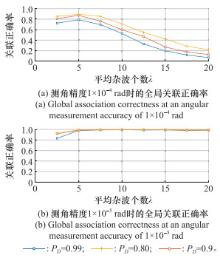
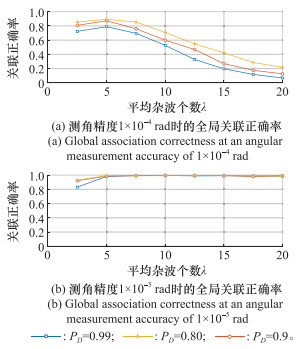
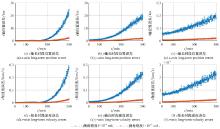
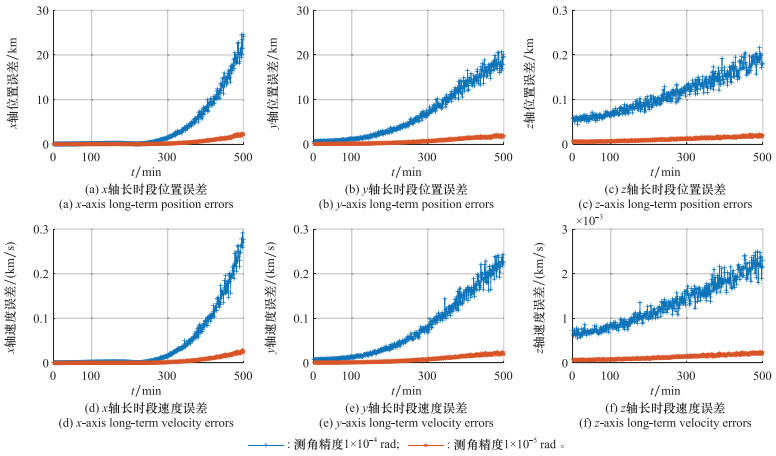
Systems Engineering and Electronics ›› 2025, Vol. 47 ›› Issue (5): 1404-1413.doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2025.05.03
• Electronic Technology • Previous Articles
Space-based passive cooperative multi-target initial orbit determination method in complex environments
Hongyuan ZHANG1, Baichun GONG1,*, Fei HAN2, Yue SUN2, Xin NING3
- 1. College of Astronautics, Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, Nanjing 211106, China
2. Shanghai Aerospace Control Technology Institute, Shanghai 201109, China
3. School of Astronautics, Northwestern Polytechnical University, Xi'an 710072, China
-
Received:2024-05-22Online:2025-06-11Published:2025-06-18 -
Contact:Baichun GONG
CLC Number:
Cite this article
Hongyuan ZHANG, Baichun GONG, Fei HAN, Yue SUN, Xin NING. Space-based passive cooperative multi-target initial orbit determination method in complex environments[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2025, 47(5): 1404-1413.
share this article
Table 1
Experimental satellite parameters"
| 标签 | a/km | e | i/(°) | Ω/(°) | ω/(°) | θ/(°) |
| 观测星1 | 42 164 | 0 | 0.01 | 0 | 0 | 89.883 6 |
| 观测星2 | 42 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.116 4 |
| 目标1 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.000 0 |
| 目标2 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 89.867 2 |
| 目标3 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.132 7 |
| 目标4 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.265 4 |
| 目标5 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 89.734 5 |
| 目标6 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.398 2 |
| 目标7 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 89.601 8 |
| 目标8 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.531 0 |
| 目标9 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 89.469 0 |
| 目标10 | 43 164 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 90.663 7 |
| 17 |
邱建杰, 蔡益朝, 李浩, 等. 基于动态估计反馈的灰色理论航迹关联算法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46 (4): 1401- 1411.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.04.29 |
|
QIU J J , CAI Y C , LI H , et al. Grey theory track association algorithm based on dynamic estimation feedback[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46 (4): 1401- 1411.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.04.29 |
|
| 18 |
HUANG J , LEI X X , ZHAO G Y , et al. Short-arc association and orbit determination for new geo objects with space-based optical surveillance[J]. Aerospace, 2021, 8 (10): 298.
doi: 10.3390/aerospace8100298 |
| 19 |
曾舒雅, 饶彬. 基于动力学守恒定律的弹道目标关联方法[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2024, 46 (2): 684- 691.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.02.32 |
|
ZENG S Y , RAO B . Ballistic target association method based on dynamic conservation law[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46 (2): 684- 691.
doi: 10.12305/j.issn.1001-506X.2024.02.32 |
|
| 20 | 龚柏春, 张洪源, 杨世航, 等. 一种天基无源协同多目标观测数据关联定位方法[P]. 中国: CN117249835B, 2024-03-29. |
| GONG B C, ZHANG H Y, YANG S H, et al. A space-based passive collaborative localization method via data association for multi-target observation[P]. China: CN117249835B, 2024-03-29. | |
| 21 |
SERRA R , YANEZ C , DELANDE E . Tracklet-to-orbit association under uncertainty applied to maneuvering space objects[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2022, 201, 526- 532.
doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2022.08.027 |
| 22 | KADAR I, EADAN E R, GASSNER R R. Comparison of robustized assignment algorithms[C]//Proc. of the Signal Processing, Sensor Fusion, and Target Recognition, 1997: 240-249. |
| 23 | CROUSE D F. Advances in displaying uncertain estimates of multiple targets[C]//Proc. of the SPIE Defense, Security, and Sensing Conference, 2013. |
| 24 | 潘迪, 周琦, 刘轩, 等. 高动态条件下星斑模拟与星点提取方法[J]. 光子学报, 2022, 51 (3): 0304002. |
| PAN D , ZHOU Q , LIU X , et al. Modeling and detection of star spot in high dynamic condition[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica, 2022, 51 (3): 0304002. | |
| 25 | 牛海鹏. 天基空间监视系统目标检测技术研究[D]. 长春: 中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所, 2024. |
| NIU H P. Research on target detection technology of space-based space surveillance system[D]. Changchun: Changchun Institute of Optics, Fine Mechanics and Physics, Chinese Aca-demy of Sciences, 2024. | |
| 26 |
MYERS K A , TAPLEY B D . Dynamical model compensation for near-earth satellite orbit determination[J]. AIAA Journal, 1975, 13 (3): 343- 349.
doi: 10.2514/3.49702 |
| 27 |
LUO Y Z , YANG Z . A review of uncertainty propagation in orbital mechanics[J]. Progress in Aerospace Sciences, 2017, 89, 23- 39.
doi: 10.1016/j.paerosci.2016.12.002 |
| 28 |
AHMED M , SERAJ R , ISLAM S M . The k-means algorithm: a comprehensive survey and performance evaluation[J]. Electronics, 2020, 9 (8): 1295.
doi: 10.3390/electronics9081295 |
| 29 |
CROUSE D F . On implementing 2D rectangular assignment algorithms[J]. IEEE Trans.on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2016, 52 (4): 1679- 1696.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2016.140952 |
| 30 |
AVANZINI G . A simple lambert algorithm[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 2008, 31 (6): 1587- 1594.
doi: 10.2514/1.36426 |
| 31 |
NELSON S L , ZARCHAN P . Alternative approach to the solution of Lambert's problem[J]. Journal of Guidance, Control, and Dynamics, 1992, 15 (4): 1003- 1009.
doi: 10.2514/3.20935 |
| 1 |
PARDINI C , ANSELMO L . Evaluating the impact of space activities in low earth orbit[J]. Acta Astronautica, 2021, 184, 11- 22.
doi: 10.1016/j.actaastro.2021.03.030 |
| 2 | KENNEWELL J A, VO B N. An overview of space situational awareness[C]//Proc. of the 16th International Conference on Information Fusion, 2013: 1029-1036. |
| 3 | WANG B C , LI S , MU J Z , et al. Research advancements in key technologies for space-based situational awareness[J]. Space: Science & Technology, 2022, 1, 176- 207. |
| 4 |
ZHANG H T , LI Z , WANG W L , et al. Trajectory planning for optical satellite's continuous surveillance of geostationary spacecraft[J]. IEEE Access, 2021, 9, 114282- 114293.
doi: 10.1109/ACCESS.2021.3104539 |
| 5 |
WOFFINDEN D C , GELLER D K . Observability criteria for angles-only navigation[J]. IEEE Trans.on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2009, 45 (3): 1194- 1208.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2009.5259193 |
| 6 | WOFFINDEN D C. Angles-only navigation for autonomous orbital rendezvous[D]. Logan: Utah State University, 2008. |
| 7 |
GONG B C , WANG S , LI S , et al. Review of space relative navigation based on angles-only measurements[J]. Astrodyna-mics, 2023, 7 (2): 131- 152.
doi: 10.1007/s42064-022-0152-2 |
| 8 | KOLITZ S E. Passive-sensor data fusion[C]//Proc. of the Signal and Data Processing of Small Targets, 1991. |
| 9 |
ROECKER J A . Track monitoring when tracking with multiple 2D passive sensors[J]. IEEE Trans.on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1991, 27 (6): 872- 876.
doi: 10.1109/7.104247 |
| 10 |
DEB S , YEDDANAPUDI M , PATTIPATI K , et al. A gene-ralized S-D assignment algorithm for multisensor-multitarget state estimation[J]. IEEE Trans.on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 1997, 33 (2): 523- 538.
doi: 10.1109/7.575891 |
| 11 |
KAPLAN L , BAR-SHALOM Y , BLAIR W . Assignment costs for multiple sensor track-to-track association[J]. IEEE Trans.on Aerospace and Electronic Systems, 2008, 44 (2): 655- 677.
doi: 10.1109/TAES.2008.4560213 |
| 12 | MA F , LU H Z , ZHANG L P , et al. Multiple hypothesis S-dimensional assignment algorithm for data association of angle-only sensors with limited fields of view[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2022, 16 (11): 1821- 1835. |
| 13 | MA M Y , WANG D J , ZHANG T , et al. Track-to-track association algorithm for passive multisensor system based on trajectory parameter[J]. IET Radar, Sonar & Navigation, 2021, 15 (4): 348- 358. |
| 14 | 翟光, 王妍欣, 孙一勇. 基于低轨星网的多目标协同跟踪滤波技术[J]. 系统工程与电子技术, 2022, 44 (6): 1957- 1967. |
| ZHAI G , WANG Y X , SUN Y Y . Cooperative tracking filtering technology of multi-target based on low orbit satellite constellation[J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44 (6): 1957- 1967. | |
| 15 | WANG L H, LI Z Y, ZHOU S H, et al. Data association with passive angle measurements[C]//Proc. of the International Conference on Control, Automation and Information Sciences, 2021: 313-318. |
| 16 |
LEGRAND K A , DEMARS K J , PERNICKA H J . Bearings-only initial relative orbit determination[J]. Journal of Gui-dance, Control, and Dynamics, 2015, 38 (9): 1699- 1713.
doi: 10.2514/1.G001003 |
| [1] | Jingyuan SHAN, Yu LU, Hanyu LING. Robust adaptive multi-target tracking algorithm for airborne passive bistatic radar [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(9): 2902-2915. |
| [2] | Linhai JIANG, Baichun GONG, Chuankai LIU, Yang YANG, Renyong ZHANG. Space multi-target tracking method for space-based distributedpassive detection [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(8): 2789-2797. |
| [3] | Siyi YAO, Wanchun LI, Lin GAO, Huaguo ZHANG, Hangwei HU. Multi-sensor multi-target tracking based on distributed PMHT [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(7): 2184-2190. |
| [4] | Yaling ZHUO, Xiang LI, Lei ZUO, Juan HU. Power allocation algorithm with random data packet loss in netted radar [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(6): 1957-1966. |
| [5] | Meibin QI, Shuo ZHUANG, Jingjing HU, Yanfang YANG, Yuankui HU. Resolvable group target tracking based on joint GLMB filter [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(4): 1212-1219. |
| [6] | Shuya ZENG, Bin RAO. Ballistic target association method based on dynamic conservation law [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2024, 46(2): 684-691. |
| [7] | Rui LI, Mengtao ZHU, Yunjie LI. Online evaluation method of radar jamming effect based on inverse filtering processing [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(9): 2706-2717. |
| [8] | Wenhao BI, Jie ZHOU, An ZHANG, Li LIU. JPDA algorithm based on maximum entropy fuzzy clustering in clutter environment [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(7): 1920-1927. |
| [9] | Zhengwei LIU, Ying CHEN, Yaobing LU. PHD filter for small-angle crossing of multi-target trajectories [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(4): 982-990. |
| [10] | Haoran LI, Wei XIONG, Yaqi CUI. An association method between SAR images and AIS information based on depth feature fusion [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(11): 3491-3497. |
| [11] | Lei AN, Zhaorui LI, Bing JI. Non-myopic scheduling method for mobile active/passive sensor in clutter environment [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2023, 45(1): 165-174. |
| [12] | Guang ZHAI, Yanxin WANG, Yiyong SUN. Cooperative tracking filtering technology of multi-target based on low orbit satellite constellation [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(6): 1957-1967. |
| [13] | Zizhuang SONG, Jiawei YANG, Dongfang ZHANG, Shiqiang WANG, Shuo ZHANG. Real-time infrared multi-class multi-target anchor-free tracking network [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 401-409. |
| [14] | Qi WANG, Zhizhong LIAO, Fei YAN. Algorithm for countering velocity gate pull-off jamming of radar seeker based on probability data association [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2022, 44(2): 448-454. |
| [15] | Lifan YIN, Yiqun ZHANG, Shuo WANG, Chenggang SUN. A survey on histogram probabilistic multi-hypothesis tracker technique [J]. Systems Engineering and Electronics, 2021, 43(11): 3118-3125. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||