Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2022, Vol. 44 ›› Issue (6): 1907-1919.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2022.06.17
• Systems Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
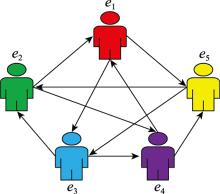
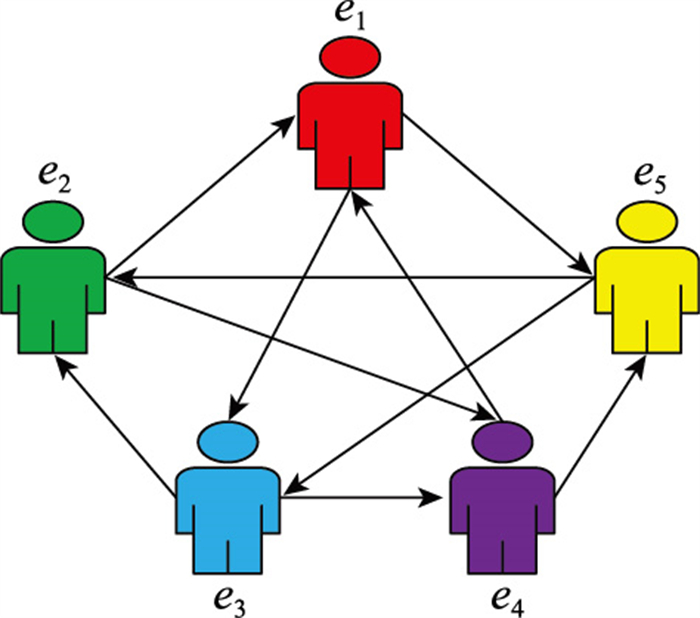
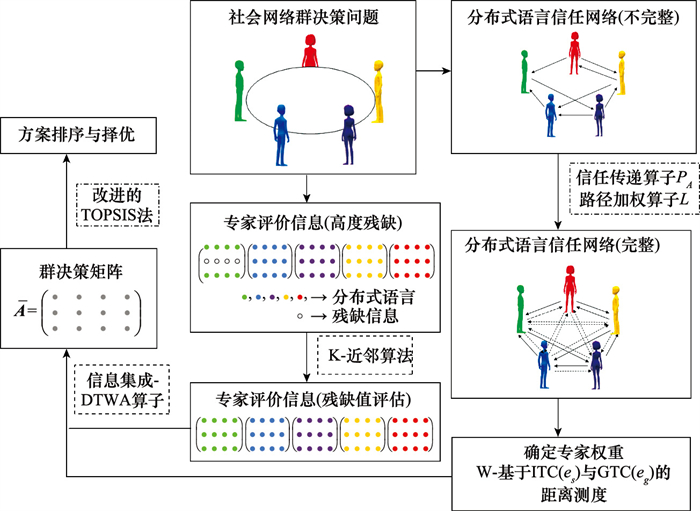
Group decision making method for distributed linguistic trust network based on highly incomplete information
Shouzhen ZENG1,2,*, Yingjie HU1
- 1. School of Business, Ningbo University, Ningbo 315211, China
2. School of Management, Fudan University, Shanghai 200433, China
-
Received:2021-06-04Online:2022-05-30Published:2022-05-30 -
Contact:Shouzhen ZENG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Shouzhen ZENG, Yingjie HU. Group decision making method for distributed linguistic trust network based on highly incomplete information[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1907-1919.
share this article
Table 1
Distributed linguistic trust evaluation matrix of expert e1"
| e1 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
| X1 | {(D1, 0.1), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.3)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.3)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.1), (D3, 0.7)} |
| X2 | - | - | - | - |
| X3 | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.2), (D3, 0.3)} | {(D1, 0.6), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.4), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.1), (D2, 0.8), (D3, 0.1)} |
Table 2
Distributed linguistic trust evaluation matrix of expert e2"
| e2 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
| X1 | {(D1, 0.1), (D2, 0.0), (D3, 0.9)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.6), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.2), (D3, 0.8)} | {(D1, 0.7), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.0)} |
| X2 | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.6), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.8), (D2, 0.2), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.0)} |
| X3 | {(D1, 0.4), (D2, 0.6), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.4)} | {(D1, 0.6), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.5)} |
Table 3
Distributed linguistic trust evaluation matrix of expert e3"
| e3 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
| X1 | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.3)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.8), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.4)} | {(D1, 0.1), (D2, 0.1), (D3, 0.8)} |
| X2 | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.7), (D2, 0.2), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.6), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.4), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.2)} |
| X3 | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.5)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.4)} | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.9), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.4), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.1)} |
Table 4
Distributed linguistic trust evaluation matrix of expert e4"
| e4 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
| X1 | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.6)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.5)} | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.3)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.3)} |
| X2 | {(D1, 0.8), (D2, 0.2), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.6), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.1)} |
| X3 | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.6), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.5)} | {(D1, 0.2), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.1), (D2, 0.9), (D3, 0.0)} |
Table 5
Distributed linguistic trust evaluation matrix of expert e5"
| e5 | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
| X1 | {(D1, 0.4), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.3)} | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.3), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.0), (D3, 0.5)} |
| X2 | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.5), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.6), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.6), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.0)} |
| X3 | {(D1, 0.3), (D2, 0.7), (D3, 0.0)} | {(D1, 0.0), (D2, 0.8), (D3, 0.2)} | {(D1, 0.5), (D2, 0.4), (D3, 0.1)} | {(D1, 0.4), (D2, 0.6), (D3, 0.0)} |
Table 6
Group decision matrix based on distributed linguistic trust function"
| eg | C1 | C2 | C3 | C4 |
| X1 | {(D1, 0.116), (D2, 0.458), (D3, 0.426)} | {(D1, 0.239), (D2, 0.519), (D3, 0.242)} | {(D1, 0.175), (D2, 0.424), (D3, 0.401)} | {(D1, 0.358), (D2, 0.185), (D3, 0.457)} |
| X2 | {(D1, 0.584), (D2, 0.297), (D3, 0.119)} | {(D1, 0.463), (D2, 0.412), (D3, 0.125)} | {(D1, 0.564 4), (D2, 0.382 3), (D3, 0.053 3)} | {(D1, 0.374), (D2, 0.544), (D3, 0.082)} |
| X3 | {(D1, 0.318), (D2, 0.480), (D3, 0.202)} | {(D1, 0.241), (D2, 0.435), (D3, 0.324)} | {(D1, 0.336), (D2, 0.584), (D3, 0.080)} | {(D1, 0.197), (D2, 0.663), (D3, 0.140)} |
Table 7
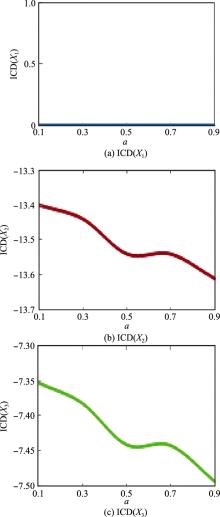
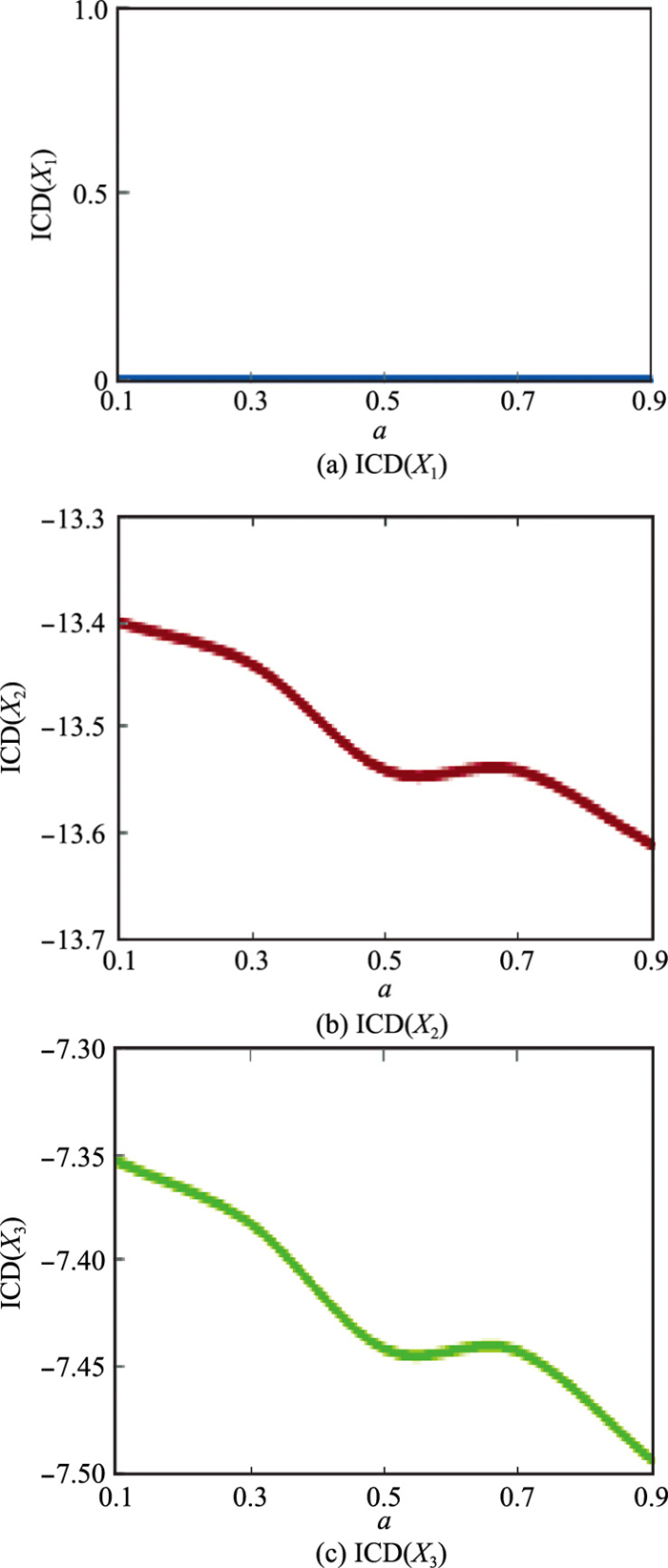
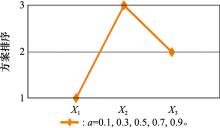
Influence of parameter a on ranking of alternatives"
| a | ICD(Xi) | 方案排序 |
| 0.1 | ICD(X1)=0, ICD(X2)=-13.40, ICD(X3)=-7.353 | X1>X3>X2 |
| 0.3 | ICD(X1)=0, ICD(X2)=-13.44, ICD(X3)=-7.382 | X1>X3>X2 |
| 0.5 | ICD(X1)=0, ICD(X2)=-13.54, ICD(X3)=-7.441 | X1>X3>X2 |
| 0.7 | ICD(X1)=0, ICD(X2)=-13.54, ICD(X3)=-7.442 | X1>X3>X2 |
| 0.9 | ICD(X1)=0, ICD(X2)=-13.61, ICD(X3)=-7.493 | X1>X3>X2 |
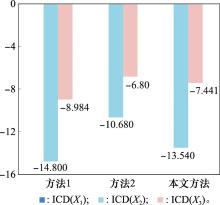
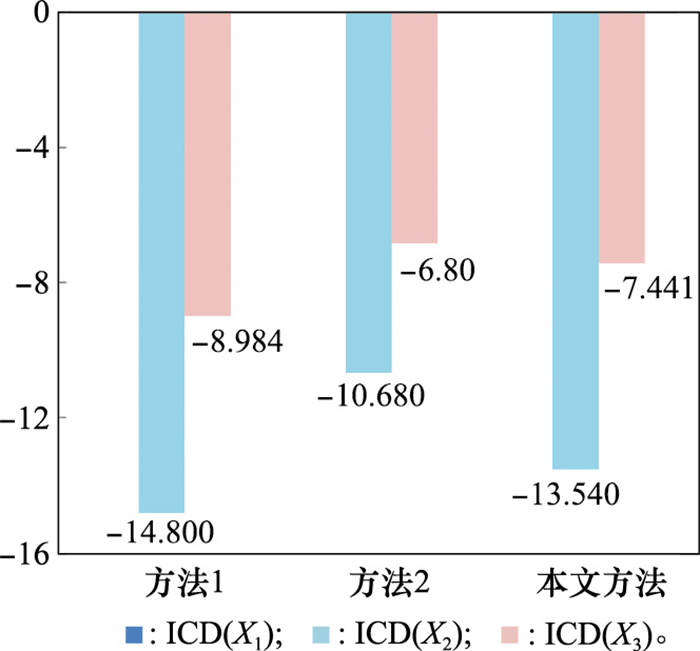
Table 8
Comparative analysis of different methods"
| 特性 | 方法1 | 方法2 | 本文方法 |
| 分布式语言信任社会矩阵 | 残缺 | 残缺 | 完整 |
| 专家权重获取 | 基于残缺的分布式语言信任关系 | 基于量词Q | 基于完整的分布式语言信任关系 |
| 专家e1权重 | 0.197 | 0.143 | 0.197 |
| 专家e2权重 | 0.219 | 0.185 | 0.200 |
| 专家e3权重 | 0.180 | 0.105 | 0.201 |
| 专家e4权重 | 0.180 | 0.120 | 0.212 |
| 专家e5权重 | 0.223 | 0.447 | 0.190 |
| 残缺信息的评估 | 基于其余专家的相对信任度 | 基于其余专家的重要度 | 基于K-近邻算法 |
| 1 |
PEI F , HE Y W , YAN A , et al. A consensus model for intuitionistic fuzzy group decision-making problems based on the construction and propagation of trust/distrust relationships in social networks[J]. International Journal of Fuzzy Systems, 2020, 22 (8): 2664- 2679.
doi: 10.1007/s40815-020-00980-0 |
| 2 |
ZHENG Y F , XU J . A trust transitivity model for group decision making in social network with intuitionistic fuzzy information[J]. Filomat, 2018, 32 (5): 1937- 1945.
doi: 10.2298/FIL1805937Z |
| 3 |
WU J , XIONG R Y , CHICLANA F . Uninorm trust propagation and aggregation methods for group decision making in social network with four tuple information[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2016, 96, 29- 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2016.01.004 |
| 4 | 向南, 豆亚杰, 姜江, 等. 基于专家信任网络的不完全信息武器选择决策[J]. 系统工程理论与实践, 2021, 41 (3): 759- 770. |
| XIANG N , DOU Y J , JIANG J , et al. Weapon selection decision-making based on expert trust network under incomplete information[J]. Systems Engineering-Theory & Practice, 2021, 41 (3): 759- 770. | |
| 5 |
YUE Z L . A method for group decision-making based on determining weights of decision makers using TOPSIS[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling, 2011, 35 (4): 1926- 1936.
doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2010.11.001 |
| 6 |
KIM Y A , SONG H S . Strategies for predicting local trust based on trust propagation in social networks[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2011, 24 (8): 1360- 1371.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2011.06.009 |
| 7 | GUHA R, KUMAR R, RAGHAVAN P, et al. Propagation of trust and distrust[C]//Proc. of the 13th International Conference on World Wide Web, 2004: 403-412. |
| 8 |
YAN L S , WEI Y , ZHU H , et al. Information theoretic framework of trust modeling and evaluation for ad hoc networks[J]. IEEE Journal on Selected Areas in Communications, 2006, 24 (2): 305- 317.
doi: 10.1109/JSAC.2005.861389 |
| 9 |
LIU X , XU Y J , MONTES R , et al. Social network group decision making: managing self-confidence-based consensus model with the dynamic importance degree of experts and trust-based feedback mechanism[J]. Information Sciences, 2019, 505, 215- 232.
doi: 10.1016/j.ins.2019.07.050 |
| 10 | WU J , DAI L F , CHICLANA F , et al. A minimum adjustment cost feedback mechanism based consensus model for group decision making under social network with distributed linguistic trust[J]. Information Fusion, 2017, 41, 232- 242. |
| 11 |
WU J , CHICLANA F , FUJITA H , et al. A visual interaction consensus model for social network group decision making with trust propagation[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2017, 122, 39- 50.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2017.01.031 |
| 12 |
WU J , CHICLANA F , HERRERA-VIEDMA E . Trust based consensus model for social network in an incomplete linguistic information context[J]. Applied Soft Computing, 2015, 35, 827- 839.
doi: 10.1016/j.asoc.2015.02.023 |
| 13 |
TIAN Z P , NIE R X , WANG J Q , et al. A two-fold feedback mechanism to support consensus-reaching in social network group decision-making[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2018, 162, 74- 91.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2018.09.030 |
| 14 | 曹清玮, 戴丽芳, 孙琪, 等. 社会网络环境下基于分布式信任的在线评价方法[J]. 控制与决策, 2020, 35 (7): 1697- 1702. |
| CAO Q W , DAI L F , SUN Q , et al. A distributed trust based online evaluation under social network[J]. Control and Decision, 2020, 35 (7): 1697- 1702. | |
| 15 | 戴丽芳, 吴坚, 曹清玮, 等. 分布式信任网络下基于最小协调成本的群体共识方法[C]//第十九届中国管理科学学术年会, 2017. |
| DAI L F, WU J, CAO Q W, et al. A group consensus approach based on minimum coordination cost in distributed trust network[C]//Proc. of the 19th Chinese Annual Conference on Management Science, 2017. | |
| 16 | WU J , CHANG J L , CAO Q W , et al. A trust propagation and collaborative filtering based method for incomplete information in social network group decision making with type-2 linguistic trust[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2019, 127, 853- 864. |
| 17 |
CHU J F , WANG Y M , LIU X W , et al. Social network community analysis based large-scale group decision making approach with incomplete fuzzy preference relations[J]. Information Fusion, 2020, 60, 98- 120.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2020.02.005 |
| 18 | 熊若云. 基于社会网络信任的网商信用评价[D]. 金华: 浙江师范大学, 2016. |
| XIONG R Y. Credit evaluation of E-enterprise based on trust social network[D]. Jinhua: Zhejiang Normal University, 2016. | |
| 19 | GAO H X , JU Y B , ZENG X J , et al. Satisfaction-driven consensus model for social network MCGDM with incomplete information under probabilistic linguistic trust[J]. Computers & Industrial Engineering, 2021, 154, 107099. |
| 20 | XU Y J , LI C Y , WEN X W . Missing values estimation and consensus building for incomeplete hesitant fuzzy preference relations with multiplicative consistency[J]. International Journal of Computational IntelligenceSystems, 2018, 11 (1): 101- 119. |
| 21 |
TAGHAVI A , ESLAMI E , HERRERA-VIEDMA E , et al. Trust based group decision making in environments with extreme uncertainty[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2020, 191, 105168.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2019.105168 |
| 22 |
XU Y J , MA F , TAO F F , et al. Some methods to deal with unacceptable incomplete 2-tuple fuzzy linguistic preference relations in group decision making[J]. Knowledge-Based Systems, 2014, 56, 179- 190.
doi: 10.1016/j.knosys.2013.11.008 |
| 23 |
URENA R , CHICLANA F , MELANCON G , et al. A social network based approach for consensus achievement in multiperson decision making[J]. Information Fusion, 2019, 47, 72- 87.
doi: 10.1016/j.inffus.2018.07.006 |
| 24 |
KLEMENT E P , MESIAR R , PAP E . Triangular norms. Position paper Ⅰ: basic analytical and algebraic properties[J]. Fuzzy Sets and Systems, 2004, 143 (1): 5- 26.
doi: 10.1016/j.fss.2003.06.007 |
| 25 | 匡继昌. 常用不等式[M]. 山东: 山东科学技术出版社, 2004. |
| KUANG J C . Applied inequalities[M]. Shandong: Shandong Science and Technology Press, 2004. | |
| 26 | CHEN H P . Hesitant fuzzy multi-attribute group decision making method based on weighted power operators in social network and their application[J]. Journal of Intelligent & Fuzzy Systems, 2021, 40 (5): 9383- 9401. |
| [1] | Nuoxi ZHENG, Wu LI, Xiaoqiang ZHOU, Gang LIU. Projection decision method for consistency of multiple attribute similarity [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(9): 2869-2877. |
| [2] | Wenqi WANG, Dengying JIANG. Linguistic intuitionistic fuzzy PROMETHEE multi-attribute group decision-making based on the probability degree [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(8): 2581-2592. |
| [3] | Xin GUAN, Haotian YU, Xiao YI. Research on evidence independence and its influence on target recognition [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(1): 192-198. |
| [4] | Xiwen TAO, Wenqi JIANG. Research on three-stage hesitant fuzzy information fusion method for group consensus [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(12): 3603-3613. |
| [5] | Wenqi JIANG, Xiaolu JIANG. Interval hesitant fuzzy PROMETHEE decision method forattribute association [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3250-3258. |
| [6] | Dubo HE, Dong HUANG, Wencheng SHI. Evaluation of supplier quality performance based on group DEMATEL and grey correlation projection [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(4): 980-990. |
| [7] | Xiwen TAO, Wenqi JIANG. Three-stage consensus improvement model under interval-valued intuitionistic multi-criteria group decision-making environment based on adjustment cost [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(11): 2570-2580. |
| [8] | Yue HU, Dengying JIANG, He LI. Probabilistic linguistic multi-attribute group decision-making based on bidirectional projection method [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2020, 42(9): 2052-2059. |
| [9] | ZENG Sheng-kui, LI Hua-fu, REN Yi, FENG Qiang. Stochastic multi-attribute decision making method of performance and reliability [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(10): 2541-2543. |
| [10] | LIU Xiu-mei, ZHAO Ke-qin, WANG Chuan-bin. New multiple attribute decision-making model with triangular fuzzy numbers based on connection numbers [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(10): 2399-2403. |
| [11] | ZHOU Si-qing, WANG Jian-qiang. Combined forecasting approach based on multi-criteria optimization [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(7): 1651-1654. |
| [12] | NIU Yan-ying, WANG Yu-jie, WANG Zeng-fu. C-DWA operator and its application in TOPSIS [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(6): 1362-1365. |
| [13] | HE Jun, ZHAO Hong-zhong, FU Qiang. Method for solving hybrid multiple attribute decision making problems based on preference matrix [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(6): 1386-1390. |
| [14] | WEI Gui-wu. Fuzzy ordered weighted harmonic averaging operator and its application to decision making [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(4): 855-858. |
| [15] | CHEN Xiao-xin, LIU Si-feng. Grey multiple attribute group decision-making method with partial weight information [J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2009, 31(4): 843-846. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||