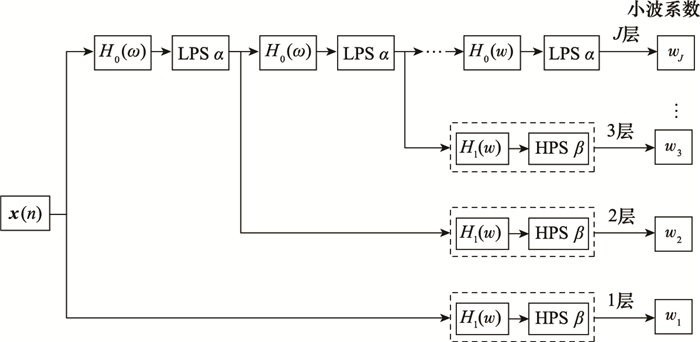
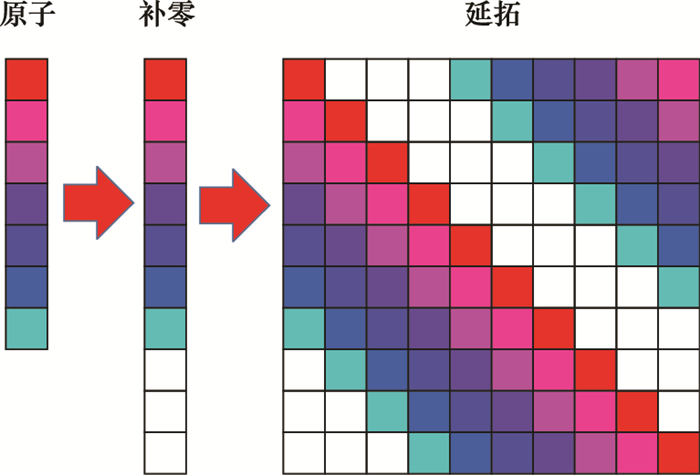
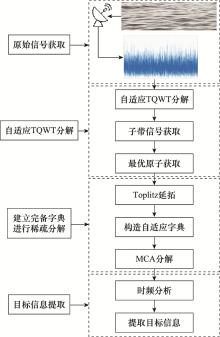
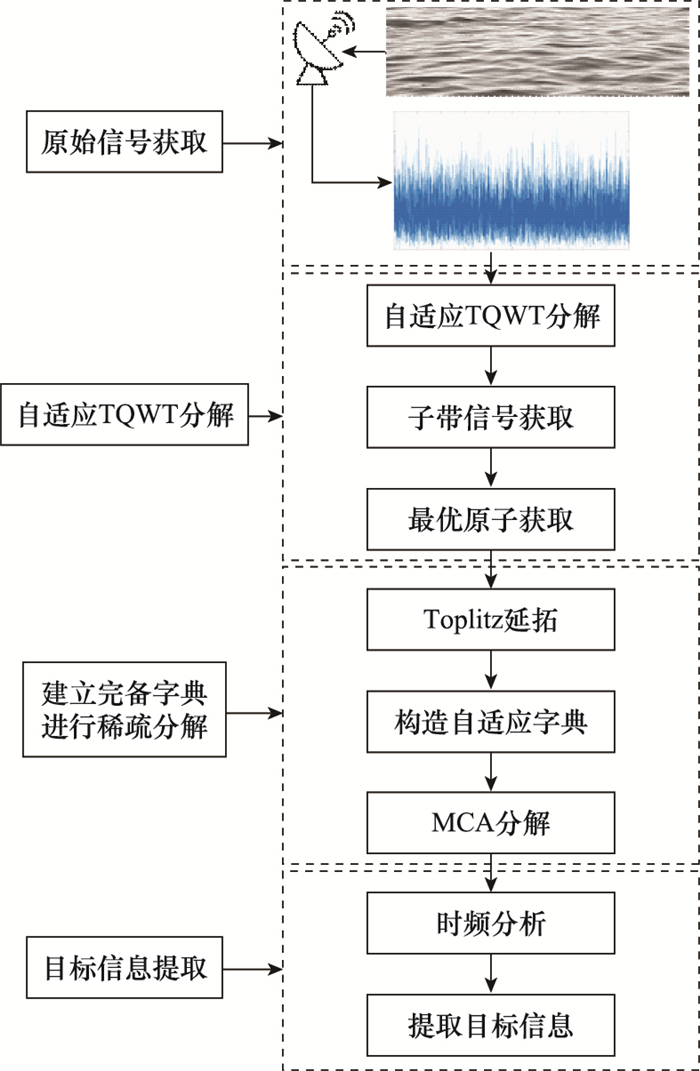
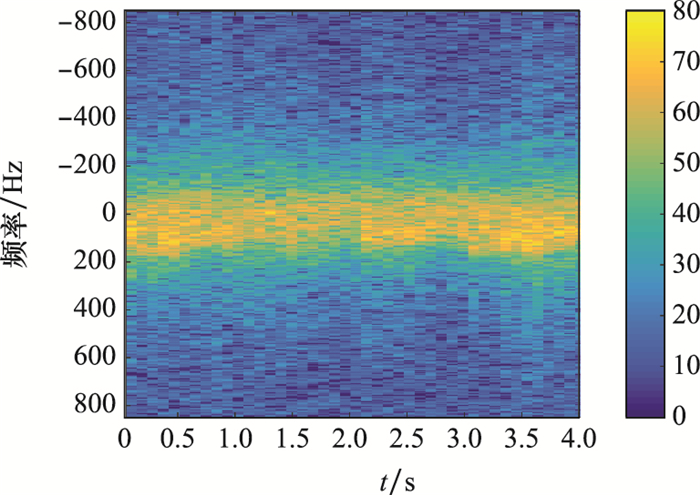
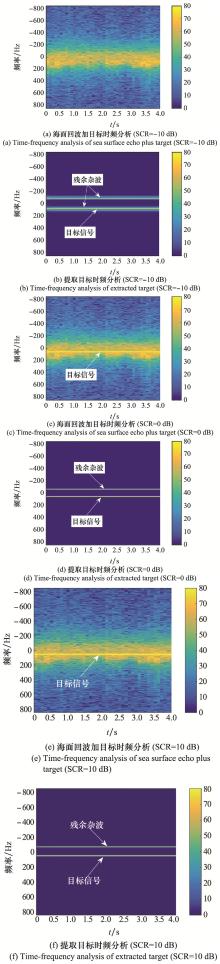
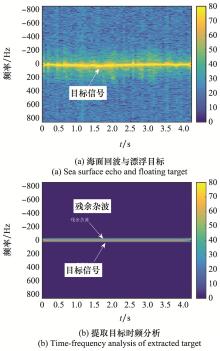
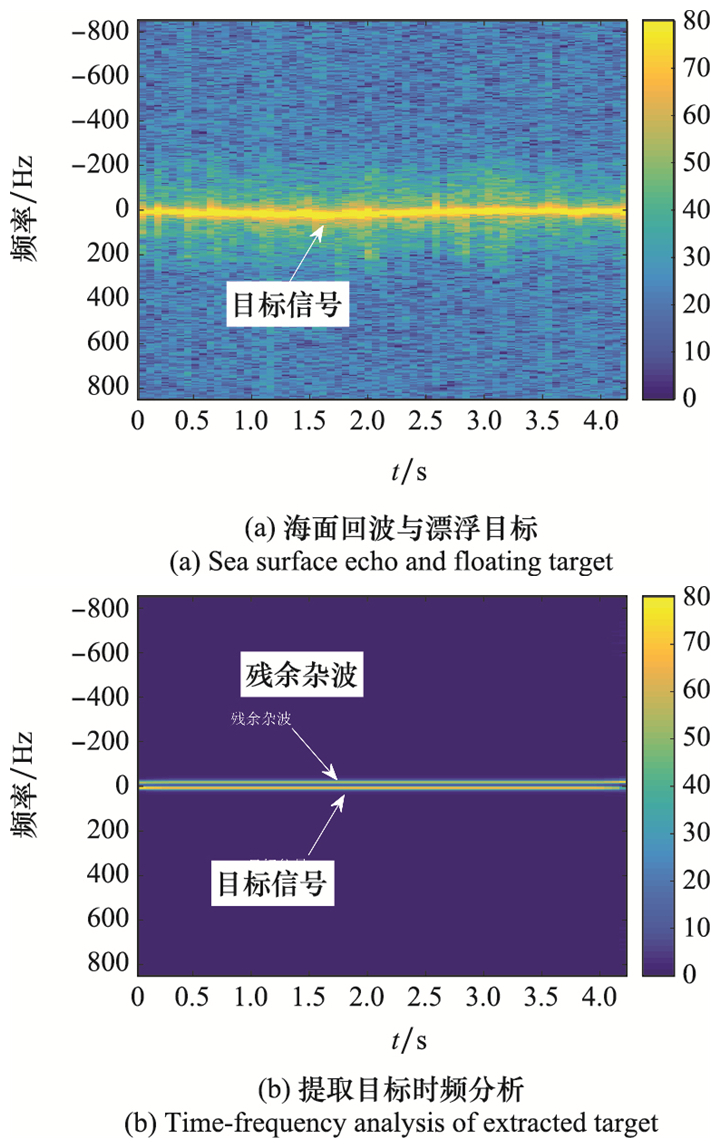
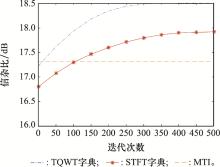
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2023, Vol. 45 ›› Issue (4): 1016-1023.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2023.04.10
• Sensors and Signal Processing • Previous Articles
Sea surface micro-moving target recognition based on sparse decomposition
Hanyi HUANG1, Shiyou HU2, Shenglong GUO2, Shanjun LI1,*, Qin SHU1
- 1. College of Electrical Engineering, Sichuan University, Chengdu 610000, China
2. Beijing Huahang Radio Measurement Institute, Beijing 100013, China
-
Received:2022-06-16Online:2023-03-29Published:2023-03-28 -
Contact:Shanjun LI
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hanyi HUANG, Shiyou HU, Shenglong GUO, Shanjun LI, Qin SHU. Sea surface micro-moving target recognition based on sparse decomposition[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(4): 1016-1023.
share this article
| 1 | ROSENBERG L . Parametric modeling of sea clutter Doppler spectra[J]. IEEE Trans. on Geoscience and Remote Sensing, 2022, 60, 5105409. |
| 2 | YAN Y , XING H Y . A sea clutter detection method based on LSTM error frequency domain conversion[J]. Alexandria Engineering Journal, 2021, 61 (6): 883- 891. |
| 3 |
GAO C , TAO R , KANG X J . Weak target detection in the presence of sea clutter using radon-fractional Fourier transform canceller[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations and Remote Sensing, 2021, 14, 5818- 5830.
doi: 10.1109/JSTARS.2021.3078723 |
| 4 |
SHI Y L , WANG L , YAO T T . Orthogonal projection constant false alarm rate algorithm in fractional domain for small surface targets[J]. IET Signal Processing, 2022, 16 (8): 975- 991.
doi: 10.1049/sil2.12137 |
| 5 | LIANG Z R, WANG Y, ZHANG X F, et al. Identification of ship and corner reflector in sea clutter environment[C]//Proc. of the 15th IEEE International Conference on Signal Processing, 2020: 622-626. |
| 6 | KIRSCHT M , MIETZNER J , BICKERT B , et al. An airborne radar sensor for maritime and ground surveillance and reconnaissance—algorithmic issues and exemplary results[J]. IEEE Journal of Selected Topics in Applied Earth Observations & Remote Sensing, 2016, 9 (3): 971- 979. |
| 7 | JI Y G , JIE Z , WANG Y M , et al. Vessel target detection based on fusion range-Doppler image for dual-frequency high-frequency surface wave radar[J]. IET Radar Sonar & Navigation, 2016, 10 (2): 333- 340. |
| 8 | LIU J , LIU S , LIU W , et al. Persymmetric adaptive detection of distributed targets in Compound-Gaussian sea clutter with Gamma texture[J]. Signal Processing, 2018, 152 (11): 340- 349. |
| 9 |
ROSENBERG L , DUK V , NG W H . Detection in sea clutter using sparse signal separation[J]. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2020, 56 (6): 4384- 4394.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2020.2989093 |
| 10 |
HUBEL D H , WIESEL T N . Receptive fields of single neurones in the cat's striate cortex[J]. The Journal of Physiology, 1959, 148, 574- 591.
doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1959.sp006308 |
| 11 |
OLSHAUSEN B A , FIELD D J . Emergence of simple-cell receptive field properties by learning a sparse code for natural images[J]. Nature, 1996, 381 (6583): 607- 609.
doi: 10.1038/381607a0 |
| 12 | STARCK J L , ELAD M , DONOHO D . Redundant multiscale transforms and their application for morphological component separation[J]. Advances in Imaging and Electron Physics, 2004, 132 (4): 287- 348. |
| 13 |
陈小龙, 关键, 董云龙, 等. 稀疏域海杂波抑制与微动目标检测方法[J]. 电子学报, 2016, 44 (4): 860- 867.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.04.015 |
|
CHEN X L , GUAN J , DONG Y L , et al. Sea clutter suppression and micromotion target detection in sparse domain[J]. Acta Electronica Sinica, 2016, 44 (4): 860- 867.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0372-2112.2016.04.015 |
|
| 14 | FARSHCHIAN M, SELESNICK I. Application of a sparse time-frequency technique for targets with oscillatory fluctuations[C]//Proc. of the International Waveform Diversity & Design Conference, 2012: 191-196. |
| 15 |
杨国铮, 禹晶, 肖创柏, 等. 基于形态成分分析的复杂背景SAR图像舰船尾迹检测[J]. 计算机辅助设计与图形学学报, 2016, 28 (10): 1662- 1671.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2016.10.007 |
|
YANG G Z , YU J , XIAO C B , et al. Ship wake detection in SAR images with complex backgrounds using morphological omponent analysis[J]. Journal of Computer-Aided Design & Computer Graphics, 2016, 28 (10): 1662- 1671.
doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-9775.2016.10.007 |
|
| 16 |
NGUYEN S , AL-ASHWAL W A . Sea clutter mitigation using resonance-based signal decomposition[J]. IEEE Geoscience and Remote Sensing Letters, 2015, 12 (11): 2257- 2261.
doi: 10.1109/LGRS.2015.2464807 |
| 17 |
TANG G , YANG Q , WANG H Q , et al. Sparse classification of rotating machinery faults based on compressive sensing strategy[J]. Mechatronics, 2015, 31, 60- 67.
doi: 10.1016/j.mechatronics.2015.04.006 |
| 18 | ZHU Y C , YANG K D , DUAN R , et al. Sparse spatial spectral estimation with heavy sea bottom reverberation in the fractional fourier domain[J]. Applied Acoustics, 2020, 160 (3): 107132. |
| 19 |
HUANG G Q , XIAO Y W , YIN Z . Denoising method for underwater acoustic signals based on sparse decomposition[J]. Journal of Physics Conference Series, 2020, 1550 (3): 032139.
doi: 10.1088/1742-6596/1550/3/032139 |
| 20 | DU D , PAN Z B , ZHANG P H , et al. Compressive sensing image recovery using dictionary learning and shape-adaptive DCT thresholding[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 2018, 55 (7): 60- 71. |
| 21 |
WU Y , ZHOU J , AKANKWASA N T , et al. Fabric texture representation using the stable learned discrete cosine transform dictionary[J]. Textile Research Journal, 2019, 89 (3): 294- 310.
doi: 10.1177/0040517517743688 |
| 22 | ZHANG X W, YANG D D, GUO J X, et al. Weak moving target detection based on short-time Fourier transform in sea clutter[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Signal and Image Processing, 2019: 415-419. |
| 23 |
SELESNICK I W . Wavelet transform with tunable Q-factor[J]. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2011, 59 (8): 3560- 3575.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2011.2143711 |
| 24 | 潘美艳, 杨予昊, 李大圣, 等. 一种基于能量选择的改进TQWT海杂波抑制算法[J]. 现代雷达, 2018, 40 (10): 32- 37. |
| PAN M Y , YANG Y H , LI D S , et al. An improved TQWT sea clutter suppression algorithm based on energy selection[J]. Modern Radar, 2018, 40 (10): 32- 37. | |
| 25 |
LI J L , WANG H Q , SONG L Y , et al. A novel feature extraction method for roller bearing using sparse decomposition based on self-Adaptive complete dictionary[J]. Measurement, 2019, 148, 106934.
doi: 10.1016/j.measurement.2019.106934 |
| 26 |
ELAD M , STRACK J L , QUERRE P , et al. Simultaneous cartoon and texture image inpainting using morphological component analysis (MCA)[J]. Applied and Computational Harmonic Analysis, 2005, 19 (3): 340- 358.
doi: 10.1016/j.acha.2005.03.005 |
| 27 | NG B, ROSENBERG L. Sparse detection in sea-clutter using orthogonal matching pursuit[C]//Proc. of the IEEE Radar Conference, 2019: 22-26. |
| 28 |
AFONSO M V , BIOUCAS-Dias J M , FIGUEIREDO M . Fast image recovery using variable splitting and constrained optimization[J]. IEEE Trans. on Image Processing, 2010, 19 (9): 2345- 2356.
doi: 10.1109/TIP.2010.2047910 |
| 29 |
SELESNICK I W . Resonance-based signal decomposition: a new sparsity-enabled signal analysis method[J]. Signal Processing, 2011, 91 (12): 2793- 2809.
doi: 10.1016/j.sigpro.2010.10.018 |
| 30 | FIGUEIREDO M, BIOUCAS-DIAS J M, AFONSO M V. Fast frame-based image deconvolution using variable splitting and constrained optimization[C]//Proc. of the 15th Workshop on Statistical Signal Processing, 2009: 109-112. |
| 31 | 刘宁波, 丁昊, 黄勇, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取年度进展[J]. 雷达学报, 2021, 10 (1): 173- 182. |
| LIU N B , DING H , HUANG Y , et al. Annual progress of sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2021, 10 (1): 173- 182. | |
| 32 | 刘宁波, 董云龙, 王国庆, 等. X波段雷达对海探测试验与数据获取[J]. 雷达学报, 2019, 8 (5): 656- 667. |
| LIU N B , DONG Y L , WANG G Q , et al. Sea-detecting X-band radar and data acquisition program[J]. Journal of Radars, 2019, 8 (5): 656- 667. | |
| 33 | OZKURT N. Signal adaptive Q factor selection for resonance based signal separation using tunable-Q wavelet transform[C]//Proc. of the 41st International Conference on Telecommunications and Signal Processing, 2018. |
| [1] | Qingyuan ZHAO, Zhiqiang ZHAO, Chunmao YE, Yaobing LU. Micro-motion fusion recognition of double band early warning radar based on self-attention mechanism [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(3): 708-716. |
| [2] | Junling ZHANG, Mei DONG, Baixiao CHEN. Sea clutter suppression algorithm based on tunable Q-factor wavelet transform [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(2): 343-351. |
| [3] | Caiyun WANG, Yida WU, Jianing WANG, Lu MA, Huanyue ZHAO. SAR image target recognition based on combinatorial optimization convolutional neural network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2483-2487. |
| [4] | Jingming SUN, Shengkang YU, Jun SUN. Radar small sample target recognition method based on meta learning and its improvement [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1839-1845. |
| [5] | Xiaoling ZHOU, Zhaoxia ZHANG, Ya LU, Qian WANG, Kunkun WANG. SAR image recognition based on improved R-FCN [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(4): 1202-1209. |
| [6] | Jingming SUN, Shengkang YU, Jun SUN. Pose sensitivity analysis of HRRP recognition based on deep learning [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(3): 802-807. |
| [7] | Yanling SHI, Lei WANG, Junhao LI. CFAR detection for small targets on sea surface based on singular value decomposition in projection space [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 512-519. |
| [8] | Yu LEI, Xiangguang LENG, Xiaoyan ZHOU, Zhongzhen SUN, Kefeng JI. Recognition method of ship target in complex SAR image based on improved ResNet network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(12): 3652-3660. |
| [9] | Chunling XUE, Fei CAO, Qing SUN, Jianqiang QIN, Xiaowei FENG. Sea-surface weak target detection based on multi-feature information fusion [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(11): 3338-3345. |
| [10] | Qi LIU, Xinyu ZHANG, Yongxiang LIU. Few-shot SAR target recognition based on gated multi-scale matching network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(11): 3346-3356. |
| [11] | Caiyun WANG, Chen YAO, Yida WU, Jianing WANG, Xiaofei LI, Panpan HUANG. Radar target recognition based on improved Dijkstra algorithm with time-frequency domain filtering [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(10): 3090-3095. |
| [12] | Xin GUAN, Haotian YU, Xiao YI. Research on evidence independence and its influence on target recognition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 192-198. |
| [13] | Yongzhen LI, Yemin LIU, Chen PANG, Datong HUANG. Chaff clouds recognition method based on layered polarization characteristics [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2099-2107. |
| [14] | Chunsi XIE, Zhiying LIU, Yu SANG. Target recognition model of ship-to-land missile based on feature matching [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(8): 2244-2253. |
| [15] | Yuan YAN, Jun SUN, Jingming SUN, Junpeng YU. Radar few shot target recognition method and application analysis [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(3): 684-692. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||