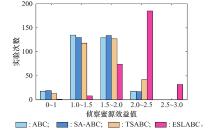
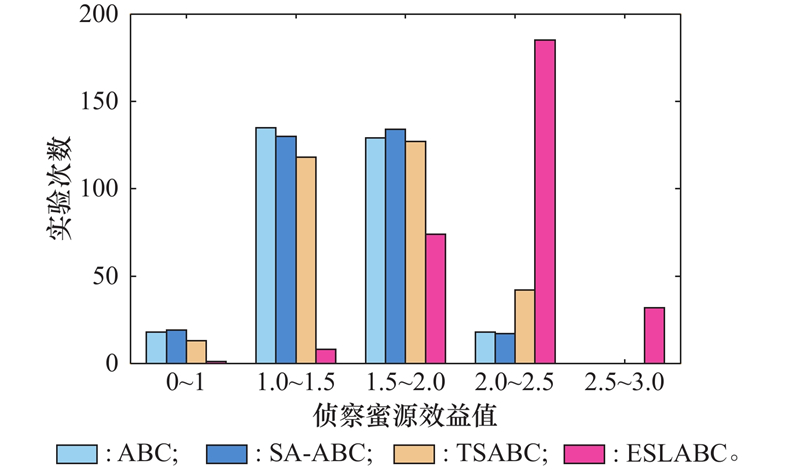
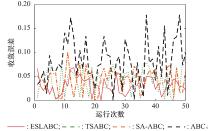
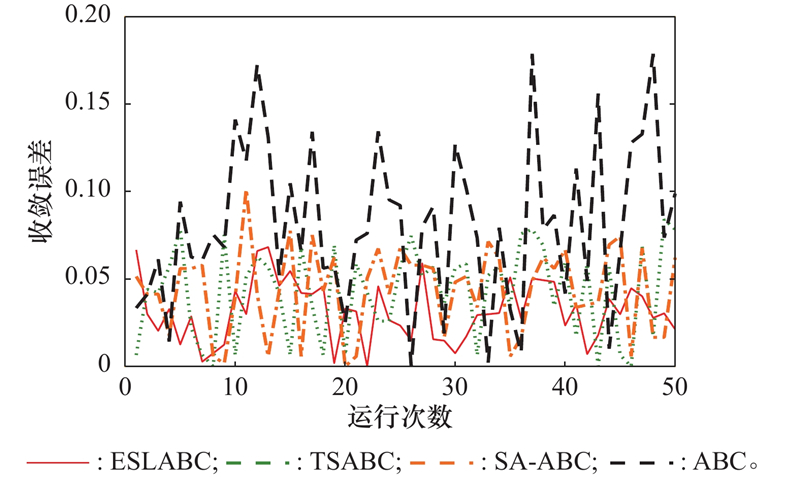
| 1 |
LU D J, WANG X, WU X T, et al. Adaptive allocation strategy for cooperatively jamming netted radar system based on improved cuckoo search algorithm[J]. Defence Technology, 2023, 24 (6): 285- 297.
|
| 2 |
沈阳, 陈永光, 李修和. 基于0-1规划的雷达干扰资源优化分配研究[J]. 兵工学报, 2007, 28 (5): 528- 532.
|
|
SHEN Y, CHEN Y G, LI X H. Optimal allocation of radar jamming resources based on 0-1 programming[J]. Acta Armamentarii, 2007, 28 (5): 528- 532.
|
| 3 |
吕永胜, 王树宗, 王向伟, 等. 基于贴近度的雷达干扰资源分配策略研究[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2005, 27 (11): 1893- 1894,1974.
|
|
LV Y S, WANG S Z, WANG X W, et al. Research on radar jamming resource allocation strategy based on proximity degree[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2005, 27 (11): 1893- 1894,1974.
|
| 4 |
任松, 司长哲, 雷军. 雷达干扰机分配的模糊多属性动态规划模型[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2008, 30 (10): 1909- 1913.
|
|
REN S, SI C Z, LEI J. Fuzzy multi-attribute dynamic programming model for radar jammer assignment[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2008, 30 (10): 1909- 1913.
|
| 5 |
薛羽, 庄毅, 张友益, 等. 基于启发式自适应离散差分进化算法的多UCAV协同干扰空战决策[J]. 航空学报, 2013, 34 (2): 343- 351.
|
|
XUE Y, ZHUANG Y, ZHANG Y Y, et al. Multiple UCAV cooperative jamming air combat decision making based on heuristic self-adaptive discrete differential evolution algorithm[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica, 2013, 34 (2): 343- 351.
|
| 6 |
LI X, ZHANG S P, SHAO P. Discrete artificial bee colony algorithm with fixed neighborhood search for traveling salesman problem[J]. Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence, 2024, 131, 107816.
doi: 10.1016/j.engappai.2023.107816
|
| 7 |
KANG Y X, YU H B, KANG L, et al. A multi-role steered artificial bee colony algorithm with variable dimensionality perturbation for multimodal optimization problems[J]. Memetic Computing, 2024, 16, 159- 178.
doi: 10.1007/s12293-024-00411-9
|
| 8 |
PHOEMPHON S. Grouping and reflection of the artificial bee colony algorithm for high-dimensional numerical optimization problems[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 91426- 91446.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3417530
|
| 9 |
KARIM F K, SIVAKUMAR N R, ALSHETEWI S, et al. An adaptive threshold-based modified artificial bee colony optimization technique for virtual machine placement in cloud datacenters[J]. IEEE Access, 2024, 12, 94296- 94309.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2024.3420173
|
| 10 |
CHEN M. Improved artificial bee colony algorithm based on escaped foraging strategy[J]. Journal of the Chinese Institute of Engineers, 2019, 42 (6): 516- 524.
doi: 10.1080/02533839.2019.1611479
|
| 11 |
ZHAI X F, ZHUANG Y. IIGA based algorithm for cooperative jamming resource allocation[C]//Proc. of the Asia Pacific Conference on Postgraduate Research in Microelectronics & Electronics, 2009: 368−371.
|
| 12 |
车飞. 认知对抗中干扰效益评估与智能决策方法研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工程大学, 2019.
|
|
CHE F. Research on evaluation of interference efficiency and intelligent decision-making in cognitive warfare[D]. Harbin: Harbin Engineering University, 2009.
|
| 13 |
尧泽昆, 王超, 施庆展, 等. 基于改进离散模拟退火遗传算法的雷达网协同干扰资源分配模型[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46 (3): 824- 830.
|
|
YAO Z K, WANG C, SHI Q Z, et al. Cooperative jamming resource allocation model for radar network based on improved discrete simulated annealing genetic algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46 (3): 824- 830.
|
| 14 |
KUYA Y, KOMATSU K, YONAGA K , et al. Quantum annealing-based algorithm for lattice gas automata[J]. Computers & Fluids, 2024, 274: 106238.
|
| 15 |
OSNER N R, PLESSIS W P. Threat evaluation and jamming allocation[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2017, 11(3): 459−465.
|
| 16 |
呙鹏程, 王星, 周东青, 等. 基于熵权的灰色关联辐射源威胁评估[J]. 空军工程大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 17 (6): 58- 63.
|
|
GUO P C, WANG X, ZHOU D Q, et al. Grey correlation emitter threat assessment based on entropy weight[J]. Journal of Air Force Engineering University, 2016, 17 (6): 58- 63.
|
| 17 |
于旺, 石艳, 赵海妮, 等. 改进粒子群算法的集群协同干扰资源分配[J]. 战术导弹技术, 2023 (2): 122- 129.
|
|
YU W, SHI Y, ZHAO H N, et al. Improved particle swarm optimization algorithm for cluster cooperative interference resource allocation[J]. Tactical Missile Technology, 2023 (2): 122- 129.
|
| 18 |
LUO S, WEI Z H, MA Z Y, et al. Multi-loitering munitions cooperative interference resource allocation based on hybrid ant colony algorithm[C]//Proc. of the Chinese Control and Decision Conference, 2021.
|
| 19 |
AHMED A, ZHANG Y D. Optimized resource allocation for distributed joint radar-communication system[J]. IEEE Trans. on Vehicular Technology, 2023, 73 (3): 3872- 3885.
|
| 20 |
HU J, LEI Z, PRAMOD K P, et al. Resource allocation for distributed multi-target tracking in radar networks with missing data[J]. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2024, 72, 718- 734.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2024.3352915
|
| 21 |
WU Z D, HU S L, LUO Y S, et al. Optimal distributed cooperative jamming resource allocation for multi-missile threat scenario[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16(1): 113−128.
|
| 22 |
HAN L, NING Q, CHEN B C, et al. Ground threat evaluation and jamming allocation model with Markov chain for aircraft[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2020, 14(7): 1039−1045.
|
| 23 |
纪慧颖, 潘明海, 张元时, 等. 基于遗传-蚁群融合算法的干扰资源分配方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2023, 45 (7): 2098- 2107.
|
|
JI H Y, PAN M H, ZHANG Y S, et al. Interference resource allocation method based on genetic-ant colony fusion algorithm[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45 (7): 2098- 2107.
|
| 24 |
ZHANG H W, LIU W J, LIU Y, et al. Joint target and user assignment as well as dwell time and spectrum allocation in a distributed radar-communication coexistence network[J]. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 60 (1): 1159- 1175.
|
| 25 |
QI X, XIN Z X, CHEN T. Cooperative jamming resource allocation with joint multi-domain information using evolutionary reinforcement learning[J]. Remote Sensing, 2024, 16 (11): 1955.
doi: 10.3390/rs16111955
|
| 26 |
GAO W F, HUANG L L, LUO Y T, et al. Constrained optimization by artificial bee colony framework[J]. IEEE Access, 2018, 6, 73829- 73845.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2018.2880814
|
| 27 |
ZHANG W C, LI Y N. A many-objective artificial bee colony algorithm based on adaptive grid[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 97138- 97151.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3093381
|
| 28 |
MA T X, DUAN X, XU Y, et al. Research on fault location in DC distribution network based on adaptive artificial bee colony slime mould algorithm[J]. IEEE Access, 2023, 11, 62630- 62638.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2023.3287322
|
| 29 |
HOUGARDY S, ZAISER F, ZHONG X. The approximation ratio of the 2-opt heuristic for the metric traveling salesman problem[J]. Operations Research Letters, 2020, 48 (4): 401- 404.
doi: 10.1016/j.orl.2020.05.007
|
| 30 |
KIRAN D N R, DETHE C G. Fuzzy rule selection using artificial bee colony optimisation algorithm[J]. International Journal of Advanced Intelligence Paradigms, 2019, 12 (1/2): 164- 177.
doi: 10.1504/IJAIP.2019.096961
|
 ), Xinyao HUANG1, Pei ZHENG3, Hu LI3
), Xinyao HUANG1, Pei ZHENG3, Hu LI3