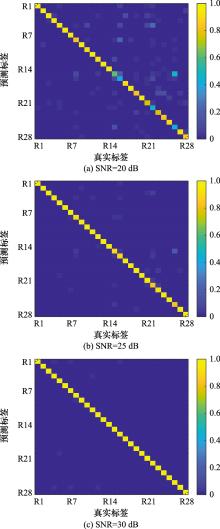
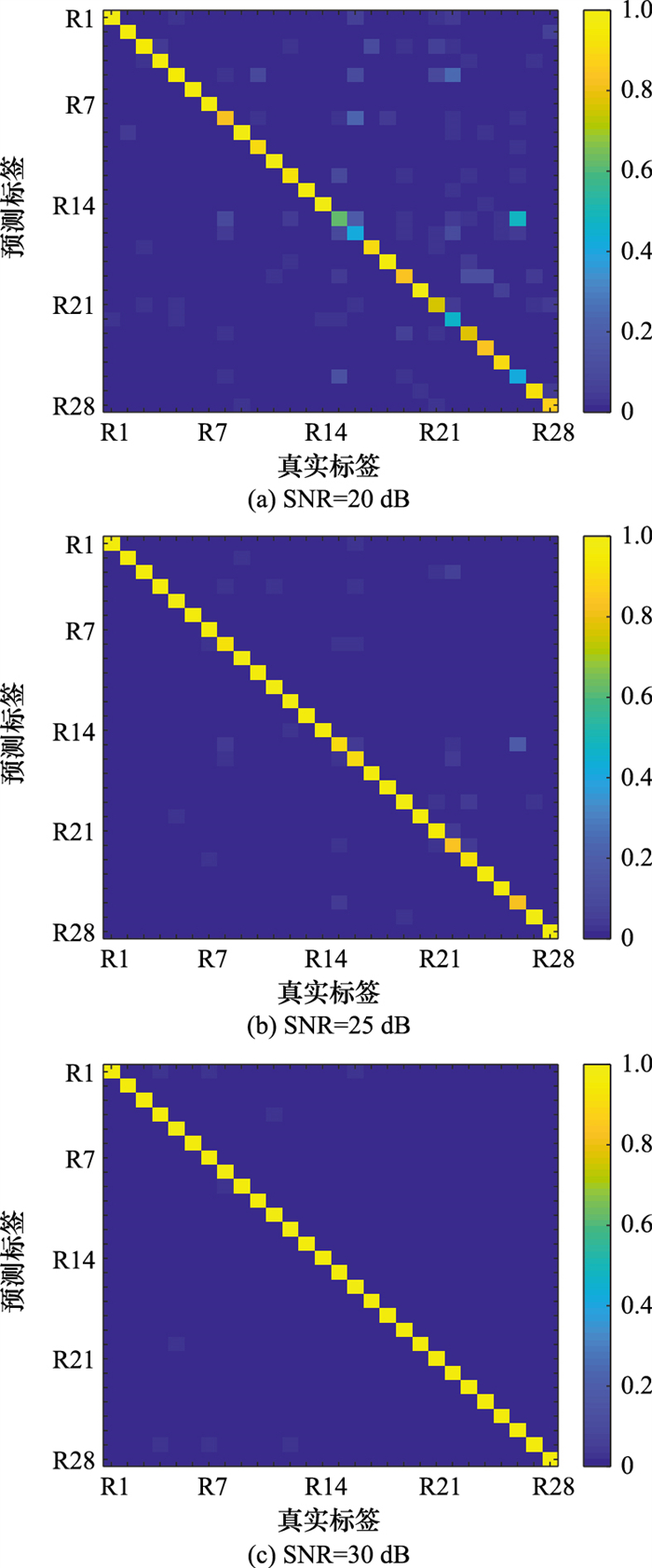
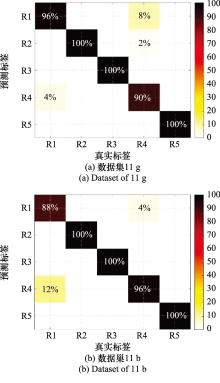
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (4): 1048-1056.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.04.03
• Electronic Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Robust radio frequency fingerprinting feature extraction method based on nonlinear dynamics
Liting SUN, Zheng LIU, Zhitao HUANG
- College of Electronic Science and Technology, National University of Defense Technology, Changsha 410073, China
-
Received:2024-03-26Online:2025-04-25Published:2025-05-28 -
Contact:Zhitao HUANG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Liting SUN, Zheng LIU, Zhitao HUANG. Robust radio frequency fingerprinting feature extraction method based on nonlinear dynamics[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(4): 1048-1056.
share this article
Table 1
Parameters setting of emitter distortion"
| 辐射源 | 滤波器失真 | I/Q不平衡 | 功率放大器 | 杂散单音与载频泄露 | |||||||
| (a0, a1, α1) | (b0, b1, β1) | G | τ | (a1, a2, a3) | aST | fST | ξ(10-3) | ||||
| R1 | (1, 0.030, 0.25) | (1, 0.030 2, 0.25) | 0.999 8 | -0.018 | (1, 0.50, 0.30) | 0.008 2 | 0.012 9 | 1.3+8.2j | |||
| R2 | (1, 0.060, 0.25) | (1, 0.029 5, 0.25) | 1.005 6 | 0.017 5 | (1, 0.08, 0.60) | 0.007 5 | 0.013 2 | 1.5+7.2j | |||
| R3 | (1, 0.085, 0.25) | (1, 0.029 0, 0.25) | 1.010 2 | 0.012 | (1, 0.01, 0.01) | 0.007 | 0.012 3 | 1.1+6.8j | |||
| R4 | (1, 0.073, 0.25) | (1, 0.031 0, 0.25) | 0.999 2 | 0.003 | (1, 0.01, 0.40) | 0.008 7 | 0.013 5 | 1.7+9.0j | |||
| R5 | (1, 0.040, 0.25) | (1, 0.031 3, 0.25) | 0.998 2 | 0.024 | (1, 0.60, 0.08) | 0.009 | 0.011 9 | 2.0+6.5j | |||
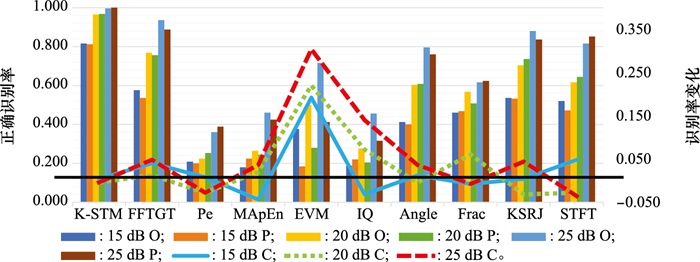
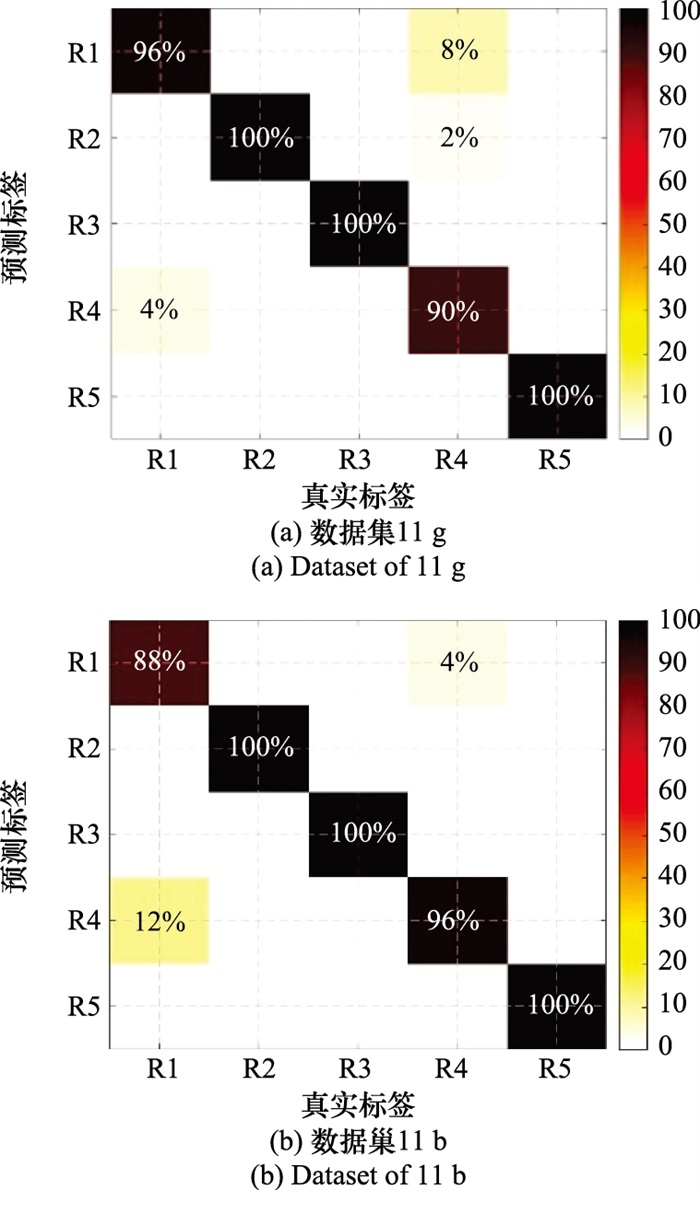
Table 3
Identification performance under multipath fading channel scenarios"
| 方法 | SNR/dB | 信道 | |||
| L1 | L2 | L3 | 均值 | ||
| K-STM | 25 | 0.956 | 0.956 | 0.960 | 0.957 |
| 30 | 0.976 | 0.976 | 0.992 | 0.981 | |
| Angle | 25 | 0.924 | 0.880 | 0.958 | 0.921 |
| 30 | 0.944 | 0.896 | 0.988 | 0.943 | |
| Pe | 25 | 0.444 | 0.336 | 0.328 | 0.369 |
| 30 | 0.532 | 0.536 | 0.496 | 0.521 | |
| EVM | 25 | 0.584 | 0.352 | 0.380 | 0.439 |
| 30 | 0.720 | 0.584 | 0.792 | 0.699 | |
| I/Q | 25 | 0.420 | 0.260 | 0.300 | 0.327 |
| 30 | 0.516 | 0.372 | 0.592 | 0.493 | |
| 1 |
XU Z W , HAN G J , LIU L , et al. A lightweight specific emitter identification model for ⅡoT devices based on adaptive broad learning[J]. IEEE Trans. on Industrial Informatics, 2023, 19 (5): 7066- 7075.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2022.3206309 |
| 2 | 陈翔, 汪连栋, 许雄, 等. 基于Raw I/Q和深度学习的射频指纹识别方法综述[J]. 雷达学报, 2023, 12 (1): 214- 234. |
| CHEN X , WANG L D , XU X , et al. A review of radio frequen cy fingerprinting methods based on Raw I/Q and deep learning[J]. Journal of Radars, 2023, 12 (1): 214- 234. | |
| 3 |
FANG Y Y , WEI S , ZHAO Y , et al. Radar-specific emitter identification with only envelope power based on multidimensional complex noncentral Chi-square classifier[J]. IEEE Sensors Journal, 2023, 23 (17): 20223- 20235.
doi: 10.1109/JSEN.2023.3298352 |
| 4 |
HE B X , WANG F G . Specific emitter identification via sparse Bayesian learning versus model-agnostic meta-learning[J]. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2023, 18, 3677- 3691.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2023.3287073 |
| 5 | 韦建宇, 俞璐. 通信辐射源个体识别中的特征提取方法综述[J]. 通信技术, 2022, 55 (6): 681- 687. |
| WEI J Y , YU L . Overview of radio frequency fingerprint extraction in communication specific emitter identification[J]. Communications Technology, 2022, 55 (6): 681- 687. | |
| 6 |
TAN K W , YAN W J , ZHANG L M , et al. Semi-supervised specific emitter identification based on bispectrum feature extraction CGAN in multiple communication scenarios[J]. IEEE Trans. on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2023, 59 (1): 292- 310.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2022.3184619 |
| 7 | YING W W, DENG P F, HONG S H. Channel attention mechanism -based multi-feature fusion network for specific emitter identification[C]// Proc. of the IEEE 4th International Conference on Civil Aviation Safety and Information Technology, 2022: 1325-1328. |
| 8 |
DUDCZYK J , KAWALEC A . Fractal features of specific emi-tter identification[J]. Acta Physica Polonica A, 2013, 124 (3): 406- 409.
doi: 10.12693/APhysPolA.124.406 |
| 9 | HUANG Y L, ZHENG H. Radio frequency fingerprinting based on the constellation errors[C]//Proc. of the 18th Asia-Pacific Conference on Communications, 2012: 900-905. |
| 10 | PAN Y W, PENG H, LI T Y, et al. High-fidelity symbol synchronization for specific emitter identification[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 3rd Information Technology, Networking, Electronic and Automation Control Conference, 2019: 393-398. |
| 11 |
PENG Y , LIU P F , WANG Y , et al. Radio frequency fingerprint identification based on slice integration cooperation and heat constellation trace figure[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications Letters, 2022, 11 (3): 543- 547.
doi: 10.1109/LWC.2021.3135932 |
| 12 |
SHEN G X , ZHANG J Q , MARSHALL A , et al. Towards scalable and channel-robust radio frequency fingerprint identification for LoRa[J]. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 17, 774- 787.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2022.3152404 |
| 13 |
SATIJA U , TRIVEDI N , BISWAL G , et al. Specific emitter identification based on variational mode decomposition and spectral features in single hop and relaying scenarios[J]. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2019, 14 (3): 581- 591.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2018.2855665 |
| 14 |
HAN G J , XU Z W , ZHU H B , et al. A two-stage model based on a complex-valued separate residual network for cross-domain ⅡoT devices identification[J]. IEEE Trans. on Industrial Informatics, 2024, 20 (2): 2589- 2599.
doi: 10.1109/TII.2023.3296871 |
| 15 |
ZHA X , CHEN H , LI T Y , et al. Specific emitter identification based on complex Fourier neural network[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26 (3): 592- 596.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2021.3135378 |
| 16 |
ZHA H R , WANG H H , FENG Z M , et al. LT-SEI: long-tailed specific emitter identification based on decoupled representation learning in low-resource scenarios[J]. IEEE Trans. on Intelligent Transportation Systems, 2024, 25 (1): 929- 943.
doi: 10.1109/TITS.2023.3308716 |
| 17 |
LIU Z M . Multi-feature fusion for specific emitter identification via deep ensemble learning[J]. Digital Signal Processing, 2021, 110, 102939.
doi: 10.1016/j.dsp.2020.102939 |
| 18 | FAN R , SI C K , HAN Y , et al. RFFsNet-SEI: a multidimensional balanced-RFFs deep neural network framework for specific emitter identification[J]. Journal of Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 35 (3): 558- 574. |
| 19 | ZHANG X L , LI T Y , GONG P , et al. Variable-modulation specific emitter identification with domain adaptation[J]. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2022, 18, 380- 395. |
| 20 | ZHANG T T, REN P Y, REN Z Y. Deep radio fingerprint ResNet for reliable lightweight device identification[C]//Proc. of the IEEE 94th Vehicular Technology Conference, 2021. |
| 21 |
MCGINTHY J M , WONG L J , MICHAELS A J . Groundwork for neural network-based specific emitter identification authentication for IoT[J]. IEEE Internet of Things Journal, 2019, 6 (4): 6429- 6440.
doi: 10.1109/JIOT.2019.2908759 |
| 22 | PEGGS C S, JACKSON T S, TITTLEBAUGH A N, et al. Preamble-based RF-DNA fingerprinting under varying temperatures[C]//Proc. of the 12th Mediterranean Conference on Embedded Computing, 2023. |
| 23 |
SUN L T , WANG X , YANG A F , et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multi-dimension approximate entropy[J]. IEEE Signal Processing Letters, 2020, 27, 471- 475.
doi: 10.1109/LSP.2020.2978333 |
| 24 | 袁英俊. 通信辐射源个体识别关键技术研究[D]. 长沙: 国防科技大学, 2014 |
| YUAN Y J. Research on key technologies of communication emitter identification[D]. Changsha: National University of Defense Technology, 2014. | |
| 25 |
ZHANG J Q , RAJENDRAN S , SUN Z , et al. Physical layer security for the internet of things: authentication and key ge-neration[J]. IEEE Wireless Communications, 2019, 26 (5): 92- 98.
doi: 10.1109/MWC.2019.1800455 |
| 26 |
SUN L T , WANG X , ZHAO Y R , et al. Intrinsic low-di men sional nonlinear manifold structure of radio frequency signals[J]. IEEE Communications Letters, 2022, 26 (9): 2185- 2189.
doi: 10.1109/LCOMM.2022.3173990 |
| 27 | DENG S Y , HUANG Z T , WANG X , et al. Radio frequency fingerprint extraction based on multidimension permutation entropy[J]. International Journal of Antennas and Propagation, 2017, 2017, 1538728. |
| 28 | 朱胜利. 混沌信号处理在辐射源个体识中的应用研究[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2018. |
| ZHU S L. Research on applications of chaotic signal processing in specific emitter identification[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2018. | |
| 29 |
CARROLL T L . A nonlinear dynamics method for signal identification[J]. Chaos, 2007, 17 (2): 023109.
doi: 10.1063/1.2722870 |
| 30 | YUAN Y J, HUANG Z T, WANG F H, et al. Radio specific emitter identification based on nonlinear characteristics of signal[C]// Proc. of the IEEE International Black Sea Conference on Communications and Networking, 2015: 77-81. |
| 31 |
POVINELLI R J , JOHNSON M T , LINDGREN A C , et al. Statistical models of reconstructed phase spaces for signal cla-ssification[J]. IEEE Trans. on Signal Processing, 2006, 54 (6): 2178- 2186.
doi: 10.1109/TSP.2006.873479 |
| 32 |
CARROLL T L . Phase space method for identification of driven nonlinear systems[J]. Chaos: an Interdisciplinary Journal of Nonlinear Science, 2009, 19 (3): 033121.
doi: 10.1063/1.3207836 |
| 33 | 吴龙文. 脉冲体制辐射源无意调制特征分析及个体识别[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2020. |
| WU L W. Research on unintentional modulation feature analysis and identification of specific pulsed emitter[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2020. | |
| 34 |
SUN L T , WANG X , HUANG Z T . Unintentional modulation evaluation in time domain and frequency domain[J]. Chinese Journal of Aeronautics, 2022, 35 (4): 376- 389.
doi: 10.1016/j.cja.2021.05.013 |
| 35 |
HE B X , WANG F G . Cooperative specific emitter identification via multiple distorted receivers[J]. IEEE Trans. on Information Forensics and Security, 2020, 15, 3791- 3806.
doi: 10.1109/TIFS.2020.3001721 |
| 36 |
FADUL M K M , REISING D R , SARTIPI M . Identification of OFDM-based radios under Rayleigh fading using RF-DNA and deep learning[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 17100- 17113.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3053491 |
| [1] | Ping YAN, Chaochang LI. Motion stability analysis of fin-controlled small supercavitating vehicle [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(7): 2456-2464. |
| [2] | WANG Ya-fei, YU Jian-qiao, WANG Lin-lin, SU Xiao-long. Bifurcation characteristics of reentry vehicle with one moving point mass [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2015, 37(6): 1338-1346. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||