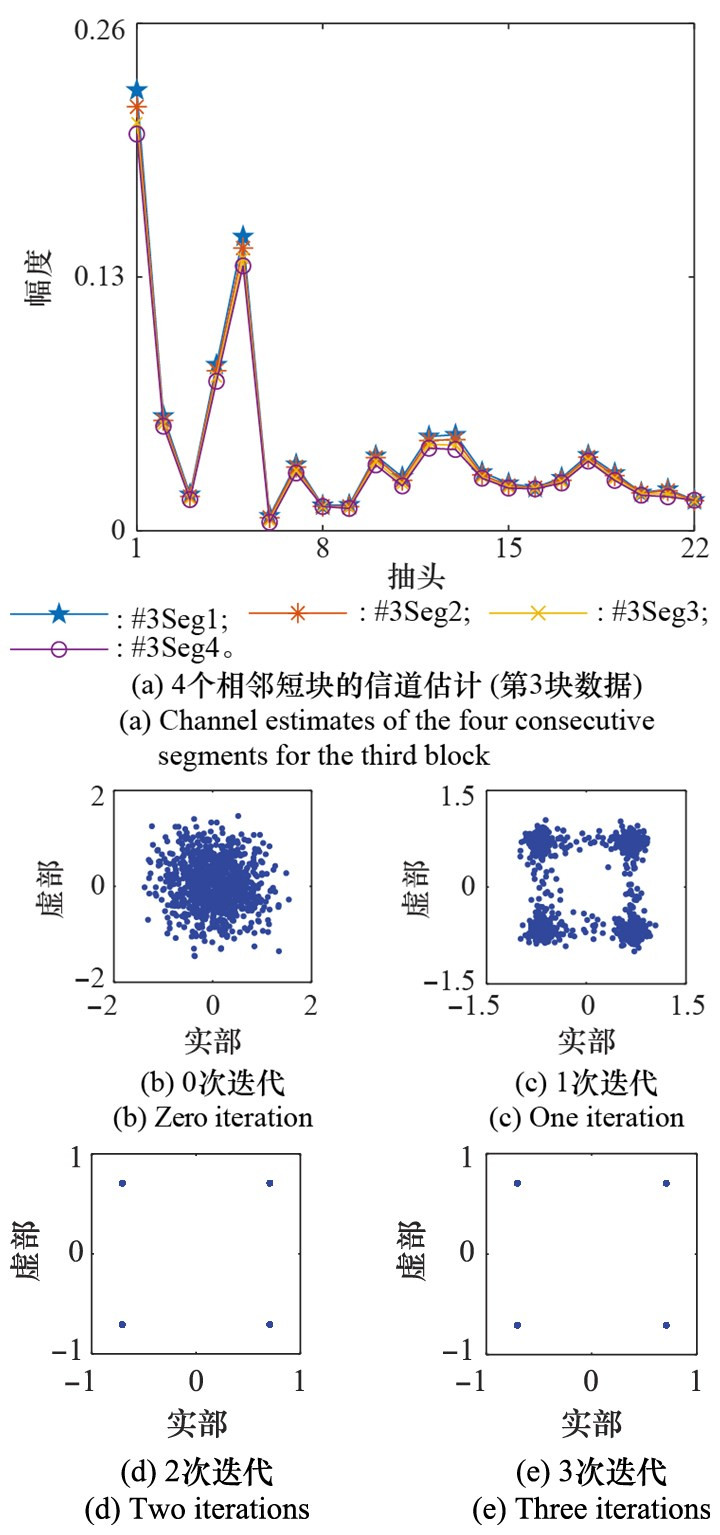
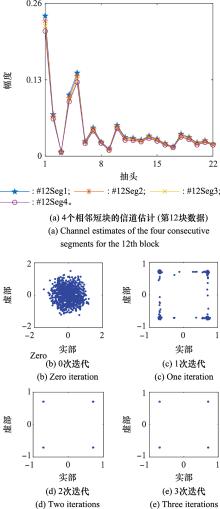
Bit error rate performance of GL algorithm with different correlation coefficients (the communication distance is about 5.5 km, and the relative speed is about 0.5 m/s) %"
| 块编号 | α=auto | α=0 | α=1 | |||||
| 迭代次数 | 迭代次数 | 迭代次数 | ||||||
| 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | 0 | 1 | |||
| 1 | 11.6 | 0 | 45.2 | 41.2 | 15.0 | 1.0 | ||
| 2 | 14.4 | 0 | 40.6 | 38.1 | 17.6 | 3.6 | ||
| 3 | 3.4 | 0 | 29.2 | 28.8 | 5.9 | 0 | ||
| 4 | 6.7 | 0 | 42.8 | 38.7 | 10.8 | 0 | ||
| 5 | 14.4 | 0 | 31.2 | 28.6 | 14.4 | 0.6 | ||
| 6 | 8.1 | 0 | 36.5 | 20.3 | 5.5 | 0 | ||
| 7 | 0.4 | 0 | 14.4 | 1.2 | 0.4 | 0 | ||
| 8 | 0.2 | 0 | 20.1 | 4.1 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 9 | 0 | 0 | 24.1 | 10.5 | 0.8 | 0 | ||
| 10 | 0.8 | 0 | 22.1 | 3.6 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 11 | 0 | 0 | 5.1 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 12 | 0 | 0 | 26.4 | 9.5 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 13 | 0 | 0 | 3.6 | 0 | 0.8 | 0 | ||
| 14 | 0 | 0 | 5.5 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 15 | 0 | 0 | 18.3 | 0 | 0 | 0 | ||
| 16 | 0.8 | 0 | 27.6 | 4.3 | 0.8 | 0 | ||
| 均值 | 3.8 | 0 | 24.5 | 14.3 | 4.5 | 0.3 | ||
| 1 |
SONG A , STOJANOVIC M , CHITRE M . Editorial underwater acoustic communications: where we stand and what is next?[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44 (1): 1- 6.
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2018.2883872 |
| 2 |
QARABAQI P , STOJANOVIC M . Statistical characterization and computationally efficient modeling of a class of underwater acoustic communication channels[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2013, 38 (4): 701- 717.
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2013.2278787 |
| 3 |
MARTINS N E , JESUS S M . Blind estimation of the ocean acoustic channel by time-frequency processing[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2006, 31 (3): 646- 656.
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2005.850915 |
| 4 | CAI J J, SU W, ZHANG S N, et al. A semi-blind joint channel estimation and equalization single carrier coherent underwater acoustic communication receiver[C]//Proc. of the OCEANS, 2016. |
| 5 |
CHO Y H , KO H L . Channel estimation based on adaptive denoising for underwater acoustic OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Access, 2020, 8, 157197- 157210.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2020.3018474 |
| 6 |
WANG S J , LIU M L , LI D S . Bayesian learning-based clustered-sparse channel estimation for time-varying underwater acoustic OFDM communication[J]. Sensors, 2021, 21 (14): 4889- 4909.
doi: 10.3390/s21144889 |
| 7 |
YIN J W , GE W , HAN X , et al. Frequency-domain equalization with interference rejection combining for single carrier multiple-input multiple-output underwater acoustic communications[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2020, 147, 138- 143.
doi: 10.1121/10.0000711 |
| 8 |
WANG B Y , GUAN X P . Channel estimation for underwater acoustic communications based on orthogonal chirp division multiplexing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2021, 28, 1883- 1887.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2021.3111569 |
| 9 |
FENG X , WANG J F , KUAI X Y , et al. Message passing-based impulsive noise mitigation and channel estimation for underwater acoustic OFDM communications[J]. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2022, 71 (1): 611- 625.
doi: 10.1109/TVT.2021.3130061 |
| 10 |
BERGER C R , ZHOU S , PREISIG J C , et al. Sparse channel estimation for multicarrier underwater acoustic communication: from subspace methods to compressed sensing[J]. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2010, 58 (3): 1708- 1721.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2009.2038424 |
| 11 |
TADAYON A , STOJANOVIC M . Iterative sparse channel estimation and spatial correlation learning for multichannel acoustic OFDM systems[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2019, 44 (4): 820- 836.
doi: 10.1109/JOE.2019.2932662 |
| 12 | 尹艳玲, 乔钢, 刘凇佐, 等. 基于基追踪去噪的水声正交频分复用稀疏信道估计[J]. 物理学报, 2015, 64 (6): 227- 234. |
| YIN Y L , QIAO G , LIU S Z , et al. Sparse channel estimation of underwater acoustic orthogonal frequency division multiplexing based on basis pursuit denoising[J]. Acta Physica Sinica, 2015, 64 (6): 227- 234. | |
| 13 | QIAO G , GAN S W , LIU S Z , et al. Self-interference channel estimation algorithm based on maximum-likelihood estimator in in-band full-duplex underwater acoustic communication system[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 62324- 62334. |
| 14 | 周跃海, 曹秀岭, 陈东升, 等. 长时延扩展水声信道的联合稀疏恢复估计[J]. 通信学报, 2016, 37 (2): 166- 173. |
| ZHOU Y H , CAO X L , CHEN D S , et al. Jointing sparse recovery estimation algorithm of underwater acoustic channels with long time delay spread[J]. Journal on Communications, 2016, 37 (2): 166- 173. | |
| 15 | ZHOU Y H , TONG F , ZAHNG G Q . Distributed compressed sensing estimation of underwater acoustic OFDM channel[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2017, 117, 160- 166. |
| 16 | QIN X , QU F , ZHENG Y R . Bayesian iterative channel estimation and turbo equalization for multiple-input multiple-output underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Journal of Ocea-nic Engineering, 2021, 46 (1): 326- 337. |
| 17 | 秦晔, 鄢社锋, 徐立军, 等. 用于单载波频域均衡水声通信的可分近似稀疏信道估计[J]. 声学学报, 2018, 43 (4): 526- 537. |
| QIN Y , YAN S F , XU L J , et al. Sparse channel estimation using separable approximation for underwater acoustic SC-FDE communications[J]. Acta Acustica, 2018, 43 (4): 526- 537. | |
| 18 | YANG G , GUO Q H , DING H X , et al. Joint message-passing-based bidirectional channel estimation and equalization with superimposed training for underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2021, 46 (4): 1463- 1476. |
| 19 | YANG G , LIU T L , DING H X , et al. Joint channel estimation and generalized approximate messaging passing-based equalization for underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 56757- 56764. |
| 20 | YANG G , WANG L , QIAO P Y , et al. Joint multiple turbo equalization for harsh time-varying underwater acoustic channels[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 82364- 82372. |
| 21 | 杨光, 丁寒雪, 郭庆华, 等. 基于叠加训练序列和低复杂度频域Turbo均衡的时变水声信道估计和均衡[J]. 电子与信息学报, 2021, 43 (3): 850- 856. |
| YANG G , DING H X , GUO Q H , et al. Estimation and equalization of time-varying underwater acoustic channel based on superimposed training and low-complexity turbo equalization in frequency domain[J]. Journal of Electronics & Information Technology, 2021, 43 (3): 850- 856. | |
| 22 | GUO Q H , PING L , HUANG D F . A low-complexity iterative channel estimation and detection technique for doubly selective channels[J]. IEEE Trans. on Wireless Communications, 2009, 8 (8): 4340- 4349. |
| 23 | GUO Q H , HUANG D F . A concise representation for the soft-in soft-out LMMSE detector[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2011, 15 (5): 566- 568. |
| 24 | GUO Q H , HUANG D F , NORDHOLM S , et al. Iterative frequency domain equalization with generalized approximate message passing[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2013, 20 (6): 559- 562. |
| 25 | 王凯, 吴立新, 张雪冬, 等. 水声通信加权反馈双向Turbo均衡器[J]. 声学学报, 2021, 46 (6): 835- 846. |
| WANG K , WU L X , ZHANG X D , et al. Bidirectional turbo equalizer with weighted feedback for underwater acoustic communication[J]. Acta Acustica, 2021, 46 (6): 835- 846. | |
| 26 | XI J Y , YAN S F , XU L J , et al. Frequency-time domain turbo equalization for underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2020, 45 (2): 665- 679. |
| 27 | 奚钧壹, 鄢社锋, 徐立军, 等. 水声通信系统中双向turbo均衡算法[J]. 声学学报, 2018, 43 (5): 771- 778. |
| XI J Y , YAN S F , XU L J , et al. Bidirectional turbo equalization for underwater acoustic communications[J]. Acta Acustica, 2018, 43 (5): 771- 778. | |
| 28 | OROZCO-LUGO A G , LARA M M , MCLERNON D C . Channel estimation using implicit training[J]. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2004, 52 (1): 240- 254. |
| 29 | YIN J W , ZHU G J , HAN X , et al. Iterative channel estimation-based soft successive interference cancellation for multiuser underwater acoustic communications[J]. The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America, 2021, 150 (1): 133- 144. |
| 30 | HE C B , JING L Y , XI R , et al. Time-frequency domain turbo equalization for single-carrier underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Access, 2019, 7, 73324- 73335. |
| 31 | ZHAO S D , YAN S F , XI J Y . Adaptive turbo equalization for differential OFDM systems in underwater acoustic communications[J]. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2020, 69 (11): 13937- 13941. |
| 32 | XI J Y , YAN S F , XU L J , et al. Sparsity-aware adaptive turbo equalization for underwater acoustic communications in the Mariana Trench[J]. IEEE Journal of Oceanic Engineering, 2021, 46 (1): 338- 351. |
| [1] | Tan GAO, Chengcai LYU, Chuan TIAN. Error control method for OFDM-MFSK underwater acoustic communication [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(5): 1701-1708. |
| [2] | Xiaoling NING, Jijin TONG, Linsen ZHANG, Yasong LUO, Han CHENG. Application of fast convergent affine projection algorithm in sparse underwater acoustic channels [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 434-439. |
| [3] | Yuzhi ZHANG, Yanjing SUN, Bin WANG, Yang LIU. Underwater acoustic adaptive OFDMA based on feedback channel state information [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2321-2331. |
| [4] | Yuan LIU, Ruiqin ZHAO, Xiaohong SHEN, Haiyan WANG. Collision-free topology discovery protocol for underwater acoustic network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(7): 1597-1604. |
| [5] | ZHOU Xiao-meng, HOU Chao-huan, YAN Jin, CHEN Peng. Approach to signal detection in doubly-spread channels based on STFT [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(10): 2506-2509. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||